Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the “Free Topic” category of the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition 2020/2021.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
We would all like to have brilliant, healthy white teeth so that we can proudly show them off to others, and those around us would immediately fall into delight from such a demonstration. But, alas and ah, the problem of caries lies in wait for our teeth literally around every corner. However, if you are “armed and dangerous”, namely, you know where the roots of caries come from, that’s already half the victory! Therefore, let's understand the biological subtleties of its occurrence.
What is caries: causes and development factors in children
Caries occurs due to the active proliferation of cariogenic microbes in the oral cavity. Children become infected with them from adults, after which these microorganisms become part of the human microflora. For a number of reasons, caries develops on baby teeth more often than on molars. These reasons include:
- Incorrect and irregular brushing of teeth. The hygienic procedure for cleaning the cavity should be carried out twice a day - in the morning and before bedtime. At the same time, you need to brush your teeth correctly, and not just move the brush from side to side. Parents should teach children regular hygiene and ensure that cleaning is done correctly. Otherwise, caries and other dental pathologies will occur frequently.
- Weak enamel. On baby teeth it is very thin, so they are more vulnerable to external factors, including cariogenic bacteria.
- Poor nutrition. Children often eat sweets, after eating which the rapid spread of cariogenic microbes begins. They feed on carbohydrates and secrete substances that corrode the enamel, disrupt the pH of the oral fluid and leach minerals from the enamel, preventing it from recovering. It becomes soft and loose. It is easier for microbes to destroy its structure and penetrate first into the dentin and then into the pulp.
- Crowded teeth, malocclusion, deep and narrow fissures. If there are many hard-to-reach places in the oral cavity that are difficult to clean from food debris and bacteria, the child often develops interdental and fissure caries. Carious lesions that occur between teeth are one of the main causes of pulpitis.
There are other risk factors for the development of caries in primary teeth: weak immunity, abrasion of enamel, predisposition to dental diseases, etc. Often this pathology occurs due to the impact of several factors on the tooth, the main of which are bacteria and non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Pulpitis during caries does not occur immediately, but only after the pathological process penetrates the dentin and soft tissues inside the tooth. This happens in the fourth stage.
Where do the roots come from?
Caries (caries - “rotting”) is one of the most common human diseases, which is increasingly gaining momentum. About 42% of the world's population has dental caries [1]. However, this problem is far from exclusively human (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Caries occurs quite widely in the animal kingdom, especially in ungulates. Above is a photo of a horse's teeth, below is a photo of a human.
Idade dos cavalos pelos dentes, “Complications in the treatment of dental caries in children”
It is now reliably known that the vital activity of oral bacteria leads to the occurrence of caries. Bacteria, like all living organisms, must eat, grow and reproduce, and also maintain their metabolism (metabolism) at the proper level. But not all bacteria in our mouths lead to tooth decay. Cariogenic bacteria include streptococci (Streptococcus mutans, Str. sanguis, Str. mitis, Str. salivarius) and some lactobacilli (Lactobacillus acidophilus) [2–4].
You can learn about who lives in the oral cavity and how individual representatives of its microflora affect our health from the article “Who lives in our mouth?” [5] special project “Biology, medicine and cosmetology of the oral cavity”. - Ed.
Like many other diseases, caries develops in several stages.
Anaerobic bacteria live in the form of a thin biofilm on the enamel of teeth - plaque. Fixing on the surface of the tooth, they produce extracellular heteropolysaccharides necessary to create comfortable living conditions for themselves, namely to reduce contact with oxygen. Often, the synthesis of such extracellular polysaccharides requires exclusively sucrose, as occurs in Streptococcus mutans (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Streptococcus mutans is a species of gram-positive facultative anaerobic bacteria whose activity is directly associated with the development of caries. Streptococci, due to their structure (form chains) and the presence of a special receptor that allows them to attach to the smooth surface of the enamel, are most often found in dental plaque. Using sucrose, they synthesize sticky polysaccharides based on dextran, forming a biofilm on the tooth, thereby providing themselves with anaerobic living conditions.
"Wikipedia"
A person eats carbohydrates, and streptococci “eat” them along with him. Hence the direct relationship: the more sugar you ate, the more plaque formed. And the sweeter a person’s life, the better for streptococci: during the fermentation of carbohydrates (glycolysis), they receive energy for their vital functions, and from sucrose they build their protective coating - a “shell” from oxygen. The average time for visible and palpable plaque to form is 3–6 hours, and it takes about 24 hours for a dense bacterial biofilm to form.
For people, the activity of plaque bacteria has its disadvantages. They produce a large number of by-product organic acids, including pyruvic, formic, acetic and propionic acids [3]. And lactobacilli also produce lactic acid. The combination of all the released acids inevitably reduces the pH (increases the acidity) of that part of the oral cavity where the most active fermentation of carbohydrates occurs - in the folds of the enamel. At first, excessive acidity is neutralized by saliva, but the longer bacteria live on the tooth (you must understand that time flows differently for bacteria), the more heteropolysaccharides they secrete, and the more difficult it is for saliva to break through the growing shell of plaque. The critical pH value for tooth enamel is considered to be 5.5. It is at this value that caries begins to develop and demineralization of tooth enamel occurs (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. pH is very important for teeth. The normal pH of the oral cavity in the range of 6.8–7.4 is ensured by the buffering properties of saliva. A shift in the indicator to the acidic side to 5.5 is critical and indicates an active process of caries formation.
drawing by Anastasia Prokhorova
What dental diseases are caused by bacteria?
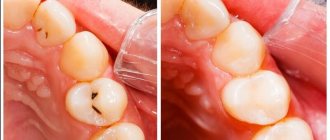
The most common problem that a person faces when pathogenic microflora develops in the mouth is caries. According to experts, caries is the most common chronic disease in humanity. Judging by the photographs taken of this disease, the treatment of advanced caries is too expensive for a person, since his teeth can be almost completely destroyed.
If you do not prevent caries and do not remove pathogenic microorganisms, they can destroy teeth even from childhood.
Another problem associated with pathogenic microorganisms on teeth, clearly visible in photos and videos under a microscope, is bad breath. Moreover, sometimes it can be so strong that it significantly limits communication. This is how bacteria can interfere with a person's social activity and even negatively affect his career.
Our teeth are like stones
Tooth enamel is the outer protective shell of the tooth, which is 97% composed of hydroxyapatite crystals (Fig. 4) - Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 - and foundation proteins: amelogenins and emellines, on which during the development of enamel (amelogenesis ) and hydroxyapatite crystals are strung [2], [3], [6], [7].
Figure 4. This is what the “closest relative” of our enamel looks like - hydroxyapatite. It’s good for him, because he doesn’t know anything about caries!
"Wikipedia"
Hydroxyapatite, although the hardest part of man, is still very sensitive to acids. Acids “stuck” in dental plaque, especially in the area of fissures (Fig. 5) - folds of enamel - begin to destroy the mineral, leading to demineralization of dental tissue, in other words, to softening. The mineral decomposes, forming calcium salts with other acids [3].
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + acid → 10Ca2++ 6HPO42– + 2H2O
Notably, hydroxyapatite can remain dissolved for up to two hours after ingestion. In addition to carbohydrates, the main role here is played by fruit acids. That is why after eating fruit you feel a feeling of cleanliness of the enamel. Over time, saliva neutralizes the effects of acids due to its buffering properties [2]. The more often high-carbohydrate foods are consumed, the more constant the acidification process in the oral cavity becomes. Thus, tooth decay does not depend on the amount of sugar you take, but on the frequency of its consumption: do not eat a bag of sweets during the day, but eat a large dessert once a day.
Figure 5. Enamel folds - fissures - are the favorite place for the “seeds” of caries. It is here that demineralization processes occur especially actively.
drawing by Anastasia Prokhorova
Why is caries dangerous if left untreated?
In this section we will talk about the complications of untreated dental caries in a timely manner, which without exception lead to the need to remove the nerve from the tooth and fill the root canals. And in case of purulent complications, in addition, contact a surgeon to make an incision on the swollen gum.
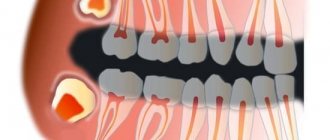
- Development of pulpitis - as the carious process spreads to the deep layers of dentin surrounding the tooth pulp, cariogenic microorganisms penetrate into the tooth pulp. The pulp is the neurovascular bundle of the tooth. As a result of infection, purulent inflammation of the pulp occurs - pulpitis. Pain due to pulpitis is usually acute and paroxysmal in nature. You can see schematically how pulpitis develops in the following pictures (Fig. 7-9) –
- Development of periodontitis – if pulpitis is also not treated in a timely manner, then pulp necrosis occurs, i.e. her death. This stage of inflammation is called periodontitis. In Fig. 11 you can see how the infection, spreading from the carious cavity through the root canals, penetrates beyond the tooth - into the periodontium and bone tissue. And as a result of this, a focus of purulent inflammation appears in the area of the apex of the tooth root (it can be designated by the term “periodontal abscess”).
On an x-ray, such an inflammatory focus looks like intense darkening around the apex of the tooth root. In addition, in Fig. 10 you can schematically see the differences between pulpitis and periodontitis. - Development of a cyst at the apex of the tooth root – as a result of infection of the near-apical tissues, their gradual destruction occurs: the bone tissue is resorbed, and in its place inflammatory granulation tissue is formed, and jaw cysts can also form. Such cysts are called radicular - from the Latin word Radix, which means “root” (24stoma.ru).
A radicular cyst is a cavity in the area of the apex of the tooth, the inner surface of which is lined with a membrane, and the cavity itself is filled with pus. Sometimes they can reach very large sizes. For example, I had to remove such cysts up to 5 cm in diameter. You can see what a radicular cyst looks like in the diagram of a section of the upper jaw (Fig. 12), as well as in the x-ray (Fig. 13), in which the cyst looks like an intense darkening at the root of the tooth.
- The development of gumboil is also a complication of pulpitis and periodontitis and includes a disease called “periostitis”, which is popularly called gumboil. Periostitis is always accompanied by severe swelling of the gums and/or cheeks. Inflammation and swelling in this case are a consequence of the spread of infection from the apex of the tooth root to the area of the periosteum, which covers the jaw from the outside. As a result, a purulent abscess occurs between the periosteum and the jaw (when the periosteum melts, pus breaks through under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity). Treatment of periostitis involves the need to make an incision in the projection of the swelling (to evacuate pus). After this, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Before starting treatment, the issue of the need to remove or preserve the causative tooth that caused the inflammation is also decided. If it is decided to save the tooth, then after the acute symptoms have subsided, the dentist will need to treat this tooth appropriately so that it does not cause purulent inflammation next time.
White caries - black caries, time plays against teeth
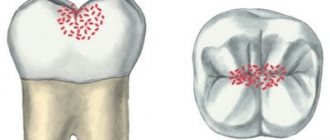
The enamel is translucent and normally ranges in color from light yellow to grayish-white. The color of dentin and any material underneath the enamel greatly affects the appearance of the tooth. Surprisingly, caries begins in the form of the formation of a barely noticeable white matte spot on the enamel (Fig. 6) [3].
Figure 6. “Dental problems.” Over time, the white spots on the enamel caused by caries darken.
drawing by Anastasia Prokhorova
Further, such a stain darkens from frequent meals: the area of the tooth softens more and more, and in the lucky ones a painless hole is formed - a carious cavity [7]. For some unfortunate people, caries is accompanied by inflammation of the tissues around the tooth, infection, and sometimes even an abscess, which can lead not to the small aesthetic problem of “black spots”, but to the loss of the tooth itself.
What do the main bacteria that cause tooth decay look like?
We cannot see what the bacteria that provoke the development of dental caries look like. But visible changes on the teeth provide an understanding of what stage the pathological process is at.
First, a barely noticeable light spot forms on the enamel. At the second stage, the spot becomes darker, its size increases, and the formation of a carious cavity begins. At the third stage, the carious cavity covers not only the enamel, but also the dentin. At the fourth stage, the disease spreads even deeper and goes beyond the dentin.
Sources:
- bsmu.by
- kraszdrav.ru
- en.wikipedia.org
Does genetics have an effect?
Some researchers attribute individual susceptibility to dental caries to genetic factors. By studying the development of caries in animal models, Japanese scientists suggested that loci on chromosomes 1, 2, 7, 8 and 17 contribute to susceptibility to caries. Genetics does not directly influence the onset of the disease, but determines its severity and duration. This is explained by the peculiarities of the structure of the oral cavity: genes involved in the development of enamel, in the formation and composition of saliva, and also those involved in the formation of the immune response are closely studied [4], [8], [9].
How long ago did humanity begin the fight against caries?
Archaeological finds indicate that humanity has made attempts to treat tooth decay already 8-9 thousand years ago. In 2001, archaeologists found a drill in Pakistan believed to be used to remove tooth decay. 11 of those buried had traces of dental treatment.
Ancient Egyptian doctors also practiced dentistry. They knew how to put fillings and made the first false teeth. The priests (or healers) of the ancient Mayan state practiced drilling teeth with a jade tube. It is not known for certain for what purposes, medicinal or ritual, the procedure was carried out.
Treatment of caries until the 19th century was aimed at eliminating pain. For this they used salt, gunpowder, herbal infusions and even smoke and moonlight.
If the pain could not be relieved, the tooth was removed with forceps. This was done not only by doctors , but also by barbers, jewelers and bathhouse attendants . Often the carious cavity was cauterized with a hot iron rod.
In the 16th-17th centuries, carious cavities were filled without preliminary cleaning. Gold, silver, and lead were pressed into them.
Reference! The first drill was invented by French doctors in 1820. The cleaned cavity was filled with silicate cement.
Is it possible to reverse tooth decay?
If you have already noticed the first stages of enamel destruction, then caries cannot be reversed, but it can be slowed down, stretching the process over decades. Ion exchange reactions always occur on the surface of the enamel, allowing one to maintain a delicate balance between demineralization (destruction) and remineralization (restoration) of the enamel. Calcium and magnesium ions, phosphate ions, carbonate ions, strontium and fluorine ions can penetrate into the hydroxyapatite crystal. Of all the listed ions, we are especially interested in the fluorine ion F⁻ . Fluorine can replace the hydroxyl group (OH⁻) of enamel hydroxyapatite, forming fluorapatite Ca₅(PO₄)₃F . Fluorapatite is more resistant to acids, so the vital activity of bacteria has little effect on it [6].
In the article “Tooth Strength: How Do Pastes Make Our Teeth Better?” [10] of the special project “Biology, Medicine and Cosmetology of the Oral Cavity” talks in detail about fluoride and other useful components of toothpastes. - Ed.
Fluoride therapy is used to prevent tooth decay. The most pronounced effect is observed with optimal intake of fluoride ions into the body during the development of primary and molar teeth, that is, in childhood, but also in the first stages of caries - in the white spot stage - such therapy can slow down its course [6], [8] . Eating a balanced diet will also help keep tooth decay at bay. Cereals (bran, whole grain flour, sprouted grains), vegetables and fruits, spices (parsley, cumin, spinach), as well as animal products (fish, meat, especially bone broth, liver, seafood) contain large amounts of fluoride.
Well, if caries is already noticeable with might and main, then radical measures will be required to eliminate it in the dentist’s chair. By the way, the filling material also contains fluorapatite.
Take care of your teeth!
This short review article has already been published by the author here: https://vk.com/@biovk-temnye-delishki-nashih-zubov-karies.
Tooth structure
The tooth is divided into two main parts : the crown , which rises above the gum, and the root , located in the periodontal canal. Between the tooth and the bone there is a layer of soft tissue called periodontium.
The hard frame is dentin . In the upper part it is covered with a thick cover made of hard enamel. On the surface of the chewing teeth there are depressions - fissures . Dentin in the cervical and root areas is surrounded by cement.
Inside the dentin there is a root canal filled with pulp, which contains blood vessels and nerves that exit the root through the apical foramina. They are connected to the neurovascular bundle. The main bundle connects to the circulatory and nervous system of the body.
Prevention of caries and pulpitis in children
To prevent dental disease in a child, you need to follow a number of rules:
- Bring him in for a dental checkup every 4 months. Convince your child that everyone goes to the doctor, including adults, so that he does not have any fear of dentists.
- Monitor your child's hygiene. Teach him to brush his teeth correctly, change his toothbrush every month, buy only special children's toothpastes: Splat Kids, ROCS Kids, Weleda with calendula, etc.
- Limit your intake of sweets. Include in your diet foods rich in microelements, especially calcium.
- Treat all childhood diseases in a timely manner, bring the little patient to the clinic at the first symptoms of any pathology, without trying to get rid of it with folk remedies.
Lead a healthy lifestyle and become an example for your child. Thanks to this, he will get sick much less often.
Treatment with preparation of hard tooth tissues
This method is based on hardware treatment of the affected areas of the tooth under anesthesia. Depending on the stage of development of the disease, there are several stages in treatment. For average caries it is:
- anesthesia
- mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals
- installation of protective lining
- filling taking into account the dental characteristics of the tooth
- grinding and polishing of tooth surfaces
Medium and deep stage treatment takes an hour on average, but in some cases it takes longer. To treat average caries, one visit is enough.
The effect of treatment procedures is determined by the professionalism of the doctor, the quality of medications and equipment, and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. The key to maintaining the result is compliance with proper nutrition and hygiene rules, as well as maintaining the protective functions of the body.
Stages of caries - when pulpitis of baby teeth occurs
Caries of primary teeth develops in 4 stages, like all other types of this disease. The difference is that temporary teeth are more fragile, and therefore the pathology progresses quickly. Hard tissues can be destroyed in just a few months, and in the case of acute disease - in 3-4 weeks.
The first stage is characterized by the formation of an area of demineralization, which looks like a white spot. The enamel in this area becomes porous and rough, but it is almost impossible to notice this with the naked eye, especially if caries has appeared between the teeth, on the root or neck. The disease is not accompanied by pain, discomfort and other symptoms. In other words, a person has no complaints, so it is usually possible to identify pathology at this stage only during a routine examination. If caries is suspected, the dentist applies a dye to the tooth surface, which turns the white spots purple.
Unfortunately, not all parents bring their children for a dental examination every 4 months, so the carious process continues to progress. At the second stage, superficial, caries penetrates deep into the enamel, but remains within its boundaries. There is no cavity yet, but the white spot gradually darkens and becomes brown or yellowish. Tooth sensitivity to sweets also increases. The child may not complain about this. Parents should periodically examine his teeth. If you find dark spots, you need to go to the dentist.
At the third stage, a carious cavity forms, indicating that caries has penetrated into the dentin. A diseased tooth becomes even more sensitive and reacts painfully to temperature changes, sour and sweet foods and a toothbrush. Pulpitis at this stage, as a rule, does not occur, since the pulp is protected by hard tissues. However, the risk of inflammation increases significantly. In addition, caries on baby teeth, in the absence of prevention and the presence of factors conducive to this, rapidly progresses.
The fourth stage is characterized by deep damage to dentin, which is accompanied by frequent pain when the tooth comes into contact with food, cold air, hot drinks, etc. The child cannot ignore or not notice these symptoms; he will definitely say that his teeth hurt. Most likely, he will refuse food and be capricious. It is difficult not to notice a carious cavity even during an external examination. It is a large hole, almost black in color. The patient constantly has bad breath even after brushing his teeth.
The fourth stage of caries is dangerous because it can at any time provoke inflammation of the pulp, that is, pulpitis. Let's take a closer look at this pathology.