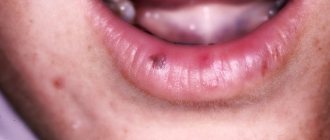
Plugs in the palatine tonsils (or tonsils) are purulent accumulations in the lacunae of the tonsils. In medicine you can find other names for this pathology: purulent plugs, caseous plugs.
Most corks are white, but can have a yellow, brown or gray tint, depending on their composition.
Tonsil plugs may be soft to the touch or harder if they contain a large amount of calcium. Their size varies from a few millimeters to a centimeter. Both men and women are equally susceptible to their appearance, regardless of age.
Some patients mistakenly think that this condition does not need to be treated. But this is fundamentally wrong! The presence of purulent accumulations in the palatine tonsils contributes to the development of complications (not only in the upper respiratory tract, but even in the joints, kidneys and heart!).
Why does an accumulation of pus occur in the tonsils? How to treat tonsil plugs? And is it possible to carry out treatment at home? You will find answers to all your questions in our new article.
Laryngeal papilloma. Symptoms
Symptomatically, laryngeal papillomatosis can be represented by hoarseness, chronic cough, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, recurring respiratory infections, and growth retardation in children. The presence of certain symptoms depends on the location of the papillomas. In children, the symptoms are more pronounced, since they have a significantly faster growth of papillomas, unlike adults. This can lead to situations in which emergency intervention is required for life-saving reasons, despite the histologically benign course of the disease. The prognosis is more favorable in terms of remission if the disease manifests itself in adulthood. The exception is the presence of HPV type 11 and the duration of the disease for more than 10 years.
Classification
Experts distinguish two types of tonsil cysts:
- Retention - formed after blockage of the ducts of the glands of lymphoid tissue, have a classic round shape, a thin capsule, filled with serous or purulent secretion. After emptying (evacuation of contents or spontaneous breakthrough), they are filled again.
- Dermoid or congenital - formed during intrauterine development, inclusions of embryonic tissue are always found in them. These true tumors, caused by genetic causes or harm suffered by the mother during pregnancy, are very rare. The capsule is usually dense and the contents are viscous.
Causes of laryngeal papilloma. Who is at risk?
The etiological factor is human papillomavirus (HPV), in most cases types 6 and 11. The latter leads to a more severe course of the disease. Less commonly, laryngeal papillomatosis can be caused by HPV types 16 and 18, which are viruses with a high risk of developing malignant neoplasms. However, the presence of HPV in the human respiratory tract does not always lead to papillomatosis. Determining factors can be immunodeficiency states and chronic infections. Concomitant infection with the herpes simplex virus and the Epstein-Barr virus contribute to a more aggressive course of the disease.
Diagnosis of a cyst
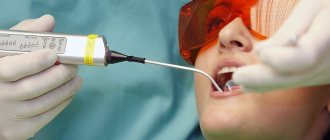
As a rule, detecting a cyst does not cause any particular difficulties, since the pharynx can be clearly seen even with the help of a backlit frontal mirror. The main thing is to contact an otolaryngologist for examination. ENT doctors use various instruments during examination - spatulas, elevators, and, if necessary, endoscopes.
The cyst is determined in different parts of the tonsils, on the surface or in the depths. It has the appearance of an opaque round formation, similar to a ball, whitish in color, elastic and mobile. There may be no signs of inflammation of surrounding tissues.
You cannot touch or put pressure on the cyst yourself - it can burst, and its contents are unknown. At best, the purulent contents will enter the stomach, and at worst, it will spread to other organs.
The doctor examines cysts larger than 1 cm very carefully, without damaging the surrounding tissues, trying not to touch the capsule.
Diagnosis of a cyst includes puncture (puncture and removal of contents). If necessary, the resulting material is examined in the laboratory to understand the nature of the disease. If a malignant process is suspected or blood is leaking from a cyst, treatment begins immediately, without waiting for the end of the examination.
Depending on age, general condition and concomitant diseases, the doctor may prescribe other clinical tests. The blood coagulation system, the functioning of the heart and lungs are required to be examined.
Laser removal of papilloma in the throat. Progress in medicine helps.
The main thing is to keep up with it and take advantage of all the new opportunities. In the treatment of papillomatosis, these include the use of CO2 laser, narrow-spectrum endoscopy and certain antiviral drugs. But there is one prerequisite to achieve the best result - everything must be performed by a highly qualified surgeon with extensive experience in treating laryngeal papillomatosis. This is extremely important to understand.
Papillomatosis is characterized by the formation of exophytic growths that affect the mucous membrane of various parts of the larynx and underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
Tonsil function
The tonsil is a lymphoid tissue located in clusters in the pharynx. The tonsils are one of the organs of the immune system that protect the internal environment of the body from harmful influences. There are six tonsils in the human pharynx: two paired and two unpaired; together they form the so-called Pirogov-Waldeyer protective ring. The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are located closest to the entrance of the pharynx, and these tonsils suffer more often than others. The lymphoid tissue of the tonsils supports general and local immunity. Lymphocytes mature in it and antibodies are produced.
The palatine tonsils play a vital role. They are the largest and differ in their structural features. Upon careful examination, it is clear that the surface has depressions or lacunae, smoothly turning into crypts or deep folds lined with mucous membrane. Only the lateral surfaces are covered with a capsule of connective tissue, and all the rest are in contact with everything that enters the pharynx.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
More than 10 years without recurrence of papillomatosis.
All patients treated by Professor Roberto Pujedo have not experienced a relapse of the disease for more than ten years .
“A comprehensive approach is a key success factor. Starting with detailed diagnostics using cutting-edge technologies, ending with careful monitoring in the postoperative period.”
Along with the expertly performed complete removal of papillomas, Professor Roberto Pujedo carries out targeted administration of antiviral drugs into the mucous membrane of the affected areas of the larynx.
Reliable source:
Enhanced contact endoscopy (ECE) in head and neck surgery
Many patients talk about dozens of surgeries in their history and endless relapses. It seems that it is impossible to cope with this disease. Each time the voice becomes worse, numerous scars form in the larynx.
Now this is history!
Help yourself?
The biggest mistake most patients make is overconfidence that caseous plugs can be removed at home using improvised means. They use a whole arsenal of objects that are absolutely not intended for this: spoons, forks, toothpicks... At best, such amateur activities simply will not bring results, at worst, they will cause injury to the surface of the tonsils and provoke severe bleeding, swelling and inflammation! This will most likely be followed by a sore throat! Plus, if you press incorrectly with a hard object on the accumulation of pus, you can push it even further into the thickness of the tonsil.
Some people try to gargle, believing that gargling will bring relief. Yes, the feeling of discomfort in the throat temporarily passes, but the accumulations of pustules do not disappear, because the rinsing solution comes into contact only with the surface of the tonsils, and getting inside it is extremely problematic, or rather, impossible. Therefore, this method is also not effective.
The best method to get rid of traffic jams is to consult an otolaryngologist!
Possible methods of treating laryngeal papillomas.
Careful removal of papillomatous growths under a microscope and using a CO2 laser is fundamental. However, removal must be carried out exclusively within the mucous membrane, where the formations are located. Moreover, the normal mucosa must be preserved. The surgeon must be experienced and thoroughly understand the mechanism of papillomas formation. Otherwise, gross surgical intervention leads to loss of voice, severe scarring, and stenosis.
Studies have shown that intraepithelial administration of antiviral drugs can reduce the number of operations to remove papillomas, leading to partial regression of the growth of formations. Also, local administration of an antiviral drug avoids systemic toxicity.
The mechanism of action of interferons in laryngeal papillomatosis is unknown, however, they are often used as an additional treatment. Interferons are naturally produced by white blood cells in response to various stimuli, including viral infection. They bind to specific cell membrane receptors and change metabolism, providing antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory effects. The clinical effectiveness of interferons in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis is ambiguous and controversial. The main limitation for their use are side effects when administered intravenously: increased levels of transaminases in the blood, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Patients may experience weakness, nausea, fever, arthralgia, and headache.
Indol-3-carbinol can be extracted from cruciferous plants (broccoli, cabbage). In vitro studies have shown promising results on the growth of papillomas by influencing estrogen metabolism. When administered orally to a small number of pediatric patients, no adverse effects were observed. However, the clinical effectiveness of this drug remains in doubt.
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine . A prospective randomized controlled trial showed that intraepithelial administration of MMR vaccine could prolong the period of remission after surgical treatment.
HspE7. A new vaccine targeting oncogenic HPV types has also been used to successfully control relapses of laryngeal papillomatosis.
The presence of GERD was associated with an increased likelihood of complications. The irritating effect on the mucous membrane can act as a trigger for the proliferation and spread of papillomatous growths. Studies have shown that the use of drugs to treat GERD promotes better control of laryngeal papillomatosis and prolongs remission.
According to a Cochrane review, photodynamic therapy has not been shown to be effective in the treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis.
Watch the video BEFORE/AFTER surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis
Relapse-free postoperative follow-up for a year. Endoscopy in NBI mode. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Look at the photos BEFORE/AFTER the operation by Prof. Roberto Pugedu
Photos “before” and “after” surgery to remove laryngeal papillomatosis. Credit: Professor Roberto Pujedo.
Move the slider to see the difference.
Symptoms
Small accumulations, as a rule, do not cause significant symptoms. With large accumulations, the patient may experience the following symptoms of inflammation:
- bad breath;
- whitish dots are clearly visible on the surface of the tonsils;
- persistent sore throat;
- pain while swallowing;
- body temperature may be increased to 37-37.7 degrees;
- a feeling of discomfort at the site of accumulation of purulent masses;
- swollen tonsils;
- weakness, lethargy, general malaise;
- decreased performance;
- loss of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain may radiate to the ears.
Traffic jams appear gradually, so in the early stages of the disease the patient experiences only discomfort when swallowing and a sore throat.
This condition is extremely dangerous for pregnant women! In addition to the fact that it has a detrimental effect on the general condition of the expectant mother, it can negatively affect the development of the fetus and, in the worst case, provoke a miscarriage. Therefore, it is extremely important to contact an otolaryngologist in time to receive competent recommendations on how to effectively treat tonsillitis during pregnancy and avoid complications.
Our doctors
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
19 years of experience
Make an appointment