2012
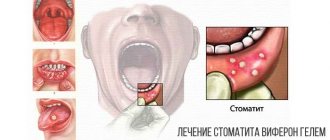
Many people are familiar with a disease of the oral cavity, in which the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, palate, and sublingual space is covered with shallow oval ulcers with a grayish film in the center.
This phenomenon called stomatitis can affect people of any age, and if left untreated, become chronic, provoking the development of a serious inflammatory process.
There are several ways to combat the disease, but the most effective, according to patients and dentists, is the use of a well-known antimicrobial drug - sodium tetraborate.
General overview
Sodium tetraborate is the sodium salt of boric acid. The popular name for this remedy is borax in glycerin.
The substance is a white, fine-crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water and glycerol.
In dental practice, a 20% tetraborate solution is used, where 100 grams of the active substance preparation contains 20 grams, and the remaining 80 grams is glycerin.
Additional components contained in the drug are sodium chloride and human albumin.
pharmachologic effect
The key active ingredient of the drug, the sodium salt of boric acid, has a pronounced disinfectant and bacteriostatic effect , which is manifested in the effective removal of the causative agent of stomatitis and in preventing its further development.
Another important component is glycerin, which helps reduce the irritant effect caused by boric acid salt. In addition, it accelerates the penetration of borax through the oral mucosa, thereby increasing the effectiveness of its effect on fungal formations that cause stomatitis.
When applied topically, the borax solution is quickly absorbed through the mucous membrane, processed by the digestive system and removed from the body through the excretory system.
Release form
The sodium salt of boric acid can be found on sale in three forms, each of which is used for the treatment of stomatitis:
- Solution for topical use. The drug, containing sodium tetraborate and glycerol in a ratio of 20:80, is packaged in glass bottles of 30 or 50 grams.
- Powder in packages of 30 grams. During the treatment of stomatitis, a tablespoon of the substance is dissolved in a glass of warm water, after which this solution is used to rinse the mouth.
- Pills . For dental purposes, the tablets are used as follows: two units of the drug are dissolved in 250 ml of slightly warmed water, and the resulting solution is used to rinse the mouth to get rid of aphthae on the mucous membrane.
Indications
The product is used in medicine to eliminate many diseases, from candidiasis to various skin lesions.
This component is included in complex preparations used to treat diseases caused by candida fungus.
In dental practice, boric acid salt helps fight the following pathologies:
- candidiasis of the oral cavity;
- microbial lesions of the palate, tongue and gums;
- mechanical damage to gum tissue due to prolonged compression by orthopedic construction.
Methods for treating tonsillitis at home - remedies, recipes and rules of use.
We will discuss here the possible symptoms of gingivitis in children.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/desnyi/plazmolifting-sovremennaya-metodika-v-stomatologii.html we will talk about the use of plasma lifting techniques in dentistry.
detailed instructions
Dentists prescribe a remedy for the treatment of stomatitis in patients of various age categories.
The substance helps fight Candida fungi, which can develop on the mucous membrane of both adults and infants.
However, to obtain maximum results, you should adhere to certain rules for applying the product, which differ slightly depending on the age of the patient and the stage of progression of the disease.
Use for infants
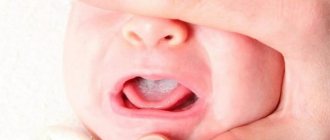
Stomatitis is quite common in children aged 1-2 years, because they have a delicate mucous membrane, and the immune system is not able to cope with the large number of pathogenic microorganisms that enter the oral cavity through a pacifier, toys and other objects.
A mild form of the disease responds well to treatment with borax in glycerin, which should be used as follows:
- Preparation of the oral cavity. With stomatitis, ulcers may form on the surface of the mucous membrane, which become covered with a dense crust, preventing the medication from being fully absorbed.
Therefore, parents need to treat the wounds with a gauze swab coated with an oil solution of vitamin A or sea buckthorn or peach oil.The movements should be careful so that the crust softens and does not break off. Since the process can cause pain to the child, you can first treat the mucous membrane with a drug based on Lidocaine.
- Treatment of the mucous membrane. A sterile gauze swab should be moistened in a solution of sodium tetraborate, and then wipe the baby’s tongue, palate, inner surface of the cheeks and lips with it.
If using a tampon is inconvenient, you can wrap your index finger with a small piece of sterile bandage, apply the solution to it and treat the baby’s oral cavity.
It is necessary to wipe ulcerative formations with borax no more than twice a day. Often, two days are enough for the disease to subside, but experts recommend continuing treatment for 2-3 days after the ulcers have healed to prevent recurrence of stomatitis.
Advice to parents! Do not forget to wash your hands thoroughly and treat them with an antiseptic before you begin to cleanse the baby's mucous membranes. This will prevent the risk of additional infection.
What is macroglossia and how dangerous the disease is.
This publication is about the most effective ointments for stomatitis.
Follow the link https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/stomatit-bpr/kak-i-chem-v-domashnih-usloviyah.html to find out how to properly treat stomatitis at home.
Application for teenagers
In children of the older age group, the number of methods for treating ulcers is expanding. Dentists recommend choosing the most convenient method among the following options:
- Spot processing . The procedure is no different from the method described for infants. Children can wipe the areas where ulcers accumulate with cotton or gauze pads soaked in a borax solution. After the procedure, you must thoroughly rinse your mouth with water.
- Applications . If rashes are present on the inner surface of the lips, to treat them, you can moisten a gauze pad with a tetraborate solution and apply it to the affected area for 5-7 minutes.
- Rinse . The instructions for use suggest this option for preparing the solution: add 5-7 drops of borax solution and a teaspoon of salt to a glass of warm water. The frequency of rinsing with this composition is 2-3 times during the day.
To increase the effectiveness of the product, before use, you must thoroughly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with water.
After applying the drug, it is advisable to refrain from eating for 30-40 minutes.
Use for adults
When treating stomatitis in adults, not only local treatment of the oral cavity is often used, but also antifungal or antiviral drugs.
The specific treatment regimen is selected by a specialist, depending on the form of the disease:
- For acute stomatitis, boric acid salt is used in the form of a ready-made solution, which is used to moisten a gauze swab, after which the ulcers located on the palate, tongue, gums and other parts of the oral cavity are wiped.
The procedure must be performed 5-6 times a day. Depending on the severity of the disease, the duration of therapy can be 1-2 weeks. Rubbing the sores can be supplemented with applications and rinses. - Chronic form of stomatitis develops as a result of the persistence of the pathogen in the oral cavity with insufficiently thorough treatment of the acute phase of the disease.
A decrease in immunity as a result of any viral disease threatens a new intensification of stomatitis. To get rid of it, experts recommend treating emerging ulcers with a solution 3-4 times a day.The duration of therapy often reaches 2-3 weeks. In this case, the dentist will definitely prescribe medications for internal use, which will speed up the healing process.
Additional measures
To avoid re-infection, you must follow the following rules:
- monitor your child’s oral hygiene;
- stop biting your nails and putting things in your mouth;
- treat dishes with boiling water: nipples, bottles, plates;
- replace a toothbrush with hard bristles with a soft one;
- treat nipples before breastfeeding;
- Do not feed your baby too hot food.
To reduce pain when eating, special pain-relieving gels are used. In case of extensive damage to the mucous membrane, the spoon can be replaced with a straw, while giving the child only liquid food.
Avoid sour and spicy-tasting foods during treatment so as not to further irritate the mucous membrane. Make sure that the diet is enriched with the necessary mineral and vitamin composition.
Attention must also be paid to the hygiene of the child’s room. It is necessary to regularly wipe surfaces from dust with a damp cloth, replace vacuuming with a damp cloth, monitor the freshness of the air, and if it is excessively dry, humidify the air in the room.
Along with treatment, it is necessary to strengthen the child’s immune forces and ensure rapid restoration of the affected tissue. For this use:
- Aekol - for applications;
- Vinylin - for quick healing;
- Solcoseryl - to restore damaged tissues;
- Sea buckthorn oil - to relieve pain and restore the epithelium.
To speed up tissue healing, rinse with herbs (between the main treatment). To do this, use chamomile, which has antiseptic wound-healing properties. You can use any herbs with an astringent and antiseptic effect (oak, sage, marigold). They also make applications of aloe juice with honey, and rinse the mouth with propolis tincture.
Baking soda with salt is a common remedy for ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane. For small children, prepare in the following proportion: a coffee spoon of soda and salt per cup of cooled boiled water. If the baby does not know how to rinse his mouth, wipe the mucous membrane with the solution - moisten the gauze and treat the mouth.
Sources used:
- Medicines in dentistry. Directory / L.N. Maksimovskaya, P.I. Roshchina. - M.: Medicine, 2001.
- “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.)
- Mashkovsky M.D. Medicines. — 15th ed. - M.: New Wave, 2005.
- https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0057.html
Side effects and overdose
With prolonged use or if a person is hypersensitive to the drug, an allergic reaction may develop.
Pathology manifests itself in redness and swelling of the area treated with the substance, and the formation of a rash on it, accompanied by itching.
In this case, the use of borax should be stopped immediately and contact a specialist to eliminate the reaction.
Sodium tetraborate is a toxic compound and can cause poisoning if accidentally swallowed. The lethal dose for an adult is 10-20 g.
Symptoms of a solution overdose are as follows:
- headache;
- skin rashes;
- abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting;
- indigestion;
- general weakness, confusion;
- impaired functioning of the kidneys and liver;
- in some cases, the development of shock is observed.
If the listed symptoms are detected, it is necessary to perform gastric lavage and call an ambulance.
Precautionary measures
An adult’s body reports an overdose
- frequent loose stools;
- general weakness of the muscular system;
- causeless urge to vomit;
- spasms of the limbs and facial muscles;
- the appearance of dermatitis.
If the above symptoms appear, you must immediately perform gastric lavage and stop using this drug.
Sodium tetraborate solution is still used to treat severe cases of fungal stomatitis in newborns, but only for the treatment of ulcers.
This medicinal drug has pronounced side effects :
- menstrual irregularities in women;
- the occurrence of seizures in children of different ages;
- noticeable redness, burning, irritation at the site of application;
- manifestations of dermatitis;
- hair loss or impaired hair growth;
- anemia or anemia;
- intoxication from long-term use;
- gastrointestinal tract malfunctions;
- partial or complete lack of appetite.
When used correctly, this drug effectively affects only areas affected by infection and prevents the proliferation of fungal spores without any negative consequences for the body.
Caution and attention are the key to successful treatment.
Price
Sodium salt of boric acid is a budget drug. In most pharmacies, the cost of a 30 gram bottle does not exceed 25 rubles.
If you go to pharmacy kiosks located in remote residential areas of large cities in the country, you can purchase the product for 9-15 rubles.
Price
Sodium tetraborate solution can be purchased at any pharmacy in the Russian Federation: pharmacies in St. Petersburg offer the drug at a price of 8.25 to 15 rubles per bottle with a capacity of 30 grams.
In Moscow, the same drug can be bought at a price of 14 to 20 rubles . Before visiting the nearest pharmacy, it is better to call several to find out the price range - when buying one bottle this does not make a significant difference, but for a full course lasting 3 weeks, the savings will be significant.
Reviews
Numerous reviews on the Internet indicate the high effectiveness of sodium tetraborate in the fight against stomatitis.
However, its use is permissible only after consultation with your doctor. This will allow you to select the optimal treatment option and avoid the disease from entering the chronic phase.
Leave your comments about the effectiveness of using borax in glycerin for the treatment of stomatitis.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags medicines stomatitis
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Treatment of older children
The use of a borax-based drug for the treatment of stomatitis in older children is carried out according to the following scheme :
- for rinsing, prepare a solution: take a glass of chilled boiled water, add 1 tbsp. l. rock salt, add ½ tsp. borax in glycerin;
- we treat ulcers or inflamed areas according to the method described in the previous section.
When using this drug for the treatment of pediatric stomatitis, an overdose is excluded, but parents should be aware of its negative manifestations:
- pain appears in the abdominal area;
- the child complains of a headache;
- frequent bouts of vomiting;
- convulsions and partial loss of consciousness;
- lack of appetite;
- development of arrhythmia.
Serious consequences of an overdose can be:
- dysfunction of the liver and kidneys;
- problems with the functioning of the heart and circulatory system.
If any of the above symptoms appear, you must immediately show your child to a doctor.