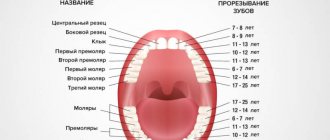
The order of eruption of baby teeth.
The first teeth that a child begins to erupt at the age of 5 - 8 months on the lower jaw are the deciduous incisors. Next, the central primary incisors on the upper jaw begin to appear. At the age of 9 - 13 months, the lateral incisors on the upper and lower jaws erupt. At the age of 13 - 19 months, the first chewing teeth (first primary molars) are cut on the upper and lower jaws. A gap is formed between the lateral incisors and molars, during which the primary canine begins to erupt at 16 months. The last to begin to emerge is the second chewing tooth (second primary molar), first on the lower jaw, then on the upper jaw. By age 3, a full set of baby teeth should have formed.
Help from folk remedies
If you do not want to give your baby medications, you can use natural formulations. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of an allergic reaction in the baby. Also follow safety precautions and remember that small objects can be swallowed or choked by the baby.
- Amber beads
. These products are made from Baltic products. They have a pronounced analgesic and regenerating effect. In addition, the product can relieve fever and fever. The beads are made in such a way that they can enhance the effect of other medications. - Plant herbs
. Herbs such as chamomile and phytolacca can help alleviate the teething condition of a child. They relieve inflammation and partially relieve gum pain. Remember that they must be used in accordance with the instructions. You should not give your baby prepared formulas to drink. Simply treat the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with the decoction.
Features of the period and symptoms of the eruption of the first teeth.
DATES OF TEETHING ARE INDIVIDUAL FOR EACH BABY AND DEPEND ON A NUMBER OF FACTORS: NUTRITION, HEREDITY, ETC. THIS IS WHY YOU SHOULD NOT WORRY MUCH IF THE LONG AWAITED APPEARANCE OF YOUR FIRST TEETH IS DELAYED.
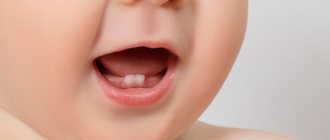
PHOTO: Gums of a child at 6 months. Before the first baby teeth erupt, the gums in the area of the future teeth turn slightly white due to tooth pressure.
It's hard to miss when children's first teeth appear. As the tooth erupts, it “tightens” the mucous membrane (the tooth can be felt with your finger under the mucous membrane) and, having “broken through” it, ends up in the oral cavity. In some children, a bluish “bump” or “ball” with transparent contents forms on the mucous membrane above the erupting tooth. This is a small eruption cyst that usually breaks out on its own WITHOUT outside help (despite the menacing name), although sometimes the intervention of a pediatric dentist is required.
The first teeth that appear may be located asymmetrically and “not evenly” - this is the norm. Such dental disorder has the right to exist until the eruption of 16 teeth: baby teeth are independently ordered as they erupt, aligning each other. This is facilitated by the intake of solid food, pressure of the tongue and lip muscles.
In a normal primary occlusion, gaps form between the primary incisors and canines (on average 1 mm), which is normal and a sign that the permanent wider incisors will have enough space in the dentition during the period of physiological change of teeth. The absence of these spaces indicates a lack of space for permanent teeth.
In most cases, teething does not cause the child any discomfort, although sometimes the process of teething can be accompanied by “itching” of the gums and lead to sleep disturbances in the child, causing a lot of trouble for the child and his parents.
First signs of teething
You can recognize the imminent appearance of a tooth in a baby by the following external signs and changes in behavior:
- Crawling babies put their fingers and everything they see into their mouths. Their gums itch.
- Saliva floods my blouse and prevents me from sleeping at night.
- Sleep and appetite are disturbed.
- The gums swell and turn red.
- A couple of days before teething, a runny nose appears and sometimes a cough.
- The stool becomes liquid, mushy with a yellow, green tint.
- The temperature rises within acceptable limits.
- Whims, tears, crying are suddenly replaced by laughter and good mood. The child does not know what he wants, often asks to be held, and worries without his parents.
A baby, even at one or one and a half years old, experiences stress. Mothers need to understand and forgive the baby for his whims and disturbing dreams. Try to help during this difficult period for everyone. Do not get angry or yell at your daughter or son under any circumstances. Newborns do not yet know how to patiently endure toothache and discomfort and require the attention and care of their parents.
Typical problems.
PHOTO: a child’s teeth at 3 years old. Gaps between baby front teeth at age 3 are normal. On the front upper teeth there is caries in the cervical area of the teeth.
There may be a slight rise in body temperature and anxiety in children when their first teeth are cut. This is due to minor inflammation and itching of the gums in the area where teeth are about to erupt. To relieve discomfort, it is recommended to treat the oral cavity with special napkins for oral hygiene, containing special antiseptic and tanning substances.
The most common problem faced by parents aged 12 - 18 months is “bottle” caries, the main cause of which is poor oral hygiene in the child and night feedings. As a result of poor hygiene, a large amount of soft plaque forms on the teeth. Plaque contains a large number of bacteria that produce acid, which “corrodes” the enamel, leading to the formation of caries.
Night feedings at the age of 12 - 18 months create the most favorable conditions for the development of caries, because... At night, saliva production is reduced - the acid of bacteria living in dental plaque is not neutralized.
BREAST-fed children are LESS likely to develop dental caries than bottle-fed children. Breast milk helps saturate the surface of teeth with calcium and phosphate ions. Breast milk contains a large number of immunological protective factors. At the same time, it has been noted that long-term night feeding (both breast and bottle feeding) leads to the development of dental caries, especially in the area of the upper front milk teeth.
PHOTO: A one and a half year old child’s teeth. The front incisors and first molars have erupted. The fang (3rd tooth) is emerging. Often at this age the first injuries occur: the child fell and hit his front upper tooth - the tooth broke.
Against the background of poor hygiene and a weakened immune system, inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane and stomatitis may develop. Stomatitis in young children is severe, accompanied by general malaise, loss of appetite and increased body temperature.
IT IS VERY IMPORTANT TO START TEACHING YOUR CHILD TO THE NECESSITY OF INDIVIDUAL ORAL HYGIENE FROM THE MOMENT OF THE APPEARANCE OF THE FIRST TEETH. GOOD ORAL HYGIENE IN A CHILD IS THE KEY TO HEALTHY TEETH FROM EARLY CHILDHOOD.
Why don't teeth grow?
The absence of at least one tooth by the age of one year should cause concern on the part of parents. The anomaly may be associated with malfunctions of internal organs or serious diseases, indicating:
- lack of calcium, vitamin D;
- intestinal problems;
- infections;
- improper metabolism;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- distorted arrangement of teeth in the gums (horizontal, with a slope);
- edentation - a congenital mutation indicating the absence of dental germs.
More often, delayed eruption is associated with heredity. Ask your grandparents about how many teeth you had in childhood, find an outpatient card, entries in development diaries. If by the age of one year the father or mother was toothless, then there is no need to wait for their baby to have dental dentition soon.
If at 1 year of age the child has no teeth and there are no signs of early teething, consult a doctor to identify diseases and analyze the medical history.
To exclude congenital edentation, an x-ray examination is performed. The picture shows the rudiments of baby teeth and molars awaiting their turn. If a serious illness is diagnosed, the baby will have to have breast augmentations or implants inserted.
Interesting fact! According to research by pediatricians, girls develop teeth faster than boys.
Treatment.
Providing QUALITY dental care to children from the moment the first tooth appears and up to 3 years of age is LIMITED to physiological reasons: mild excitability, restlessness, fear of unknown manipulations in the oral cavity. An attempt to cure teeth by talking to a child or holding him by force in his arms ends with POOR-QUALITY treatment, as a result of which various local complications can develop.
REMEMBER: FORCED TREATMENT WITH CHILDREN RESTRAINT CAUSES IRREPAIRABLE PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAUMA TO THE CHILD!
Like
If your child has a fever
A temperature of 37 degrees is considered normal; up to 37.5 this will also not be considered a special or complicated situation. Children usually feel fine with such a slight increase in temperature. Naturally, there is no point in giving an antipyretic in this case.
If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, it is worth saying that inflammation or infection has joined the teething process. This situation requires seeing a doctor (he needs to be called to your home), and only his recommendations will be your tactics in future behavior.
During this period, children experience pain, malaise, and weakness that were not typical before, so their behavior changes, sleep disturbances and refusal to eat are noted, which only aggravates the temperature reaction. First of all, the child needs rest, calm and healthy sleep, because temperature, on the one hand, is a protective reaction, and on the other, a debilitating process, which, if unfavorable, can cause overstrain of all organs and systems with the development of pathological reactions: weakness, drowsiness, tachycardia and even febrile seizures.
And remember that the antipyretic should be strictly for children, ideally recommended by a doctor. These are usually paracetamol-based drugs. If they do not help, you can give the child Ibuprofen (but it is prescribed to children from one year old).
But under no circumstances should children be given medications of the aspirin and analgin group. These are toxic drugs that cause side effects.
An excellent tactic for high temperatures would be to humidify the air in the room, regularly ventilate (while the child is in another room), drink plenty of fluids and eat as desired. The child should drink a lot of warm drinks and eat only when he wants to. Avoid dry air, wrapping yourself up in three pajamas and two blankets. If a child wants to play at a high temperature, there is no need to force him to go to bed.
It is important to understand that if the temperature is elevated for more than three days, it is unlikely that the problem is teething. And when it still doesn’t go astray, urgently call a doctor and look for the real reason for this reaction of the body.
Teething is not a very long period. By the age of three, it is definitely completed, and then you will already wait for the loss of milk teeth and the growth of permanent ones. As a rule, the child tolerates these processes normally. To make sure everything is in order, visit your pediatric dentist every six months. You can take care of baby teeth from the moment they appear. Teach your child to brush his teeth twice a day, monitor the quality of brushing.