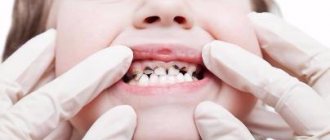
Tooth decay can occur at any age, but is most often diagnosed in children with baby teeth and newly erupted molars. This is due to various factors: internal and external. In this article we will consider the main causes of carious lesions in adolescence and methods of treating this disease.
In this article
- Causes of caries in adolescents
- Symptoms of caries
- Diagnosis of caries
- Treatment of caries in adolescents
- Prevention of caries
By about 12-13 years of age, all molars have grown in. But they will continue to form until their enamel gets stronger. During the entire period of formation, it is more vulnerable to pathologies, especially caries. It occurs due to the influence of many factors on the tooth.
Small teeth need a lot of attention
One of the main problems that pediatric dentists have to face is the treatment of caries of primary teeth in children. The enamel of children's teeth is much thinner than that of adults; it is “weaker” and therefore wears off faster; the dentin layer is also quite thin. Because of these features, baby teeth are more susceptible to the harmful effects of bacteria and other damaging factors. But young children are big fans of sweets and sweet fruits, and their tooth enamel is constantly exposed to aggressive “attacks” from sugar. Therefore, caries in children is a very common disease.
Diagnosis of caries
Treatment of caries depends on the stage, which is detected during a diagnostic examination. If a carious lesion is suspected, the dentist may prescribe the following procedures:
- Test staining: a solution is applied to the enamel, which colors the areas of demineralization purple. The method is suitable for the first and second stages.
- X-ray: the pictures show even hidden carious lesions, including under the gums and on the tooth root.
- Laser diagnostics: allows you to identify caries and assess the extent of its spread.
This pathology is treated therapeutically or with filling.
Is it necessary to treat childhood caries of primary teeth?
Despite constant explanations from dentists, some parents still believe that it is not necessary to treat baby teeth. They still have to be replaced by permanent ones, so why bother your child with trips to the dentist? As a last resort, you can simply remove such a tooth if it hurts a lot. This is very wrong!
It is necessary to treat, because the infection can spread to the germ of a permanent tooth, and it will erupt already damaged. Early removal, which disrupts the bite, is no better.
Timely treatment of caries of primary teeth in children is the main factor in the future health of the entire oral cavity.
It is better to carry it out at the first signs of the disease, since the infectious process spreads very quickly to the pulp, and treatment of pulpitis in children will require several visits to the doctor and will be more complicated.
Symptoms of caries
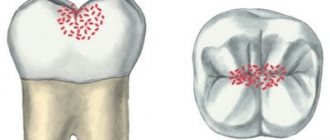
Molar caries manifests itself differently depending on the stage. The initial stage is asymptomatic and is characterized by the formation of a white spot on the enamel - an area of demineralization. At the second stage, superficial, the carious process penetrates deep into the enamel surface, but remains within its boundaries. A person feels pain after eating sweets, which immediately goes away if the irritant is eliminated.
At the third stage, caries penetrates the dentin. There are complaints of pain when a person eats sweet, sour, hot and cold foods. But even at this stage, this symptom goes away quickly if you brush your teeth after eating. At the fourth, deep stage, the pain intensifies, since the carious process is located next to the pulp. At any moment it can provoke pulpitis - inflammation of the soft tissues located inside the dentin.
How is superficial and deep caries of primary teeth treated in children?
Treatment of superficial caries of anterior primary teeth in children (and often chewing teeth) is now possible even without drilling. The Icon technique makes it possible to simply fill such teeth, and the special filling composition that is used in it reliably closes the cavity and stops the further development of infection. In addition, you can use the method of silvering teeth, which will help stop the development of caries in the initial stages and prevent disease in neighboring teeth.
When treating deep caries in children, baby teeth will still have to be prepared, since tissue damage in this case will be significant and all “infected” areas will need to be removed. Then the dentist will fill the tooth - usually children are recommended to have glass ionomer fillings, which contain active fluoride and thereby strengthen the enamel.
It also happens that a child is brought to the doctor with complicated caries, multiple tooth lesions, or the child is simply categorically not in the mood for treatment. In such situations, treatment of complicated caries of primary teeth under anesthesia may be a good solution. Modern drugs used for such anesthesia are completely safe for the child, and all procedures are carried out under the supervision and with the participation of an experienced anesthesiologist.
Prevention of caries
You can prevent the development of caries if you follow the following rules:
- Brush your teeth 2 times a day;
- change the brush every 2-3 months;
- limit consumption of sweets;
- rinse your mouth after every meal;
- use dental floss and irrigators;
- include foods containing calcium in your diet;
- take vitamins;
- Visit the dentist every six months.
At the first signs of caries, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to prepare a child for treatment of caries of baby teeth?
So that the child is not afraid and makes good contact with the doctor, he can and should be prepared a little for the upcoming treatment.
The dentist-therapist at the 32 Dent clinic, Margarita Mikhailovna Plaksina, advises: “You should not focus the child’s attention on the upcoming visit to the dentist so that he is less worried and capricious. You can explain to older children that it is necessary to treat their teeth and that it does not hurt at all. The presence of parents in the office is very desirable - it will help the child feel more confident and calm. For his part, an experienced pediatric dentist knows how to find a common language with a child. And a TV, toys, and bright office design will help the child perceive the healing process as a game.”
Psychosomatics of caries in children
Children differ from adult patients in their increased emotionality and mobility. Treatment of caries is usually accompanied by feelings of anxiety and fear. Parents need to prepare their child for a visit to the dentist, and doctors need to provide emotional support during the treatment process.
- 1.5-2 years.
The baby's perception is associated with muscle sensations. He is afraid of falls: a sudden lowering of a chair or a bright light can frighten him. Parents go to treatment with their child: they hold hands and sit in a chair together.
- 3-4 years.
Children are sociable. The presence of a parent gives a sense of self-confidence and creates a sense of security.
- 5-6 years.
The child may be in the doctor's office without a parent. His behavior changes: before he wanted to touch everything, now he asks questions.
- 7-10 years.
The child becomes more balanced and can overcome the fear of dental procedures. When communicating with him, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of treatment.
- Adolescence.
It is characterized by hormonal changes in the body and frequent mood swings.
Treatment of caries without a drill
Modern pediatric dentistry offers treatment of caries without the use of a drill:
- Silvering . This method is excellent for treating initial caries. The dentist cleans the affected surface and treats it with a 30% silver nitrate solution, after which a protective film is formed that prevents the further development of caries. The procedure takes only a few minutes and is absolutely painless and non-toxic for the baby.
- Remineralization . The procedure is aimed at restoring the mineral composition of enamel and dentin.
- Ozone therapy also makes it possible to treat initial caries without preparation. The method is based on the destruction of carious lesions using ozone molecules.
- Laser treatment of caries has been successfully used in pediatric dentistry. The treatment is painless and does not require anesthesia.
- Chemicals . Treatment is carried out without a drill; the doctor removes damaged tissue using a special gel.
- Icon is a modern method of treating initial caries. To prevent the development of caries, the affected area is sealed using a special polymer.
Tooth preservation
In our clinic, doctors follow the most important principle when treating small patients: do everything possible to keep the pulp alive! Only thanks to it will the tooth be completely formed, its roots will become stronger, and the enamel will increase to the required thickness.
Therefore, pediatric dentists at the Dentville clinic use materials that are biologically compatible with the child’s body - constant monitoring of pulp regeneration processes allows it to be restored even in cases of deep nerve damage by caries.
Instead of empty spaces - tabs
The Dentville Clinic pays close attention to young patients! If our doctors are faced with the impossibility of saving a tooth, then we offer unique solutions that will help avoid bite problems that may arise due to voids:
- microprosthetics;
- lightweight crowns suitable for children's teeth;
- installation of lightweight tabs.
In the future, microprostheses, inlays and crowns can be replaced with ceramic structures, for example, crowns - and then the “adult” dentists of the Dentville clinic will be waiting for you!
How the disease develops
At the initial stage, a stain appears on the enamel, then its destruction gradually occurs. Most often, there is no pain, so the problem continues to grow.
The consequence of this process is deep caries, which is accompanied by:
- A pronounced reaction to hot, cold and sweet foods;
- Severe pain;
- Tooth decay.
The pain does not subside, the child refuses to eat and cries.
If measures are not taken at this stage, inflammation that is dangerous to health develops - pulpitis or periodontitis.
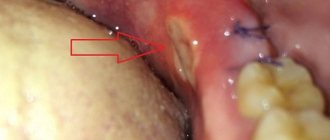
Treatment with preparation and filling
To treat medium and deep uncomplicated caries, we use traditional preparation of the carious cavity and subsequent filling. Preparation is not always painful; it only hurts when removing pulp with moderate or deep caries. In most cases, regular local anesthesia is used by applying an anesthetic gel that reduces sensitivity to injections, and then an anesthetic injection is given. After preparation, a permanent or temporary filling with a medicinal preparation is installed in the carious cavity. The temporary filling is removed after a few days and the tooth is filled with a durable material.
Why are teenagers especially susceptible to tooth decay?
Caries affects both adults and children. But the course of the disease progresses differently. When forming permanent teeth, there are two factors influencing the process:
- Anatomical features of recently erupted permanent teeth. Due to insufficiently formed delicate enamel, the disease quickly progresses on the fissures of chewing units;
- During a turbulent transition period, adolescents may avoid oral hygiene, refuse regular teeth brushing, and avoid medical examination. The problem is compounded if you had a negative experience at the dentist's office as a child.
Causes of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years of age in mixed dentition
The tooth is nourished through a neurovascular bundle called the pulp. Its inflammation is called pulpitis.
- Typically, pulpitis develops as a complication of untreated caries, when the carious process “goes” deep into the tooth tissue, destroys the pulp chamber and bacteria infect the pulp. Such a diagnosis requires serious intracanal (endodontic) treatment.
- In adolescence, children have a habit of not telling their parents that something is bothering them, so very often they do not receive timely treatment. As a result, patients often come to the appointment already with severe pain, complications and deterioration of their general condition (fever, headache, weakness)
- Read more about other non-carious causes of pulpitis, its main forms, symptoms and possible treatment methods in Treatment of pulpitis (dental canals/endodontic treatment).
How to diagnose and treat caries in teenagers
In order for your permanent bite to remain healthy throughout your life, you must initially carefully care for your oral cavity. Following simple but effective rules will allow your child to have a beautiful smile:
- Ensure thorough hygiene not only at home, but also by visiting a professional cleaning at the dentist;
- Come regularly to the clinic for examinations every 6 months. Being in the transition period, caries quickly develops in the mixed dentition, so control is needed;
- For prevention, it is recommended to seal fissures. A filling material is used whose active component is fluorine. The procedure allows you to close vulnerable areas of the tooth and at the same time strengthen the enamel.
"Microscopic" treatment
Due to the fact that tooth enamel in adolescents and children is very thin, dental treatment can be difficult - there is a high risk of tooth destruction and damage to the enamel. To avoid risks, specialists at the Dentville clinic use a special dental microscope, which helps to enlarge teeth many times over and, with pinpoint precision, clean and sterilize dental canals and install miniature fillings that will last much longer than massive ones. Thanks to a microscope, the likelihood of keeping the tooth nerve alive and not damaging it is significantly increased.
What happens if caries in a child is left untreated?
- progresses very quickly and causes the development of periodontitis - inflammation of surrounding tissues. This process can cause the death of the molar tooth germ, as a result of which it will not erupt in time.
- early loss of baby teeth is fraught with disturbances in the normal growth of the maxillofacial system and problems with permanent occlusion;
- If even one baby tooth is missing, the child cannot chew food fully for a long period of time, which can cause digestive problems.