Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Today, almost everyone knows that teeth need especially careful care. We buy expensive pastes and use special thread. But, unfortunately, when taking care of our teeth, we completely forget about the tissues surrounding them, while the health of our gums needs to be monitored no less carefully.
Many people are familiar with the symptoms when the gums begin to hurt when pressing between the teeth. And many, unfortunately, ignore this unpleasant pain. Let's figure out what can cause it, what these sensations indicate, and how to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of pain in the gums when pressing
Remember, discomfort in your gums is a reason to see a dentist. No matter what kind of pain you feel, relatively mild or severe, you need to determine the cause of the problem as soon as possible and begin treating it.
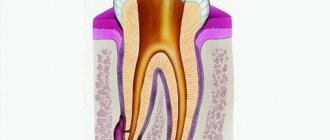
As a rule, pain in the gums when pressed is provoked by three diseases:
- Gingivitis. This disease is accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and bleeding. Inflammation is provoked by microbial plaque, which occurs due to non-compliance or improper oral hygiene.
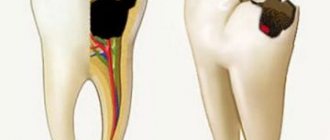
- Periodontitis. The disease, as a rule, is accompanied not only by unpleasant sensations, but also by a general deterioration in well-being. The patient feels which tooth is bothering him, as his “elevation” is felt above the other teeth.
- Periodontitis. The disease occurs due to untreated gingivitis. With periodontitis, the necks of the teeth open, pus oozes from the gums, and the teeth become mobile. The problem affects the entire cavity and can lead to tooth loss.
Painful eruption and incorrect position during germination
Periods of active wisdom teeth eruption often cause discomfort. Many people experience pain during this process, swelling and inflammation of the gum tissue. The reason for this manifestation is the absence of the previous milk tooth in the place where the figure eight grew. Third molars are forced to find a path of growth and break through dense bone tissue, which, given the large size of these teeth, becomes the cause of discomfort. Often, the lack of space for the normal position of the figure eight leads to its complicated germination.
In particularly difficult cases, the tooth takes on a dystopic position. It grows in an atypical direction, not upward, but at an angle. It causes injury to neighboring teeth and displacement of the entire dentition, up to bite deformation. A wisdom tooth growing horizontally can injure the cheek, tongue and roots of its “neighbors”.
Treatment of gum pain
It is important to treat gum disease as soon as possible. Any, even the most harmless pathology, can turn into periostitis with high fever, swelling of the mucous membranes and loose teeth. Moreover, inflammation in the gums releases toxins that provoke the development of blood poisoning.
You should not discount the possibility of pain in the gums when pressing due to illiterate treatment by a dentist. Normally, pain after treatment persists for 1-2 weeks. If the pain continues longer and does not subside, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. It happens that after poor-quality dental canal filling, bacteria appear in the voids, which provoke an infectious process.
The dentist may also leave the edges of the filling uneven, causing damage to the gums. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor so that he can improve his work.
Attacks of pain when pressing on the gums are also common with increased sensitivity of the teeth and gums. However, with proper care, this pain goes away quite quickly. When it occurs, you should use toothpastes and rinses for sensitive teeth.
For example, ASEPTA Sensitive preventive toothpaste allows you to perform oral hygiene without irritating sensitive gums. The combination of 3 desensitizing components - potassium citrate, hydroxyapatite, thermal mud - significantly reduces the sensitivity of teeth and gums.
For more effective prevention of pain in the oral cavity, it is recommended to use ASEPTA gum gel with propolis. In this product, propolis is produced in the form of a gel, which makes it easy to apply to the gums. Prolonged contact with the painful area of the gum allows the gel components to penetrate deeper and promotes rapid healing.
The cause of pain when pressing on the gums can also be various injuries to the gums and teeth, received, for example, when trying to crack nuts or toffee. Such injuries also need to be shown to the dentist as soon as possible, otherwise there is a possibility of an inflammatory process.
Diagnosis and treatment
To determine the cause of pain, dentists conduct a visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity. To confirm the diagnosis you may need:
- overview x-ray of the upper or lower jaw,
- results of a general blood test and a smear from the oral mucosa,
- cytological examination of the contents of periodontal pockets.
The treatment regimen is drawn up individually for each patient, taking into account the diagnosis and clinical picture.
How to relieve pain when pressing on the gums
Remember, only a dentist can help eradicate the pain experienced when pressing on the gums or teeth. It is important to quickly determine the cause of the discomfort and prescribe proper treatment. However, to eliminate discomfort before visiting a doctor, you can try the following methods:
- Take painkillers, such as paracetamol or analgin. The main thing is not to overdo it with such drugs, as they can be addictive and negatively affect the functioning of internal organs.
- Brush your teeth properly, trying to free the inflamed cavity from plaque and food particles.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution of baking soda, furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Remember, it is strictly forbidden to warm your cheeks and gums or apply warm compresses to the sore spot. Heat can trigger more severe inflammation. Also, you should not take antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
It is also prohibited to put analgesics into the cavity of a diseased tooth. This popular method is far from safe: you can not only cause an infection, but also get a serious burn to the mucous membrane.
Specialist help
In case of inflammation of the gingival tissues around the eights, the best solution is to immediately visit a dentist. The specialist will conduct an x-ray and a visual examination of the condition of the tooth and the surrounding area. Based on the examination results, competent treatment will be prescribed:
- Medication - by prescribing antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, special ointments and gels, antiseptic baths.
- Surgical - cutting the gum or gingival hood, removing the figure eight that caused the problem.
If inflammation is accompanied by unbearable acute pain and severe swelling of the gums, a specialist performs a novocaine blockade. Sometimes laser therapy is prescribed, which has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area.
Treatment for gum pain
The treatment tactics for pain in the gums when pressing depends on the cause of the disease. If the pain appears due to problems with the teeth, the canals are filled or refilled. The doctor removes the source of inflammation. Advanced stages of the disease are treated with surgery and removal of the diseased tooth.
If the cause of pain in the gums when pressing is their inflammation, it can be relieved with medications prescribed by the dentist. As a rule, in such cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or other penicillin drugs. Rinse must be prescribed.
Folk remedies – decoctions of medicinal herbs – also help relieve pain and inflammation. Oak bark, chamomile, and sage perfectly remove unpleasant sensations. A solution of baking soda with a few drops of iodine also helps relieve inflammation.
Other popular methods for treating inflammation at home are:
- Propolis tincture
has antibacterial and antimicrobial effects. To prepare it, dilute a teaspoon of tincture in 200 ml of water. You need to rinse your mouth with propolis up to five times a day. - Massage with oils
has a beneficial effect on the gums. It is not at all difficult to do: apply a few drops of tea tree, eucalyptus, juniper or fir oil to the pads of the thumb and index fingers of one hand. You need to massage the gums gently for 5-10 minutes. After the massage, you should not rinse your mouth. - Aloe
also contains many anti-inflammatory components. For gingivitis or stomatitis, you can chew a fresh leaf of this plant a couple of times a day.
Help with inflammation after removal
Due to their inaccessible location, full or partial impaction, and large tooth sizes, removal of third molars is often painful and traumatic. If after surgery to remove figure eights there is severe swelling, and it is accompanied by increasing pain for more than three days, this may be a sign of a disease called alveolitis. It occurs due to the entry of bone fragments, pathogenic bacteria into the wound formed after extraction, or due to the blood clot being washed out of the hole too quickly.
Signs of alveolitis are sharp pain in the wound area, redness of the gums, swelling of the extraction site, absence of a blood clot in the first week after the removal procedure, purulent discharge, fever, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, general weakness.
It is very important to treat alveolitis immediately. This condition, without proper help, can cause tissue necrosis, abscess, phlegmon and osteomyelitis. In addition, alveolitis can lead to blood poisoning. If there are any signs of this problem, an urgent visit to the dentist is indicated.
Swelling of the gum tissue around the wisdom tooth is the first signal about the development of complex and dangerous dental diseases. Therefore, it is important not to rely on self-medication, but to consult a specialist in time.
Nutrition: prevention of inflammation
If gingivitis is the cause of pain when pressing on your gums, it is important to review your diet by including healthy foods in your diet. To prevent future diseases, first of all, you need to consume plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables:
- Apples and pears contain a lot of pectin, which helps accelerate tissue regeneration.
- Citrus fruits are a real storehouse of vitamin C, which also helps reduce bleeding and inflammation.
- Black currants, blackberries, and raspberries contain a large amount of minerals and vitamins that increase the body's resistance.
- Carrots, cabbage and zucchini are valuable fiber and vitamins that enhance metabolic processes in the body and accelerate tissue regeneration.
To prevent gum inflammation, professional teeth cleaning is also recommended. The procedure is carried out by a dentist and allows you to eliminate all accumulated deposits and tartar.
So, now you know the most common causes of pain in the gums when pressing. Remember: when your gums or teeth bother you, you should never put off visiting the dentist. The sooner the doctor determines the cause of the problem and begins treatment, the greater your chances of saving your teeth, gums and avoiding possible complications.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
How does pericoronitis occur?
If a wisdom tooth grows for a very long time or grows atypically, then partial gum loss above the surface of the tooth may occur. This creates a gum hood over the figure eight. This formed hood contains food debris that is very difficult to remove. They cause the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which ultimately leads to pericoronitis. In addition, if there is an upper double figure eight, then the gingival hood is constantly injured when biting, which becomes the cause of a non-infectious inflammatory process in the gum tissue. Pericoronitis can be acute (purulent or catarrhal) or chronic. Signs of pericoronitis:
- acute pain radiating to the neck or ear;
- soreness of the gum tissue during palpation and chewing;
- inability to open your mouth;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- specific odor from the mouth;
- temperature increase;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
If the disease has taken a chronic form, then you will not have to wait long for noticeable painful manifestations. Pericoronitis regularly recurs with all the symptoms of an acute purulent form. Complications of untreated pericoronitis can be periostitis, abscess, osteomyelitis of the jaw or phlegmon. Therefore, if signs of pericoronitis are detected, urgent dental care is needed. The specialist, taking into account the phase and form of the disease, will select the appropriate treatment. Medication or surgery may be needed.
Gum recession: why gums recede
The formation of gum recession occurs when the surface of the tooth root is exposed. Without consulting a dentist, you will never be able to determine the exact reason why your gums are receding. This is due to a whole range of possible reasons, and in addition there are a large number of predisposing factors that make the risk of recessions more likely. Let's look at them.
1) Occlusal trauma, overload of teeth –
Occlusal trauma means that the contacts between your lower and upper teeth are not ideal, and in some areas there may be so-called “super contacts” (areas of premature overbiting). Normally, when the jaws are closed, the contact of the premolars, canines and molars should first occur, and only lastly the incisors. But if your incisors close first, then after all the other teeth have closed, they will experience overload, which will lead to bone resorption and a decrease in gum level (see photo below).
In addition to improper contact between the upper and lower teeth, bruxism (excessive uncontrolled clenching of the jaws, most often at night) can lead to occlusal injury. Patients usually refer to this condition as teeth grinding during sleep. You can learn more about this disease using the link above.
Exposure of tooth roots as a result of occlusal trauma:
Excessive chewing pressure on the teeth for a long time leads to resorption of the bone around them. Accordingly, in parallel with the decrease in bone level, there is also a decrease in the level of the gums, which primarily becomes noticeable in the area of the lower anterior teeth. For example, if you are missing part of your lateral chewing teeth, this leads to a redistribution of the chewing load on the remaining teeth, which will cause them to be overloaded. The front teeth are not physiologically designed for chewing at all - their function is to bite off food. In the absence of lateral chewing teeth, chewing food occurs with the front teeth, which quickly leads to their overload.
The absence of even 1 chewing tooth on each side can quickly lead to a decrease in the bite height in the lateral parts of the jaws, and this in turn will lead to excessive contact of the upper and lower front teeth (which will also cause bone resorption and gum recession with exposure of the roots of the teeth) . Moreover, a decrease in bite in the lateral parts of the jaws can occur not only due to the loss of several teeth. This can also occur due to excessive abrasion of dental tissues (on the chewing surfaces of molars), due to errors in prosthetics or restoration of teeth with filling materials, as well as as a result of the gradual abrasion of old fillings.
What to do - if you do not have missing teeth, then you need either a “gnathologist” or a very good orthopedic dentist to carry out “selective grinding of teeth” (this procedure will normalize the contacts between the upper and lower teeth, removing all “super contacts”) . If you have a reduced bite height in the chewing parts of the jaws due to the absence of some teeth, you need prosthetics. We are talking about replacing missing teeth with artificial crowns, replacing old fillings on the chewing surfaces of molars with ceramic inlays... But you need to start with a consultation with a prosthetist.
2) Chronic generalized periodontitis –
We have already said above that one of the main reasons why gums recede is their inflammation. It all starts with a completely harmless superficial inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), which is manifested by bleeding gums, their swelling and pain when brushing your teeth. But in the absence of treatment or improper treatment of gingivitis, the attachment of the gums to the neck of the teeth is gradually destroyed, inflammatory bone resorption and the formation of periodontal pockets begin to occur.
Reduced gum level due to gum inflammation –
When bone destruction reaches a certain degree, tooth mobility also joins the symptoms. Destruction of the periodontal attachment, bone resorption, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility - these are all symptoms of the next stage of gum inflammation, which is called periodontitis. Accordingly, because When periodontitis occurs, the level of bone tissue around the teeth decreases, and the level of the gums will also decrease.
Important: please note that a decrease in the level of gums in the area of 1-2 teeth is possible even with the most initial form of gum inflammation - even with catarrhal gingivitis. And for this it is enough simply to have microbial plaque in the area of the necks of the teeth (+ the presence of some predisposing factors, for example, a thin gum biotype). But with chronic generalized periodontitis, subsidence of the gum level occurs immediately in the area of a large group of teeth.
What to do - you need to start with a consultation with a periodontist (this is a dentist who specializes in the treatment of gum inflammation). Treatment of periodontitis includes not only anti-inflammatory therapy and removal of dental plaque, but also splinting of movable groups of teeth and prosthetic replacement of missing teeth. Therefore, in addition to consulting a periodontist, you may also need to consult an orthopedic dentist.
3) Incorrect movements of the toothbrush –
If you brush your teeth with a horizontal motion (instead of a sweeping motion) every day year after year, this can lead to gum recession - especially in the area of the lower front teeth. Typically, such patients not only have receding gums, but also hard tissue defects of non-carious origin appear in the area of the necks of the teeth. Incorrect brushing technique plays an important role in the formation of gum recession - especially in the presence of predisposing factors (thin gums, small height of attached gums, concomitant catarrhal gingivitis, etc.).
4) After correcting the bite with braces -
After correcting the bite with braces, you can often notice a decrease in the level of the gums. What I want to say here... There are only a few good orthodontists, so most of them plan orthodontic treatment without taking into account factors such as the height of the attached gum, the biotype of the gum, the thickness of the cortical plate of the jaw in the area of the teeth being moved. And as a result, we have what we have...
5) In the presence of predisposing factors –
Below we present a number of factors that sharply increase the risks of gum loss and root exposure. In some cases, they themselves can be the cause of gum recession (such as a highly attached frenulum of the lower lip), but most often they increase the damaging effects of the causes that we described above. These predisposing factors relate to the individual anatomical features of the gum structure in different patients.
- If you have a thin gum biotype, thin biotype means a small gum thickness. With the same force of the damaging factor, in patients with thin gums, recession will occur faster and be deeper than in patients with thick gums.
- Thickness of the cortical plate of the alveolus - if your cortical plate of the jaw (the front wall of the alveolus) is too thin.
Let's look at this using the example of the lower incisors. The anterior surfaces of the roots of the lower incisors are covered with a thin layer of bone, on top of which soft gum tissue is already located. In some patients, this layer of bone may be too thin (less than 0.5 mm), which, in the presence of a damaging factor, leads to too rapid bone loss, followed by a decrease in gum height. In some patients it can be even worse. For example, on the front surface of the roots of the lower incisors (in the area of their upper thirds) there may be no bone plate at all. In this case, the upper third of the roots will be covered only by the gum. This situation creates a risk of a recession, i.e. the fact that the gums will recede and the tooth root will be exposed - maximum.
- The height of attachment of the frenulum of the lips - for example, the frenulum of the lower lip may be attached too high to the gum edge, and then the movement of the lips (during conversation and facial expressions) will lead to the frenulum “tearing” the edge of the gum from the teeth. The same will apply to the low-attached frenulum of the upper lip.
- Insufficient level of attached gum – the gum is usually divided into “attached” and “unattached” (see photo below). Above the dotted line is the attached gum, and below it is the non-attached mobile gum. The peculiarity of the attached gum is that it is firmly fused with the underlying tissues and therefore immobile. The unattached gum is mobile, and its peculiarity is that it follows the movement of the lips and cheeks.
Very often the gum recedes on a tooth that has a very small height of attached gum. There is a clear relationship - the lower the level of attached gums, the higher the risk of recession (recession of the gums and exposed roots). When the level of attached gum is low, dentists often recommend performing special surgical operations on the gums, which can increase the level of attached gum and prevent exposure of the roots of the teeth.
Symptoms
Inflammatory processes can be asymptomatic for a long time, but at some time it becomes painful when pressing on a tooth, biting or chewing on it. Acute pain indicates a serous or purulent lesion near the tooth. It puts pressure on the surrounding tissues, the pain is felt constantly, either subsiding or worsening. When the aching pain under the crown of the tooth is short-term in nature, occurring only when the prosthetic structure is loaded or when chewing, then the inflammation has become chronic, but this does not make it any less dangerous.
Other symptoms may accompany the pain:
- swelling, redness of the gums is a clear sign of an inflammatory process;
- flux (periostitis) - swelling affects not only the gums, but the face in the area of \u200b\u200bthe inflammatory focus, the prosthetic unit and the teeth nearby ache. The purulent cavity must be opened, drained, and treated with antiseptic;
- cyst under the crown - forms near the root apex due to periodontal inflammation. Initially, a granuloma is formed, grows, becomes covered with a durable membrane of connective tissue, and transforms into a capsule with purulent contents (cyst). It grows, accompanied by pain, swelling, redness of the gums;
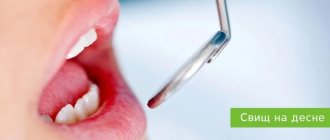
- formation of a fistula - the purulent contents increase in volume, a channel is formed for its outflow. In the best case, it forms in the gums, in the worst case, pus spreads deep into the tissues, affecting the jaw bone, causing osteomyelitis.
During the first days after treatment, slight pain when loading the prosthesis is a normal physiological reaction of tissues to the intervention. But if a pulpless tooth under the crown hurts for a week or more, the pain is severe and interferes with eating, sleeping, and speaking, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Prosthetics with crowns
Installing a crown on a tooth is a procedure to restore its anatomical shape, color, chewing function and aesthetics.
In practice, any tooth under a crown (with or without a preserved nerve) can begin to hurt. In this case, only a specialist can provide assistance. Lack of professional treatment or late contact with a doctor aggravates the situation; removal of the causative tooth may be necessary.
After professionally performed prosthetics, pain should not occur. At first, you may experience some discomfort associated with getting used to the new product in your mouth. If you have a crown installed and your tooth hurts, you should immediately tell your doctor about it.
What will the dentist do if the gums become inflamed after installing a crown?
First of all, the doctor will order an X-ray to determine the cause of inflammation of the gums under the crown. Treatment by the dentist will also be selected based on this information.
Most often in these cases it is necessary to remove the crown. Additionally, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory treatment and antibiotics. It is possible to re-prosthetize a tooth after the gums have become inflamed only when the anti-inflammatory treatment has ended. And only then will a new crown be installed.
It is important to understand that folk remedies will not be effective in this case and will not replace seeing a doctor. If you realize that discomfort continues for more than three days, be sure to consult a doctor. Inflammation is a serious process that affects the body as a whole, so it is important to recognize the cause as early as possible and determine effective treatments for inflammation.
Why does a tooth hurt under a denture?
A crown is a prosthetic structure in the form of a cap that covers a previously prepared tooth. The cause of tooth pain under the crown in many cases is associated with poor preparation of the unit for prosthetics. Most often, this is a mistake when filling dental canals after pulp removal. The source of pain can be:
- Untreated caries
- the doctor did not remove all the affected tissue, which led to a relapse of the carious process under the crown. - Defects during
canal filling - when filling the canal with composite material, voids are formed, which are quickly populated by pathogenic microflora, which causes inflammation and pain. - Perforation of the canal wall
- when the canal walls are damaged, the filling material begins to extend beyond its boundaries, irritating the periodontium; a complication of the current inflammation can be the formation of granulomas and cysts. - Instrument fragment in the canal
- treatment is carried out with thin instruments, which may break during treatment. If the root is severely curved and difficult to pass, it is often impossible to remove the fragment. It promotes the development of inflammation, even if the canal is sealed hermetically. - Poor quality prosthetics
– the crown does not fit well to the supporting tooth or puts pressure on the gum, causing inflammation. In this case, the teeth under the crown hurt when pressing or biting. - Pulp burn
- occurs if, during the preparation of dental tissues, the doctor allowed overheating of the dentin and the neurovascular bundle hidden under it. The pulp becomes inflamed, reacts painfully to temperature stimuli, and acute pain periodically occurs, turning into aching pain.
If a tooth without a nerve hurts under the crown, this is a sign of periodontal pathology or poor-quality installation of the prosthesis. When a crown is placed on a living tooth that has not undergone depulpation, the painful syndrome, as a rule, indicates pulpitis.
Reasons for the inconvenient placement of the prosthesis
The main reasons for the appearance of severe discomfort while wearing an orthopedic system include the following factors:
- psychological unpreparedness of the patient for dentures,
- incorrectly manufactured design,
- initially inflamed gums, which were not treated,
- poor hygienic care of the structure and the entire oral cavity,
- features of the condition of the temporomandibular joint,
- uneven relief of the alveolar ridge.