Symptoms
Acute periodontitis is characterized by an attack of severe pain, during which swelling and swelling of the gums is observed, but the root top of the tooth is not yet destroyed. The chronic course of periodontitis practically does not manifest itself and is often asymptomatic; occasionally there is pain when biting. This stage of the disease can only be identified by contacting a dentist, who will make an accurate diagnosis using x-rays.
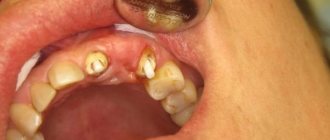
The acute form of the disease will not show any significant changes in the tooth area, but the chronic form will manifest itself in the appearance of a purulent sac, an abscess at the top of the root. In order not to cause damage to the oral cavity and save the tooth, long-term treatment will be required, which will take quite a lot of time, but it is also worth noting the fact that with modern medicine this process will be painless.
Predisposing factors
Bleeding gums can be caused by injury or disease. But there are a number of factors that make the risk of this symptom appearing higher.
Gums bleed in patients:
- with chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- with xerostomia - dry mouth;
- with reduced immunity, including HIV and AIDS;
- with vitamin deficiency, especially C and K;
- with mouth breathing;
- with poor or irregular oral hygiene.
These factors cannot be called the cause, but they contribute to the development of bleeding gums. Those for whom none of the points apply have a much greater chance of not learning about such a problem.
If your gums bleed in the morning or at night
Peak bleeding at night or in the morning indicates an unsuitable toothbrush. During brushing, the gums are injured. In this case, you need to visit the dentist and take a hygiene lesson with the selection of personal hygiene products.
Bleeding gums may not be normal. It is definitely worth finding out the cause and treating it before the disease reaches a chronic stage.
Treatment
When the pain can no longer be tolerated and medications do not help, you should immediately visit the dentist. When examining the patient, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment, which will not be quick, but will lead to a complete recovery. The main goal of any dentist is to save the tooth.
During the initial examination, an x-ray is taken, with its help you can see the most complete picture of the disease. When the source of inflammation is found, you can begin to determine the form of the disease and treat the root. Today in dentistry, anesthesia is used not only for tooth extraction, as it was in Soviet times; modern drugs are mostly hypoallergenic, non-addictive, do not have a large list of contraindications, and can also be used in the treatment of children's teeth.
When treating a tooth root, the doctor ensures maximum comfort for the patient, anesthetizes the treatment site, then opens the tooth root and cleans it of purulent accumulation, then a special medicinal mixture is placed into the hole. Having covered the top with a special gasket, the doctor closes the tooth with a temporary filling.
Next, you need to wait a few days for the inflammation to subside. You need to wait about 5-7 days and take another picture to confirm that the inflammatory process has stopped. Next, the cleaned dental canals are re-filled and a new temporary filling is installed. Filling protects against new infections, which contribute to inflammation.
After three days, a final follow-up visit is made to the doctor, who, after examining the patient, making sure that there are no inflammatory processes and successful treatment, closes the tooth with a permanent filling and polishes it.
Subsequently, a restoration process occurs, during which the gums may still be sore, the tooth may even become loose, but after a while, the unpleasant symptoms will disappear. To avoid recurrent disease of the root of the treated tooth, the doctor’s appointment is repeated six months later.
Bad breath due to bleeding gums
Bleeding from the gums is often accompanied by bad breath. There are several reasons for this:
- proliferation of bacteria against the background of inflammation;
- accumulation of soft and hard dental plaque;
- the presence of deposits under the gum that are not visible to the naked eye.
An unpleasant odor is a formidable symptom, since it does not appear immediately. This means the disease is already progressing. It is impossible to find out the cause and eliminate it on your own (without a dentist); The pathology will become chronic and it will be more difficult to cure.
How to relieve tooth inflammation
If inflammation of the root does not give you peace, then it is best not to delay a visit to the doctor. Traditional medicine at home is not intended to treat such a complex disease - we can say with confidence that self-medication will not bring the expected results. Relieving painful spasms and swelling with herbal infusions will only bring calm to the patient for a while, but the inflammatory process will develop and return after a while with more severe consequences.
The following will help to tame the pain for a while:
- Painkillers. They will help you endure acute pain, which is not advisable to endure, but it is best to drink them 12 hours before going to the doctor so that he can make a correct diagnosis;
- To relieve pain, you can rinse your mouth several times with a special solution, mixing a teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of water, adding four drops of iodine;
- Using calendula tincture, you can relieve inflammation, mix a tablespoon of tincture with a glass of water, rinse your mouth up to 5 times;
- One of the modern recipes for relieving toothache: place two drops of propolis tincture on cotton wool and apply to the painful tooth, the pain should subside within an hour;
- Boil one teaspoon of chamomile and oak bark in a liter of water, leave for 20 minutes, cool slightly, rinse for inflammation;
It is important to remember that applying warm compresses to a sore spot is strictly prohibited! Rinsing and taking painkillers cannot be considered treatment, because even if you managed to relieve the pain, the inflammatory process has not been stopped, it will proceed unnoticed and will resume with renewed vigor, the consequences of which can be unpredictable.
Periodontitis or Periodontal disease
Despite the fact that the names are very similar, periodontitis and periodontal disease are two completely different diseases that are connected by only one thing - they develop in periodontal tissues.
The periodontium is the gums, the cement of the tooth root, the bone tissue surrounding the tooth, the periodontium (the ligament connecting the tooth and the bone), nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels that supply this area.
The difference between the diseases is that periodontitis is an infectious inflammatory process, and periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory process of destruction of periodontal tissue caused by insufficient blood supply.
Inflammation of a wisdom tooth
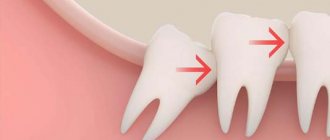
The location of this tooth in the oral cavity is sometimes difficult to reach for a doctor and is therefore considered the most difficult to treat. The wisdom tooth begins to erupt closer to the age of eighteen, which is why it received the name “comes with wisdom.” When it erupts, painful discomfort is felt, the reason is the absence of milk teeth in this place previously, so the incisor, growing, cuts through the gum. Swelling of the cheek and inflammation of the gums begins, which covers the area of the wisdom tooth; various symptoms may also appear, the lymph nodes become inflamed, swallowing becomes difficult, and the temperature rises.
A slight swelling can be considered normal, and the cause of the inflammatory process can be several factors:
- The wisdom tooth is looking for a place to come out, but not finding it creates inflammation in the gum and nerve;
- When the gums come out, there is not enough free space for normal growth, it begins to put pressure on the teeth in the neighborhood, which causes inflammation;
- The location of the growth of wisdom teeth depends on the structure of the oral cavity; if the shape is irregular, inflammation often occurs and cysts form.
To determine the presence of an inflammatory process in a wisdom tooth, you will need an x-ray; there are characteristic signs of inflammation:
- Sensation of unpleasant taste;
- Swelling of the gums around the tooth;
- The resulting pus spreads in the oral cavity, forming a pungent odor;
- When a wisdom tooth grows, the pain radiates to the temple or ear.
In this case, consulting a doctor is mandatory. If proper treatment is not started on time, it can lead to severe pain and many complications, the formation of purulent abscesses and phlegmons, which are subsequently resolved surgically.
Today, more and more dentists are of the opinion that the wisdom tooth does not need to be treated, but should simply be removed, because it's more trouble than it's worth. The complexity of treating its roots is determined by its location, and the doctor will make a decision in each individual case: to treat or remove a wisdom tooth.
Why do gums become inflamed?
Before you think about how to relieve gum inflammation, you need to understand the cause of the problem.
6 common factors that provoke inflammation:
- Mechanical damage during dental care. People brush their teeth incorrectly and use mouthwashes that are not suitable for them. Sometimes the inflammatory process is also provoked by the use of dental floss, when it goes too deep and begins to cut the gums.
- Deposits on enamel. They appear due to improper oral hygiene, when a lot of plaque remains on the teeth. Often the problem is caused by a gradual build-up of tartar.
- Problems with wisdom teeth. When third molars begin to emerge, dental patients often experience discomfort and pain. The gums at the location of the tooth begin to become inflamed, and the process gradually spreads further.
- Dental diseases. Often inflammation becomes the first sign of pulpitis or caries.
- Incorrectly performed dental procedures. The problem manifests itself if the doctor committed violations in compliance with sanitary standards or violated disinfection technology during treatment, removal, prosthetics, or implantation.
- Complicated recovery period after surgery. Even if everything was carried out in accordance with the rules, there is a risk of complications from the human body. And such complications manifest themselves precisely in the inflammatory process. When it occurs, you need to quickly consult your doctor.
Also, do not forget about proper oral hygiene. The activity of bacteria and insufficient attention to brushing your teeth lead to inflamed gums.
Knowing the first of the above reasons, it is worth remembering to maintain balance and proper cleaning. It's best to consult with your dentist about which brush, toothpaste, and mouthwash are right for you.
To prevent this problem from occurring, it is important to undergo treatment only from an experienced dentist. Then reasons such as improper cleaning of canals or filling, or violation of sanitary standards in the workplace will be excluded.
We should also not forget that systemic damage to the body is also provoked by problems with the gums.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common provoking diseases. Gums become inflamed with reduced immunity, taking a number of medications, hormonal imbalance, and gastrointestinal lesions.
Therefore, the dentist often gives recommendations on visiting doctors of other specialties.
Inflammation after tooth extraction - treatment
When there is no way to save a tooth, there is only one option left - to remove it. When removing, anesthesia is used, when its effect wears off, the tooth socket may ache, if the pain does not disappear within 2-3 days and painkillers do not help, most likely the inflammatory process of the tooth socket has begun. What could be causing it:
- Injury during tooth extraction;
- Foreign particles entering the hole cause inflammation;
- Improper hygiene;
- Infection in the hole.
To relieve inflammation after tooth extraction, you should not self-medicate; in this case, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Self-medication in this case can lead to the development of abscesses and sepsis. The doctor will correctly select the right antibiotic and dosage of the medicinal drug, an antiseptic solution for rinsing the mouth.
What complications can there be?
Even if the pain has dulled, the symptoms have become less pronounced, you should not postpone your visit to the dentist. This situation may be a signal indicating the death of the root and the further spread of infection to the organs of the head or neck.
The area cannot be heated. This approach will bring short-term relief, but will accelerate the formation of the fistula and stimulate the release of pus.
Possible serious complications: brain inflammation, pneumonia. There is a risk of sepsis, development of osteomyelitis, damage to the nasal sinuses or meninges.
Inflammation of the bone tissue of the tooth
The inflammatory process is the primary source of osteitis in the bone tissue of the jaw; if proper treatment is not provided in time, it will develop into periostitis (the periosteum becomes inflamed), osteomyelitis (the bone marrow becomes inflamed). With osteitis, pain is felt, the affected area swells, difficulties arise in chewing food, and the entire jaw gradually begins to ache. The cause of symptoms of osteitis is:
- Received traumatic actions, blows, bruises, jaw fracture;
- Surgical complication;
- tuberculosis and syphilis;
Treatment of osteitis occurs through surgery with the use of antibiotics and immunostimulating medications. Decaying teeth harbor bacteria and must be removed to prevent further inflammation. Patients with tuberculosis or syphilis first cure the underlying disease, then proceed to eliminate osteitis.
The slightest suspicion of pain in the bone tissue in the oral cavity is a reason to consult a doctor. Treatment of osteitis started in the first stage will make it possible to save teeth and protect against painful complications. Successful treatment depends on correct implementation of the dentist’s recommendations and careful oral care.
How to eat healthy
To improve the condition of the bone tissue of the teeth, you need to correctly formulate your diet, which should contain foods with a high calcium content. These are fermented milk products, cheeses, red fish, almonds and dark garden herbs (parsley, cilantro, dill).
Foods rich in vitamin C help maintain healthy gums, which strengthens the walls of blood vessels, which means it improves blood supply to the gums, delivering all the beneficial substances to them.