While pregnant, women experience changes in their bodies. Sensitive and emotional expectant mothers already in the first weeks of pregnancy experience toxicosis, hormonal imbalance, and sudden mood swings. The growing fetus gradually begins to put pressure on the woman’s bladder and stomach. Heartburn and frequent urge to go to the toilet become companions for a pregnant woman.
It is believed that one of the most popular remedies for combating unpleasant symptoms is baking soda. It does not contain toxins and is always at hand. However, despite the harmlessness of the treatment method, it is worth considering whether it poses a threat to the health and life of the fetus?
A folk remedy during pregnancy is used to solve problems:
- heartburn;
- thrush;
- throat diseases;
- toothache;
- when determining pregnancy.
Use for heartburn
Heartburn during pregnancy is common. A burning sensation and a sour taste in the mouth are familiar to many expectant mothers. A soda solution helps to quickly cope with the problem and eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
The effect of heartburn is weakened by a folk remedy that neutralizes acid, which is the source of fire in the chest. But is it safe to use the method during pregnancy? No!
Sodium bicarbonate, accumulating in the body, causes swelling and irritates the intestinal mucosa. The traditional method should be used only in rare cases.
It is important to prepare the medicinal drink correctly: add a couple of pinches of baking soda to a glass of milk. Afterwards, the resulting product should be drunk. The folk method extinguishes heartburn instantly. However, this is only apparent relief.
Indications for the procedure
Doctors recommend the procedure for the following diseases 3,4,5.
1. Sore throat (acute tonsillitis).
Acute tonsillitis is an infectious disease accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils. In children aged 3 to 7 years, bacteria are the cause in 77% of cases3,7. In adults, most sore throats are caused by viruses4, but subsequent activation of bacterial microflora leads to the development of a bacterial inflammatory process4.
In severe cases of tonsillitis, doctors immediately prescribe antibiotics3,7; local therapy complements general therapy and helps cleanse the tonsils. In mild cases of the disease, accompanied by moderate intoxication, low fever, slight redness and swelling of the tonsils and their arches, only local therapy is sufficient3. Of course, in such cases we are not talking about gargling with a soda solution - only about antiseptics specially designed for this.
Pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis, or inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, is rarely isolated4. In the vast majority of cases it develops as part of the clinical picture
nasopharyngitis, that is, in addition to rhinitis during ARVI, or tonsillopharyngitis - in combination with inflammation of the tonsils4.
Viral pharyngitis is more common than bacterial pharyngitis. In this case, inflammation caused by viruses dominates only at the very beginning of the disease. Hypothermia, drinking cold drinks, inhaling dusty and chemically contaminated air, smoking and other factors that lead to irritation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and decreased immunity often lead to the activation of opportunistic bacteria and the development of bacterial inflammation4. Isolated pharyngitis rarely takes a severe course, so systemic therapy is used only in exceptional cases4.
More often, doctors recommend local therapy - gargling.
Candidiasis of the oral cavity and pharynx
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida can be found in most people3. This microorganism belongs to the opportunistic representatives of the microflora and is activated only when immunity decreases3. The development of candidal stomatitis and pharyngomycosis is facilitated by intestinal dysbiosis and such severe general diseases as diabetes, cancer, and HIV infection. In addition, candidiasis often develops against the background of long-term use of antibiotics, as well as due to improper use of local glucocorticoids (sprays) for bronchial asthma3.
Small white “islands” appear on the mucous membrane, which increase in size and, merging, form films. Externally, the films resemble pus, but they are not removed; when they are rejected, red spots and erosions remain on the surface of the mucous membrane3. Swallowing liquids and food causes pain, which causes adults to lose their appetite, and small children to refuse to eat altogether. Along with antifungal agents, microflora-restoring prebiotics and probiotics, and immune-strengthening medications, local therapy is used3.
Up to contents
Use for thrush
The appearance of thrush is an unpleasant surprise for every expectant mother. Drug treatment is contraindicated. Baking soda comes to the rescue. You won’t be able to forget about thrush with the help of a medicinal solution, but it will relieve severe itching. This method does not pose any threat to the fetus, so it can be safely used.
For douching, prepare the mixture: 1 tsp. dissolve soda in 200 ml of warm boiled water. However, it is important to consult a doctor before use.
Does gargling with baking soda help?
To carry out the procedure, use ordinary baking soda, which is found in almost every kitchen. In terms of chemistry, it is the sodium acid salt of carbonic acid with the formula NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate)2.
Sodium bicarbonate, as an active ingredient, is in the register of medicines2. Indications for its use include acute infections of the upper respiratory tract and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity2. It also describes its action and indicates how much soda is needed to gargle. However, it must nevertheless be recognized that as a means of local therapy for tonsillitis, pharyngitis and stomatitis, it is hopelessly outdated. Its mentions are rare and found in medical articles dating back to the last century. Experts who keep up with the times excluded it from their recommendations. Sodium bicarbonate is not only ineffective, but also not as safe as it might seem at first glance5.
Why shouldn't you use baking soda?
- Questionable effect. Statistics show that 90% of patients who turn to ENT doctors with pharyngitis independently and repeatedly gargle and, nevertheless, they had to resort to medical help5.
- Violation of natural defense mechanisms. The mucus produced by the glands of the pharynx performs a protective function. Microbes that get inside “get stuck” in mucus, lose their activity and partly die under the influence of biologically active substances - interferon, immunoglobulins, lysozyme and others. When rinsing, mucus is washed away, as a result of which the mucous membrane becomes dry, vulnerable and vulnerable to bacterial viruses5. From this point of view, it is probably better to use antiseptics for the procedure, which not only remove mucus, but also kill pathogenic microbes.
- Dryness of the pharyngeal mucosa. This is especially true for chronic pharyngitis, accompanied by thinning of the inner lining of the pharynx and decreased mucus secretion7. Sodium bicarbonate dries out the mucous membrane even more and thereby opens the entrance gates to bacteria that live in the upper respiratory tract and enter through the nose and mouth.
- Effect on stomach acidity. This mechanism is realized when the sodium acid salt of carbonic acid enters the stomach, which often happens in children who do not know how to gargle. By reacting with the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice, sodium bicarbonate literally immediately reduces the acidity of the stomach6. However, soon it not only recovers, but also becomes higher compared to the initial level. This is due to irritation and increased activity of acid-producing cells6. It is because of this that it is not used as an antacid, that is, a means to reduce stomach acidity6. Soda can be dangerous for people with hyperacid gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as for children with underdeveloped protective mechanisms of the digestive system6.
- During pregnancy. The specific taste of soda can provoke vomiting in pregnant women, which is associated with a physiological increase in the gag reflex. In addition, in late pregnancy, when many pregnant women suffer from heartburn, sodium carbonate entering the stomach can cause increased symptoms6.
- Acidosis. Of course, for the development of acidosis, that is, a violation of the acid-base state of the body, accompanied by acidification, you need to take much more soda orally than is needed for gargling. However, we cannot ignore this complication. Even a short-term shift in acid-base status in patients with renal failure can significantly worsen the condition2. In patients with heart disease, it provokes the appearance of edema and the development of heart failure2.
Self-medication is, in principle, dangerous to health, and taking into account all of the above, it is better to remove soda from the medicine cabinet and not use it even for adults. But the question deserves special attention: is it possible to gargle with soda for a child? Due to their age and lack of skills in performing the procedure, young children often swallow solutions5. They are at higher risk of developing sodium bicarbonate side effects than adults5. Special products have been created for children5 in the form of sprays with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory components - these are in the HEXORAL® line of drugs.
Up to contents
Use for throat diseases
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's immunity decreases. Therefore, there is a risk of influenza, ARVI, and colds. Most medications are prohibited. An excellent option for treating the disease is a soda solution. This method is extremely beneficial, so it can be safely used.
To prepare a medicinal solution, add 1-2 tsp to 250 ml of warm boiled water. baking soda. The resulting product can be used to rinse the mouth for sore throat, laryngitis, pharyngitis, and stomatitis.
It is important to consult a doctor before starting treatment.
Treatment and prevention of acute respiratory infections and influenza in pregnant women
This is especially true for pregnant women. The relevance of the problem of acute respiratory diseases of a viral nature is determined by their prevalence, uncontrollability, and high contagiousness.
Modern urbanization conditions create the basis for women to frequently encounter various respiratory viruses throughout pregnancy. Among the pathologies of pregnant women, ARVI ranks first in prevalence - more than 2/3 of the total incidence of acute infections. This is due to the high susceptibility of pregnant women to viral infections, which is due to the peculiarities of the immunity of pregnant women.
The influence of a viral infection on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus is characterized by possible infection of the placenta, amniotic membranes, as well as the fetus itself, indirect influence as a result of the development of fever in the pregnant woman, imbalance, constancy in the body, etc. The variety of clinical effects is explained by the time of infection to the gestational age, properties and virulence of the virus, the state of the placental barrier and the protective forces of both mother and fetus.
Pregnant women are characterized by a protracted course of ARVI in the absence of severe clinical manifestations. This is explained by the ability of respiratory viruses to reproduce in the placenta, as well as the peculiarity of the pregnant woman’s immune system (a state of physiological immunodeficiency).
The main clinical symptoms of ARVI: malaise, weakness, increased fatigue against a background of low-grade or normal temperature, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, turning into a superficial cough.
The erased ARVI clinical picture, which is most typical for pregnant women, is often the reason for insufficient attention to the very fact of the disease, believing that “a common cold is completely harmless.”
But that's not true. A viral infection can have a negative impact on the course of pregnancy, including premature rupture of amniotic fluid. In addition, the virus, penetrating the placenta to the fetus, can cause infection of the fetus.
WHAT IS FLU? The symptoms of influenza are known to everyone - high fever, general weakness, headache, pain in the muscles of the arms, legs, lower back, pain in the eyes, nasal congestion, sore throat, dry cough. Dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea may occur. You cannot catch the flu by simply getting your feet wet; this infection enters the body through airborne droplets from an infected person.
The influenza virus, having entered the body, infects the epithelium of the respiratory tract, especially the trachea, and begins to multiply rapidly. Increased permeability of the vascular wall leads to the appearance of a petechial rash on the skin and mucous membrane of the cheeks and soft palate, hemorrhage in the sclera of the eyes, and, less commonly, hemoptysis and nosebleeds. Influenza reduces immunity and thereby contributes to the exacerbation of chronic diseases, such as bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, kidney diseases, etc.
In addition to pneumonia, influenza also causes complications such as inflammation of the heart muscle, which can lead to the development of heart failure, sinusitis, otitis media, etc. In addition, a bacterial infection - pneumococcal, hemophilic, staphylococcal - will often accompany a body weakened by influenza. Flu during pregnancy is dangerous due to its complications, as it can cause disruption of the functions of all systems of the pregnant woman’s body.
The most unpleasant thing is the threat of miscarriage or premature birth. The influenza virus causes oxygen starvation of the fetus due to the development of a complex of disorders of the fetus and placenta (fetoplacetal insufficiency), intrauterine infection (septic condition, congenital pneumonia, etc.) and fetal death, deviations in the physical and mental development of the baby.
TREATMENT OF ARVI AND FLU DURING PREGNANCY When the first signs of ARVI appear (general weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, headache, fever, sore throat, cough, runny nose), you should consult a general practitioner, general practitioner or Call a doctor to your home rather than self-medicate. The doctor will assess the condition and prescribe examination and treatment.
For mild colds, treatment can begin with the use of folk remedies. A warm, generous drink is recommended (green tea with lemon, raspberry jam, honey, cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks, infusion of chamomile flowers, linden, berries and black currant leaves). A healthy rosehip drink is prepared from the proportion of 5 tablespoons of crushed dry fruits per 1 liter of boiling water. The mixture is infused in a thermos for 8-12 hours. Warm infusion is consumed 1 glass 3-4 times a day. Rose hips and black currants are rich sources of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It must be remembered that in late pregnancy, drinking too much can cause edema.
When suffering from ARVI and influenza, food should be high in calories and easily digestible (preference is given to carbohydrates). The diet should include porridge (semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat, etc.), potato and vegetable puree, honey, jam, jam, fruits (kiwi, oranges, bananas, etc.). Spicy, fried, salty foods are excluded. Fresh onions and garlic can be a useful addition to dishes.
Onions and garlic should be used at the first sign of illness. If for some reason you cannot eat these vegetables internally, it is enough to place these aromatic products finely cut into pieces in the room and inhale the vapors, which contain phytoncides that have a detrimental effect on viruses and bacteria.
If there is no allergy, it is recommended to carry out aromatherapy using essential oils, the vapors of which kill pathogens, freshen breath, and reduce swelling of the mucous membrane.
Horseradish can be used as a herbal immunostimulant. Grate the horseradish root on a fine grater, mix in equal proportions with sugar, place the mixture in a warm place for 12 hours, squeeze out the juice and take 1 tablespoon every hour during the first 2 days of illness.
A warm hand bath helps with acute respiratory viral infections by affecting the receptors in the palms. When using a bath, water vapor is inhaled, which moisturizes the respiratory tract. To enhance the effect, you can add sea salt and infusions of medicinal herbs to the water. After taking a bath, you need to put on mittens and warm woolen socks.
For a sore throat, nasal congestion and cough, it is useful to prescribe inhalations with Borjomi, soda solution, with an infusion of chamomile flowers, calendula, sage leaves, eucalyptus, etc. using a nebulizer or wide containers. Inhalations are recommended to be done 2-3 times a day for 7-10 minutes.
For sore throat and sore throat, it is recommended to gargle with an infusion of herbs (chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, oak bark), a solution of salt and iodine (1 teaspoon of salt and 2-3 drops of iodine per glass of warm water). Gargling is necessary until you feel better.
If you have a runny nose, be sure to regularly ventilate and moisten the room, rinse your nose with saline solution of sodium chloride, which you can prepare yourself (dissolve ½ teaspoon of kitchen or sea salt in a glass of warm boiled water) or buy saline solution at the pharmacy. You can use medications made from sea salt and water, such as Salin, Aqua Maris, Humer, Dolphin, etc. Washing must be repeated 4-6 times a day.
When the temperature rises above 38°, cool water compresses on the forehead, rubbing the areas of the armpits and popliteal cavities, wrists, and elbows with a solution of vinegar (take three parts of water for one part vinegar) will help.
When prescribing folk remedies, it is necessary to take into account the presence of allergic reactions to medicinal herbs, honey, lemon, etc. During pregnancy, it is forbidden to steam your feet, apply mustard plasters, visit baths and saunas, take hot baths, use licorice root for coughs, since licorice (licorice) causes swelling and increased blood pressure. Active treatment with honey and raspberries is not recommended, as this can lead to an increase in the tone of the uterus and provoke the development of allergies in the child.
If treatment with folk remedies is ineffective, but only on the recommendation of a doctor, for acute respiratory viral infections and influenza, you can use a number of medications approved during pregnancy.
To reduce body temperature, paracetamol is indicated; aspirin, complex drugs (Coldrex, Fervex, Theraflu, etc.), ibuprofen, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated.
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops are contraindicated for pregnant women, as they cause vasoconstriction of the placenta and increase blood pressure. To treat a runny nose in pregnant women, you can use Pinosol if the patient is not allergic to essential oils, as well as Sinupret in the form of dragees and tablets.
When coughing, it is allowed to use mucaltin; from the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, ambroxol is allowed.
For sore throat, throat sprays and gargling solutions are safe for pregnant women: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Ingalipt, Argento Sept, Lugol, Strepsils Plus, Tantum Verde, Stopangin (allowed from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy).
Not all drugs with antiviral effects can be prescribed to pregnant women, since some of them have a toxic effect on the fetus, and there is not enough information about the safety of others. For the treatment and prevention of acute respiratory viral infections, you can take Oscillococcinum and Influcid throughout pregnancy. It is necessary to start taking these drugs at the first symptoms of the disease.
Interferon group drugs and interferon inducers that have antiviral and immunomodulatory effects are indicated. Of these drugs, the following are allowed for use during pregnancy: from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, you can use Viferon suppositories; during pregnancy, you can take Grippferon and Genferon (nasal spray and nasal drops).
Umifenovir (arpetol, arbidol) has a wide spectrum of antiviral action, in addition, it has low toxicity, which allows it to be used as an antiviral agent for the treatment of influenza in pregnant women.
The prescribed dose of umifenovir is 200 mg 4 times a day (every 6 hours) for 5 days.
The question of prescribing antibiotics for ARVI and influenza is decided by the doctor. During pregnancy, antibacterial agents of the penicillin and cephalosporin series, as well as macrolides, are allowed for use. Tetracyclines (doxycycline), fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin), co-trimoxazole and other sulfonamides, aminoglycosides (kanamycin, gentamicin, amikacin) are contraindicated during pregnancy.
WAYS TO PREVENT ARVI AND FLU DURING PREGNANCY: A. Nonspecific prevention 1. Compliance with personal hygiene rules :
- Cough etiquette is to cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. After use, throw the napkin in the trash. If a tissue is missing, sneeze and cough into the crook of your elbow.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coughing or sneezing.
- Using alcohol-based hand washes.
- Avoid close contact with sick people (distance of at least 1 meter), hugs, kisses and handshakes.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with your hands.
- Mandatory nasal rinsing and mouth rinsing after returning home.
2.Prevention of infection and spread of infections:
- Isolation of sick people, use of separate utensils.
- Wet cleaning and frequent ventilation of premises.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Avoid staying in crowded places and contact with sick people.
- Cancellation of public events.
- Use of protective equipment (gauze bandages, respiratory masks).
- Lubricating the nasal mucosa with oxolinic ointment before going out during ARVI epidemics.
3.Increasing the body's resistance:
- Taking vitamin preparations, herbal infusions rich in vitamin C (infusions of rose hips and black currants), lemon, cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks).
- A balanced diet including fresh vegetables and fruits, taking plant phytoncides (onions, garlic, horseradish).
- Drug prophylaxis after contact with a sick person (Grippferon, Viferon, Oscillococcinum).
B. Specific prevention of influenza. The most effective method of preventing influenza is immunization of pregnant women and their close relatives.
It is better to get vaccinated at the planning stage of pregnancy. If this does not happen, you can get vaccinated starting from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Modern vaccines of the second generation - Fluvaxin (China), Begrivak (Germany), Vaxigrip (France), Fluarix (Belgium) and third generation - Grippol and Grippol plus (RF), Agrippal SI (Italy), Influvac (Netherlands) are approved for use in pregnant women, starting from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, during lactation and in children from 6 months of age.
Making a choice in favor of preventive vaccination is a step towards maintaining health during a flu epidemic.
Miksha Yadviga Stanislavovna, Associate Professor of the Department of Polyclinic Therapy of BSMU, Ph.D. honey. sciences
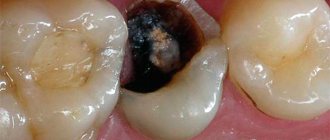
Use for toothache
Often pregnant women face the problem of a toothache. The first thing you should do is make an appointment with the dentist. However, not every expectant mother has this opportunity. A folk remedy will help get rid of discomfort.
To solve the problem, you should prepare a solution: 1 tbsp. add 2 tsp warm boiled water. soda Rinse your mouth thoroughly with the resulting solution until the unpleasant symptoms disappear.
To reduce the risk of toothache, it is important for a woman to carefully monitor oral hygiene. However, toothache does not harm either the expectant mother or the child, but it negatively affects the emotional state of the pregnant woman.
General principles of rinsing
Its undoubted advantage is the lack of systemic action. The components of the solutions are practically not absorbed, do not penetrate into the general bloodstream, and do not affect the functioning of the organs and systems of the body3,4. This allows the procedure to be used not only in the treatment of adults, but also in children and pregnant women3.
The generally accepted local procedure has a versatile effect.
- Mechanical cleansing of the mucous membrane. More precisely, its disposal of pathogenic microorganisms, mucus and pus, which contains pathogens and toxins formed as a result of their vital activity 3.4. By the way, this basically limits the effect when gargling with soda for a child or adult.
- Antiseptic effect. Pharmaceutical preparations contain components that have a detrimental effect on most bacteria, viruses and fungi, which most often cause diseases of the pharynx and oral cavity4,5.
- Creating conditions unfavorable for the proliferation of microbes. The normal acidity of human body tissues ranges from pH 7.32 to 7.45, which corresponds to an alkaline environment. Inflammation, especially purulent inflammation, is accompanied by acidification of tissues and a decrease in pH to 6.5-5.39, which contributes to the further development of infection1. Many rinses alkalize the environment and create conditions unfavorable for the development of viruses and bacteria1, but the majority of drugs inhibit the growth of bacteria due to the action of their antiseptic component3.4.
- Pain relief. Of course, when gargling with baking soda, you can’t really count on relieving a sore throat. But the use of pharmaceutical preparations specially designed for this purpose, containing local anesthetics, can significantly alleviate suffering3,4.
- Reducing signs of inflammation. The action of the medicine leads to a decrease in swelling, pain and redness of the inflamed mucous membrane. At the same time, discomfort in the oral cavity, sore throat and cough caused by irritation of the receptors of the upper respiratory tract are reduced.
- Thinning mucus and making it easier to expectorate4. Some solutions dilute sputum by shifting the pH of mucus to the alkaline side, others contain special components that reduce the viscosity of mucus and thereby facilitate its removal4.5.
Up to contents
Safe treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women
The dentist is included in the list of mandatory specialists to visit during pregnancy. He will be able to detect the disease in time and prescribe safe treatment for gingivitis. The peculiarities of therapy for pregnant women are that measures aimed at eliminating gingivitis include only the removal of tartar and plaque, anti-inflammatory therapy and the prevention of re-development of inflammation, that is, therapeutic measures only imply relief of symptoms.
The first stage of treatment that the dentist will perform will be professional teeth cleaning. Dental plaque will be removed mechanically using Air Flow or ultrasound. The idea that ultrasound, which is used in this procedure, harms the fetus is absolutely groundless: throughout pregnancy, a woman undergoes scheduled ultrasound examinations at least three times. As an anti-inflammatory therapy, the doctor will select drugs that can act as gently as possible on the vulnerable body of a pregnant woman. Their use comes down to a local effect on the gum tissue: rinsing, baths, irrigation.
Salt and soda - what are their benefits for the human body
Salt (sodium chloride) is used medicinally to treat many diseases. An excellent sorbent, it removes excess fluid from the body. And along with it all foreign and harmful substances: viruses, bacteria, etc. There is a method for treating many inflammatory diseases with salt dressings.
Soda (sodium carbonate) is also actively used in folk medicine. It dries out inflamed areas of the skin and mucous membranes, and relieves swelling.
Sodium carbonate and chloride have a positive effect in the treatment of throat inflammations of various natures, including in pregnant women.
Whims or symptoms of gingivitis during pregnancy?
The first symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women begin to appear between 8 and 12 weeks. Expectant mothers, as a rule, suffer from two forms - catarrhal and hypertrophic; ulcerative gingivitis develops less often.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease is manifested by the formation of a fairly large amount of soft yellow plaque on the surface of the teeth, swelling of the gums, their soreness and significant bleeding when pressed with a sharp object. Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by the spread of inflammation over the entire surface of the gums, sometimes the process affects the tissues of both the upper and lower jaws.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
The first symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis usually appear no earlier than the twentieth week of pregnancy. Inflammation affects the lower jaw, gums in the area of incisors, canines and small molars. The hypertrophic form of gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the volume of gum tissue, an inflammatory process in it and bleeding. Gum pockets also appear - grooves formed between the tooth and gum due to the growth of gum tissue.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most severe form of gingivitis occurs in pregnant women. It occurs against the background of serious health problems accompanying pregnancy, in the last trimester, or under the influence of stressful situations. The main signs of ulcerative gingivitis are severe itching, burning, bleeding of the gums, swelling and ulceration.