If, after removing or treating a tooth, pus appears in the gums, you should immediately consult a dentist. Suppuration of tissues in the oral cavity always indicates an acute inflammatory process and is a very dangerous condition. It is often accompanied by fever, weakness, and chills. During the inflammatory process in the oral cavity, the soft tissues swell greatly, which is why a person cannot chew or talk. If treatment is not started, the infection can spread throughout the body. Find out what causes inflammation and how to deal with it.
Causes
Each patient's response to pain relief is different. It depends on the condition of the oral cavity, the level of vulnerability and age. The appearance of severe pain indicates the development of complications. In such a situation, the dentist must find out the cause of the problem. A private dental clinic is exactly the institution where modern diagnostic methods, the latest equipment, and advanced therapy technologies are used. Common triggers include:
- Development of inflammatory processes;
- Suppuration in the tooth root;
- Formation of a fistula or abscess;
According to indications, a minor surgical intervention is performed. During such procedures, nerve fibers may be affected. It happens that incision of mucous tissues is required. The main causes of the problem are:
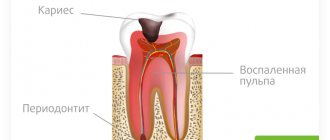
Development of an infectious focus
If your gums hurt after an anesthetic injection, it can be assumed that the soft tissues are infected. After all, the oral cavity always contains many microbes and bacteria, both beneficial and opportunistic. When performing an injection, they quickly penetrate into the puncture sites, thereby provoking inflammation. As a result, exudate accumulates in the affected areas and flux may develop. Patients complain of edema, swelling of soft tissues, burning and throbbing pain of the mucous layer.
Nerve trunk injury
The problem often arises when the masticatory organs are injured. Even an experienced dentist can accidentally hit very sensitive fibers of nerve endings with a sharp thin needle. This disrupts their work. After all, the nerves of the oral cavity are closely connected with the facial muscles and the muscular system of the eyelids. Therefore, the cheek hurts after an anesthetic injection during dental treatment. Discomfort is felt in the ear, temple. The patient may experience voluntary lacrimation. In addition, others notice the asymmetry of the face on the side of the inflamed area. The pain may be jerky. Its duration ranges from several days to several weeks.
Hematoma formation
It is important to carefully monitor the health of the oral cavity and chewing organs. Timely consultation with a doctor will help prevent complications. The sooner you contact a dentist, the easier and faster the therapy will be; it is possible to treat caries without drilling teeth. Therefore, preventive examinations should not be skipped. Visiting the doctor once every six months is the key to a healthy oral cavity.
If you violate the schedule of preventive examinations or ignore the doctor’s recommendations, bruises often appear on the affected areas. In such areas, the accumulation of blood is limited, as blood vessels rupture. The resulting cavities contain liquid blood, as well as coagulated blood cells. Hematomas in the oral cavity form quickly, because the periodontium is penetrated by an extensive network of blood vessels. Small capillaries nourish the gum tissue and tooth roots. It is through them that complete nutrition is delivered. When the vessels are damaged during injection, some blood accumulates under the mucous layer. This results in the formation of a convex dark lump or spot. Sometimes the patient does not feel the lump until complications arise, requiring thorough cleaning.
Necrotization of soft gum tissue
It happens that a tooth hurts after anesthesia for serious reasons. The provoking factor may be the death of mucosal tissue. The patient should be alerted to swelling, whitish or dark spots. Often causes necrosis:
- Rapid injection of an anesthetic substance, which damages the vessels, as they are compressed;
- High portions of the drug contain a substance such as adrenaline, which promotes spasms;
- Poor blood circulation in chronic diseases and diabetes;
- Rejection of the mucous membrane from the bone tissue;
Causes of cheek swelling after dental treatment.
It should be noted right away: such a picture may be a natural consequence of the treatment itself. If the cheek is swollen after tooth treatment, but recovers in a matter of hours, then we are talking about normal post-therapeutic swelling.
In addition, people suffering from hypertension (high blood pressure) may experience bleeding for a long time after surgery, even the simplest one, along with a swollen cheek.
Most often, a person discovers that his cheek is swollen after tooth extraction. However, such situations are also considered normal. Indeed, during the extraction of a tooth from the alveoli, tissues are damaged and many vessels are torn, and this, naturally, leads to swelling of the gums, and with it half of the face. Our doctors always inform their patients about this consequence before tooth extraction surgery, and after it they tell them how to reduce pain and eliminate inflammation in a matter of hours.
In all other cases, edema is considered a pathology that needs to be eliminated, and very urgently.
Attention! If after dental treatment your cheek is swollen, but has not recovered within two days, immediately contact your dentist. The sooner you do this, the sooner he will carry out all the necessary examinations, identify the cause of the pathology, eliminate the tumor and thereby prevent the development of serious complications, including gum suppuration. And, if pus has already formed in such a short period of time, then a dental surgeon will get down to business and eliminate the source of infection. You will then undergo a therapeutic course of treatment using injections or oral medications.
Dangerous symptoms
Today, laser caries treatment is often used. Such manipulations do not cause pain if the dentist follows the technology. No painkillers are required. This therapy technique is especially suitable for those who are afraid of injections. The use of this method of treatment eliminates the drill and vibrations from it. This therapy is also comfortable for the patient.
If you experience an unpleasant symptom after the injection and it does not go away within 3-4 days, you should consult a doctor. Serious symptoms that indicate a problem may include gumboil and abscess, ulcers and spots on the gum tissue, or the formation of a large cyst. In such a situation, you should not hesitate to visit the doctor, so as not to worsen the consequences.
First aid if your cheek hurts after tooth extraction
Each of us has encountered a situation where, after tooth extraction, the gums and cheek hurt. Constant pain interferes with normal activities and prevents you from concentrating on work. You need to be as careful as possible to get rid of pain at home. If you carry out the procedure inaccurately, you can wash out the formed clot and provoke infection into the open wound.
The onset of the inflammatory process is indicated by:
- pulsation in the wound;
- swelling;
- sensation of pain in other parts of the face;
- the appearance of pus;
- weakness.
What can you do at home?
When discomfort is felt in the gum tissues, or a sore throat after dental anesthesia, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. Before going to the clinic, you need to follow simple rules.
- Do not include too cold or hot foods in your diet, as the gums are vulnerable and react painfully to irritants.
- Teeth should be brushed with a cool brush.
- It is impossible to mechanically influence the gingival tissue. The pressure should be light.
- Do not apply garlic, pepper, or mustard to the affected mucous membrane.
- Several times a day you should rinse your mouth with a salt solution, a water decoction of chamomile or sage. Particular attention should be paid to diseased areas.
Such activities will ease the condition before visiting a doctor. After the procedure, the dentist may prescribe medications to relieve pain. The most commonly prescribed drug is Nise, a strong drug that relieves muscle pain. Ketanov is an effective remedy. Dexalgin acts for a long time and quickly. For minor pain, baralgin is used. Nurofen works well on soft tissues. At elevated temperatures and inflammatory processes, it is recommended to use paracetamol.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
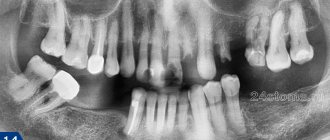
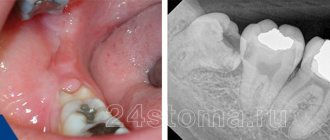
To exclude hidden lesions of the tooth and soft tissues, the doctor refers the patient to an X-ray. Treatment always begins with removal of pus. The specialist carefully opens the gum and cleans it of dead tissue, after which he treats the cavity with antiseptics. To defeat the infection, the patient must take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by the doctor. If pathogenic microorganisms have not penetrated into the deep layers of tissue, this is usually enough to stop inflammation.
If the image shows that the main source of inflammation is in the canals of the tooth, then the filling will have to be removed. The doctor will remove it, thoroughly clean the root canals, place a temporary filling and set a date for a follow-up examination. It will be possible to fill the tooth again only after the photo shows that the inflammatory process has stopped.
Sometimes the cause of suppuration is damage to the apex of the tooth root. To save it, the doctor performs an operation - resection. During it, only the affected root tissue is removed.
Treatment of gum suppuration always includes taking antibacterial drugs. They help destroy infectious agents and prevent relapse.
Physiotherapeutic methods are also widely used in dentistry. Electrophoresis, ultrasound and laser help speed up tissue restoration, increase local immunity, and relieve swelling. Physiotherapy is prescribed only after the inflammatory process has stopped. The duration of the course for each patient is determined individually.
The main causes of pain after injection in the oral cavity
It should be understood that when a needle passes through soft tissues, it injures them and the occurrence of unpleasant sensations is always present. This is considered normal and can persist for even 1-2 days, and even longer in more sensitive people.
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the person and his neuropsychic perception. This condition does not require treatment and goes away on its own after a certain time.
Another question is when the pain does not subside, and also intensifies in direct proportion to the period of limitation of the treatment. This condition may indicate the development of a complication that can result in a serious complication. The symptoms of such problems are varied and depend on what led to the pain reaction.
Development of an infectious focus
A person, even without the development of inflammation, has a huge number of bacteria in the oral cavity. In a normal position, they do not develop, but are in a certain balance.
Attention!!! If any complication develops after anesthesia, it is prohibited to use warm compresses and self-medicate. This can lead to even more serious consequences that will require long-term hospital treatment.
When a pathological focus appears, there is a sharp increase in the number of pathogenic microbes. This is especially noticeable against the background of decreased immunity. When an injection is given, they easily penetrate into the resulting wound and cause inflammation.
Gradually, an abscess or phlegmon begins to form, which captures more and more areas of healthy tissue. In principle, we can say that the problem arose due to a violation of pain relief according to the rules dictated by generally accepted instructions.
Against this background, manifestations such as:
- severe pain reaction;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, weakness, lack of appetite;
- headache;
- facial asymmetry;
- local hyperthermia in the affected area.
This complication is dangerous due to blood poisoning and the development of septic shock. Therefore, if your gums hurt very badly after anesthesia and your general condition begins to suffer, you should immediately contact a dentist.
Nerve trunk injury
Damage occurs directly from the needle as it moves into the soft tissues. With this complication, the gums can hurt from 5 to 10 days, and sometimes up to several months.
Symptoms largely depend on the severity of the injury. When infiltration is carried out, small nerve tissues are usually damaged and the intensity of unpleasant sensations is insignificant.
Conduction anesthesia is very deep and is carried out directly in the area where the nerve trunk passes. In this case, there is a significant risk of developing complications. Due to damage to a major nerve, temporary numbness may occur, followed by severe pain. They can radiate to other parts of the maxillofacial region.
The manifestation of damage to the nerve trunk will be the following symptoms:
- impaired mouth opening;
- difficulty eating;
- facial asymmetry without swelling;
- swelling of the gums in the injection area;
- severe unbearable pain that cannot be relieved by painkillers.
Treatment of such a complication is carried out only in a hospital. Medications and physical therapy are used. If ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
Hematoma formation
Occurs due to damage to a blood vessel by a needle. Blood is not able to completely escape from a small wound into the oral cavity, so it penetrates directly into the gum tissue. Typically, the hematoma is located in the superficial layers of the periodontal mucosa.
Hematoma in the area of the central incisor on the upper jaw on the right
Initially, complaints were about the unusual appearance of the gums and the appearance of aching pain. Unpleasant sensations depend on the volume of the hematoma. The pain usually persists for about 1-2 days.
Hematoma does not require treatment, especially if it is small in size. Gradually, the formation resolves on its own without consequences. If it is large, it must be opened and treated with medication.
Necrotization of soft gum tissue
This complication occurs rarely. There are various reasons why soft tissues die.
The main provoking factors are the following:
- large volume of injected anesthetic;
- a sharp spasm of blood vessels due to an anesthetic;
- poor circulation in the injection area due to concomitant diseases;
- sudden administration of a medicinal substance;
- the addition of an anaerobic infection.
Another serious reason may be the introduction of another substance instead of the anesthetic. This constitutes a medical error. The most dangerous may be the use of calcium chloride or alcohol. The cost of such a mistake is the very rapid development of necrosis, and not only the gums, but also the bone tissue of the alveolar process can suffer.
Necrosis is accompanied by severe acute pain. If this is the result of the introduction of another substance, then the pain reaction occurs instantly. The resulting wound takes several weeks to regenerate. Healing occurs with the formation of a rough scar.
The photo shows tuberal anesthesia on the upper jaw
That is why after anesthesia the gums hurt and the general condition suffers. The negative consequences can be much more serious than it seems. Therefore, with the appearance of unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to begin a therapeutic effect on the pathology as soon as possible.
Features of anesthesia
Today in dentistry, pain relief is very often used by injecting an anesthetic with a syringe. This is convenient for the dentist and makes it possible to reliably turn off sensitivity during any surgical interventions. You can learn how the most common types of pain relief in dentistry are performed by watching the video in this article.
Infiltration and conduction techniques are mainly used. The big advantage is that this allows you to act locally without having a toxic effect on the entire body.
Infiltration anesthesia is carried out directly in the area of the problem area. Conduction anesthesia affects the branch of the nerve responsible for a specific area of innervation. This technique is necessary for more extensive medical interventions.
Infiltration anesthesia on the upper jaw
Many people are concerned about the question: does it hurt to give anesthesia to the gums? Of course, the procedure is not pleasant.
Before carrying out the manipulation, for particularly sensitive patients, dentists irrigate the injection site with anesthetics in an aerosol. However, recently very thin needles have been used for carpule syringes, which minimally injure soft tissues.