Bactericidal and modified cements
— Unitem (Vladmiva) is a universal, improved zinc-phosphate dental cement with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The powder consists of zinc oxide, with modifying additives, and the liquid consists of orthophosphoric acid of reduced activity.
— Unicem bactericidal (Vladmiva) is a universal improved zinc-phosphate dental cement containing the optimal amount of a bacteriostatically effective form of silver. Used in pediatric dentistry for filling temporary teeth.
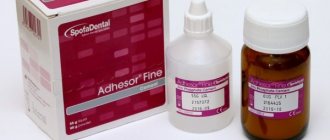
— -Adhesor (Spofa Dental) – zinc-phosphate cement, Adhesorfine (Spofa Dental) – modified zinc-phosphate cement with a fine structure.
— Phosphate cement containing silver. To improve the bactericidal properties, silver (1.547%) is added to the powder composition. The material is recommended as an insulating gasket when filling molars with metal and other fillings, for filling canals, in pediatric dentistry for filling temporary teeth. Analogs: Bactericidal Unitem (Vladmiva).
— Visphat cement refers to zinc phosphate cements. Its powder contains about 3% bismuth oxide. It hardens faster, is stronger than phosphate cement, and is less soluble. It is used as an insulating lining when filling teeth with metal fillings, silicate cements, acrylic and epoxy resins.
— Dioxyvisfate Dioxidine is included in the composition of this cement. Dioxyvisfate powder is a mixture of visfate and dioxidine, the liquid is orthophosphoric acid, partially neutralized with zinc oxide and aluminum hydroxide. Cement has bactericidal properties, has high mechanical strength, is slightly soluble, and is intended for filling temporary teeth, as a therapeutic and insulating spacer, for fixing inlays, pin teeth, and bridges.
Homework to understand the topic of the lesson:
Control questions:
1. What is the chemical composition of zinc phosphate cement powder and liquid?
2. What is the chemical composition of polycarboxylate cement powder and liquid?
3. What is the purpose of zinc phosphate cements?
4. What is the purpose of polycarboxylate cements?
5. Name the materials from the group of zinc-phosphate cements of domestic and foreign production.
6. Name the materials from the group of polycarboxylate cements of domestic and foreign production.
Filling (restorative) materials to restore the anatomical shape and function of the tooth
| Heading | Medicine |
| View | abstract |
| Language | Russian |
| Date added | 02.06.2015 |
| file size | 49.6K |
Agreement on the use of site materials
We ask you to use the works published on the site exclusively for personal purposes. Publishing materials on other sites is prohibited. This work (and all others) is available for download completely free of charge. You can mentally thank its author and the site team.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar documents
Advantages of composites, their additional components. Classification of fillers. Light-curing filling materials that combine the main advantages of composites and glass ionomer cements. The use of lamps in dental practice.
presentation [1.0 M], added 04/03/2016
Modern filling materials, their division into groups. Classification of materials for therapeutic linings. Materials for dressings and temporary fillings. Composition of polymer cements. Properties of filling (restoration) material, its classification.
presentation [7.0 M], added 09.14.2016
Modern filling materials. Artificial dentin. Materials for dressings and temporary fillings. Zinc phosphate, polycarboxylate, silicophosphate and glass ionomer cements. Metal filling materials, composites, plastics and ormocers.
course work [41.7 K], added 12/03/2013
Direct filling using composite materials as an integral part of modern dentistry. Composites are polymer filling materials consisting of three components. Features of the classification of composite materials.
presentation [737.2 K], added 12/17/2014
Dental filling. Powder-liquid system. Composition and indications for use of silicate and silicophosphate cements. Studying their positive and negative properties. Method of application, preparation technique, chemical composition and hardening of cement.
presentation [593.8 K], added 05/27/2014
Anatomical classification of carious cavities according to Black. Instrumental treatment of hard dental tissues, its goals and objectives, evaluation of results and effectiveness. Basic shapes of cavities created using a fissure bur. Principles of caries treatment.
presentation [9.3 M], added 10/25/2014
The concept and types, functions and features of the use of composite filling materials, assessment of their main advantages and disadvantages. Methods, instruments and materials used in dentistry. Classification and types, distinctive properties of composites.
presentation [826.5 K], added 06/08/2014
Unitem white (50g+30ml), VladMiVa
Cement for fixing pins, crowns, bridges and inlays. Unitem has high mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
- Description
- Shipping and payment
- Reviews
Description
Unicem is a universal zinc phosphate cement formed by mixing zinc oxide powder and phosphoric acid solution.
Indications
- Fixation of crowns, bridges, pins, inlays.
- Filling teeth that are to be covered with a crown.
- Can be used as an insulating gasket when filling with silicate and silica-phosphate cements, as well as amalgams.
Characteristics
- Powder: 50 g.
- Bottle of liquid: 30 ml.
- Powder measuring cup: 1 pc.
- Dropper cap: 1 pc.
Compound
- Zinc oxide powder with modifying additives.
- Orthophosphoric acid of reduced activity.
Cement mixing process
Advantages
- High mechanical strength (90-120 MPa, depending on the ratio of powder and liquid).
- High adhesion to metal, plastic, porcelain, metal ceramics and other dental materials.
- Cement is resistant to the aggressive action of the moist environment of the oral cavity.
Instructions for use
- If the material has been stored or transported at low temperatures, it should be kept at room temperature for one hour before use.
- On a dry glass plate, gradually mix the powder and liquid in the required proportion.
- The mixing time should not exceed 1 minute.
- Apply cement to the previously treated and dried tooth surface.
- The hardening time of the cement is 2 hours; during this period it is recommended to cover the filling with varnish or hydrophobic gel to protect it from the action of saliva.
Fixation of prostheses
- 1 scoop of powder (0.25-0.30 g) + 4 drops of liquid (0.18-0.20 g).
- The dough remains plastic on glass for 2-2.5 minutes, and hardens in the oral cavity within 8 minutes.
Dental filling
- 1 scoop of powder (0.25-0.30 g) + 3 drops of liquid (0.13-0.15 g).
- The dough remains plastic on glass for 1-1.5 minutes, and hardens in the oral cavity within 6 minutes.
Storage
- Store in a dry place, protected from direct sunlight, in a tightly closed container.
- Storage temperature: from +5°C to +25°C.
- Avoid exposure to moisture.
- Shelf life: 5 years.
The Nika Dent company is the official distributor of VladMiV products. We supply dental materials and consumables throughout Russia.
Shipping and payment
PAYMENT METHODS
| Cash to the courier upon receipt of the goods. Possible: in Moscow, Moscow region, St. Petersburg, Leningrad region. |
| By bank transfer for legal entities by account. |
TRANSFERING THE ORDER TO THE DELIVERY SERVICE
For cash payments:
the next day after receiving the order, unless a different delivery date has been agreed upon.
For non-cash payments:
the next day after receiving the money to the bank account.
Please check with your manager about the possibility of same-day delivery.
DELIVERY METHODS
Delivery by our transport is carried out in Moscow, Moscow region, St. Petersburg and Leningrad region.
To all other regions, delivery is carried out by transport companies.
Pickup of goods from the warehouse and company office is not provided.
COST OF DELIVERY
| Within the Moscow Ring Road: when ordering over 3,000 rubles - free. Up to 3,000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. |
| IN ST. PETERSBURG : when ordering over 3,000 rubles - free. Up to 3,000 rubles – delivery cost 350 rubles. |
| IN THE MOSCOW REGION: up to 50 km from the Moscow Ring Road: for orders over 5,000 rubles - free. Up to 5000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. 50-100 km from the Moscow Ring Road: for orders over 30,000 rubles - free. Up to 30,000 rubles – we temporarily do not deliver. |
| IN THE LENINGRAD REGION: up to 20 km from the Ring Road: for orders over 5,000 rubles - free. In all other cases - individually |
| TO OTHER REGIONS The minimum order amount to the regions is 3,000 rubles. Delivery is carried out by a transport company. The cost of delivery to the Moscow base of the transport company is free. Payment for the services of the transport company is at the expense of the client. We work with any Transport companies convenient for you! |
Repeated delivery due to the buyer's fault will be paid in any case!
Reviews
There are no reviews for this product yet. Be the first to leave a review!
Classification of sealers (endosealers)
The classification of sealers includes, of course, not only newer materials, but also those that are no longer used in modern dentistry or are used in budget appointments. But for the historical aspect, and for general development, it would be nice to orientate ourselves in them.
Sealers are divided according to their consistency and combination of properties into:
- Plastic;
- Filers are primary solid.
Plastic sealers include non-hardening sealers and hardening sealers in their group. Currently, non-curing sealers are not used. Firstly, it is quite difficult to qualitatively fill the space between the dentin of the canal and gutta-percha, so as not to remove the material beyond the apex of the root, secondly, this group of materials has the super ability to dissolve under the influence of moisture, and at the end we have a poor-quality root canal filling, a newly developed pathological process.
A wide range of materials is included in the group of plastically hardening materials, including:
- Sealers based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin;
- Sealers based on phosphate cement;
- Sealers based on epoxy resins;
- Sealer based on zinc oxide and eugenol;
- Sealer as an adhesive system;
- Polymer sealer with calcium hydroxide;
- Sealers based on silicone resin.
Sealer based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin
Here you won’t open America to anyone - sealers based on resorcinol and formaldehyde resin are not used, because:
- A sealer based on resorcinol - formaldehyde resin has a high shrinkage, therefore, loss of high-quality sealing;
- Tooth staining pink;
- Formalin not only has a toxic effect on the body, but is also carcinogenic!
The course of the hardening reaction
Ion formation , dissolution stage. The acid reacts with the upper glass particles, forming calcium, fluorine, aluminum and sodium cations;
Primary gelation , hardening - polyacid molecules quickly cross-link with each other and with aluminum and calcium ions. At this stage, the pH of the cement increases markedly, and the polyacid molecules turn into a gel;
Final hardening - strong ionic cross-links are formed, mainly from fluorine and aluminum polyalkenate. This stage lasts about a day. It also completely stops the formation of silica gel on glass particles.
Due to the fact that aluminum is a trivalent element, a very high degree of cross-linking is ensured, which ultimately makes the cement extremely strong.
When cement hardens completely, it is structurally composed of glass particles surrounded by silica gel. All particles are located in a matrix created from cross-linked polyacid molecules, along with insoluble phosphate and fluorine salts.
Insulating gaskets must perform the following functions
- be non-toxic to the dental pulp;
- remineralize dentin tissue;
- protect soft and hard tooth tissues from irritants, as well as reduce tooth sensitivity after filling and preparation procedures;
- promote better fixation of the filling;
- do not affect the physical and chemical properties of the permanent filling;
- be sufficiently resistant to the effects of liquids formed in the oral cavity;
- have fast hardening and excellent adhesive properties in relation to tooth tissues;
- provide a hermetic coating of the bottom of the carious cavity;
- be resistant to chewing loads.
Insulating spacers are also used as separating planes when the components used for filling are incompatible, for example, composite fillings and eugenol-based pastes.