Causes of tonsillitis in children
The disease occurs due to the ingress of bacteria or viruses. Tonsillitis is often caused by streptococcus bacteria. The disease is also caused by adenoviruses, influenza and parainfluenza viruses, herpes, etc.
Other reasons:
- staphylococcus, pneumococcus, hemophilus influenzae and other microbial associations;
- enterovirus infection;
- mushrooms;
- parasites – membrane and intracellular (mycoplasma and chlamydia);
- disruption of the process of self-cleaning of lacunae against the background of restructuring of lymphoid tissue and dysbiosis of the respiratory tract;
- a single or multiple history of tonsillitis;
- ARVI, sinusitis, adenoiditis, caries, stomatitis, periodontal disease;
- anatomical features of the pharyngeal part of the lymphatic system - deep and narrow lacunae, adhesions, multiple fissure passages;
- burdened by concomitant diseases - food allergies, perinatal pathologies, rickets, impaired breathing through the nose, intestinal infections and other factors that reduce immunity.
Reasons for appearance
Purulent tonsillitis in a child is of an infectious nature, and is provoked by the increased activity of pathogenic pathogens such as staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, diplococcus. When identifying the causative agent of infection, one should not exclude the penetration of influenza, parainfluenza, and adenovirus viruses into the child’s body. Other provoking factors for inflammation of the tonsils are presented below:
- Treatment of sore throat with beets and vinegar
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- environmental factor and climate change;
- physical or emotional fatigue;
- decreased immunity;
- diseases of the ENT organs.
Types of disease
- Spicy. Most often, the acute form develops after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, due to reduced immunity. Source: A.D. Vetrova Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64
- Chronic. Occurs after relapses if the patient has not fully recovered. Diseases in the mouth, nose, and structural features of the tonsils contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2021 Sep; 10(9): e3343
Classification of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is inflammation that just arose (suddenly), and chronic is a disease that persists for a long time, and it may not bother a person, but under certain circumstances again cause complaints and anxiety.3
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Classification of pharyngitis due to its occurrence: | a comment: | viral bacterial fungal allergic traumatic caused by exposure to irritating factors caused by gastrointestinal diseases (gastroesophageal reflux, stomach diseases, etc.) |
| classification: | Pharyngitis associated with specific pathogens: | a comment: | Epstein Bar virus for infectious mononucleosis Yersinia enterocolitica for yersinial pharyngitis gonococcus for gonorrheal pharyngitis Leptotrix buccalis for leptotrichosis of the pharynx |
| classification: | Types of chronic pharyngitis: | a comment: | hypertrophic (enlargement of the mucous membrane) atrophic (depletion of the mucous membrane) catarrhal (standard inflammation) mixed |
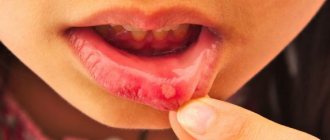
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of tonsillitis in children that require immediate treatment are:
- pain when swallowing and yawning;
- heat;
- general intoxication of the body (weakness, decreased appetite, headaches);
- swelling and redness of the tonsils;
- formation of whitish or yellowish plaque on the tonsils;
- blisters, sores on the throat;
- loss of voice, hoarseness;
- bad breath;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes (this sign can indicate not only tonsillitis, it accompanies many other diseases in children).
Treatment for sore throat
Treatment is carried out mainly at home. Moreover, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest. A sick child is hospitalized when he is less than 3 years old, his high fever (39°-40°) does not subside, he has difficulty breathing, swallowing food and liquids, an abscess is detected on the tonsils, and there is a real threat of complications.
Drug treatment
In order to prevent complications of purulent tonsillitis in a child, treatment is carried out with antibiotics, local agents for the inflamed tonsils, and drugs to eliminate painful symptoms.
Treatment with antibiotics
Penicillin-based drugs (phenoxymethylpenicillin, amoxicillin) are used. If you are allergic to penicillin or need re-treatment with antibiotics due to recurrent sore throat, use antibacterial agents of a different group (macrolides), such as sumamed, azithromycin, erythromycin.
In severe forms of the disease or when complications occur, even stronger antibiotics (cephalosporins) are used for treatment.
Treatment with topical drugs
To speed up the cleansing of the surface of the tonsils from pus, gargle with antiseptic solutions of miramistin or chlorhexidine. Sprays that have an antiseptic effect and contain an antibiotic are used: for example, hexoral, bioparox.
To eliminate pain and sore throat with purulent sore throat in children, you can use lozenges (strepsils, falimint). They contain components with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
Warning: If the child does not yet know how to gargle and suck tablets, treatment can only be carried out with sprays. It is recommended to give him slightly warm tea to disinfect the oral cavity.
Diagnostic methods
During the consultation, the doctor will examine the patient’s throat and palpate the lymph nodes. The examination should be carried out by a pediatrician and pediatric ENT specialist. In case of decompensation of the chronic form, the child requires consultation with a pediatric cardiologist, rheumatologist, nephrologist, because tonsillitis can cause concomitant diseases. To rule out pockets of infection in the oral cavity, the child should be examined by a dentist. Laboratory and instrumental studies are also prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- pharyngoscopy;
- blood test to determine C-reactive protein;
- definition of ASL-O;
- bacterial culture from the pharynx for flora.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, additional studies may be required - ECG, x-ray of the sinuses, etc.
ICD - pharyngitis:
- J02 - acute pharyngitis
- J02.0 - streptococcal pharyngitis
- J02.8 - acute pharyngitis caused by other specified pathogens
- J02.9 - acute pharyngitis, unspecified
- J31.2 - chronic pharyngitis
- J31.1 - chronic nasopharyngitis
Pharyngitis is rarely isolated as a separate disease; the diagnosis is usually acute respiratory viral disease (ARVI).
ARVI is a general name; the doctor usually specifies how exactly ARVI manifests itself.
This may be rhinitis (runny nose), pharyngitis (red throat), nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat), etc.1,2
It is important not to confuse pharyngitis with tonsillitis.
To do this, let's understand the structure of the pharynx and oral cavity.
Treatment of tonsillitis in children
With properly selected medications, treatment of tonsillitis in a child takes about a week. The patient is prescribed bed rest, plenty of fluids and a gentle diet, excluding spicy and fatty foods. Medicines are selected according to the type of tonsillitis, accompanying symptoms, and the age of the child. Medicines should only be prescribed by a doctor.
The treatment program includes:
- painkillers;
- washing and rinsing;
- sprays and lozenges;
- physiotherapy. Source: T.V. Spichak Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the perspective of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135
Antibiotics are prescribed to children only in severe cases, as they cause side effects (abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.).
Removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is used in exceptional cases, if frequent relapses of the disease are observed, conservative treatment is ineffective, and complications from internal organs are identified.
In case of exacerbation of the chronic form of tonsillitis, the child requires bed rest, diet correction with the exception of fatty, fried, smoked, sweet foods, as well as drug therapy, which includes antibiotics, vitamins, desensitizing drugs, and immunomodulators.
Necessary:
- wash the lacunae of the palatine tonsils with antiseptics;
- treat the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils with solutions of fucorcin, Lugol;
- the child should regularly gargle with antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
You also need to do inhalations, use antiseptic aerosols, and take antimicrobial lozenges.
Physiotherapy may be prescribed :
- Ural Federal District;
- UHF;
- microwave;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- laser therapy.
Complications of the disease:
- descent of purulent infection into the heart sac;
- abscess;
- bleeding from the tonsils;
- eustacheitis;
- otitis;
- purulent inflammation;
- swelling of the larynx with the development of asphyxia, which can be fatal.
How to cure the disease?
In order for the child’s well-being to improve quickly, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. You can treat purulent sore throat in children by following a number of rules:
- drink plenty of fluids;
- take antibiotics, antipyretics and antihistamines;
- gargle;
- take vitamins;
- take eubiotics.
It is important not to carry out warming procedures if the child has a fever. Treatments include:
- compresses;
- warming creams and ointments in the neck area;
- inhalation.
These activities are not recommended if you are ill.
Your child needs plenty of fluids. Since he will sweat when drinking large amounts of fluid, it will be easier for the body to regulate body temperature, and bacterial toxins will be eliminated from it faster. Thanks to the consumption of fluid, it happens that there is no need to take antipyretic drugs or their use is canceled before the due date.
How to gargle a child's throat?
One of the main methods of treating sore throat is rinsing the throat, which can be used for children of the older age category, but for preschoolers and younger children, sprays and aerosols are used.
- Causes of knee arthritis in children, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Sprays include:
- orasept;
- Lugol;
- hexoral;
- miramistin;
- stopapangin;
- chlorophyllipt;
- antiangin;
- tantumverde;
- cameton.
These drugs are allowed to be used to treat sore throat in children over 2 years of age.
Rinsing is considered an auxiliary method, since antibiotics are the main thing in the cure.
For older children, you can prepare decoctions of various herbs for gargling, which have a mild anti-inflammatory effect.
- Chamomile.
- Sage.
- Calendula.
If you gargle frequently, you can eliminate the pain and restore the tonsils earlier than expected.
Rinsing is carried out 5 times a day for no more than 2 minutes. There is no need to carry out the procedure often and for a long time, due to the opposite effect occurring with constant vibration of the tonsils, their tissues will take longer to recover.
The following solutions are used for rinsing:
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution;
- 1% iodinol solution;
- potassium permanganate;
- 2% boric acid solution;
- rotokan;
- stomatophyte;
- solution from furatsilin tablets;
- a solution of iodine, table salt, baking soda and water.
If the child cannot rinse the throat, then lozenges can be used.
- Septolete.
- Faringosept.
- Grammidin.
- Strepsils.
- Strepfen.
- Doctor Mom.
- Karmolis.
Medications
It is important to know that there is no quick cure for sore throat. Even if you are treated actively for 3 days, the results will be satisfactory. The minimum duration of illness is a week, the maximum is 14 days.
If, after taking the prescribed medications for 3 days, the child feels better, the fever has gone away, and an appetite has appeared, you should not deviate from treatment, as the microorganisms could simply hide. Therefore, in order to avoid new outbreaks of sore throat and prevent complications from developing, follow the doctor’s recommendations and take the medicine as much as prescribed in the prescription.
- Sore throat - treatment at home. Quick treatment of sore throat in adults
Many pediatricians recommend consuming B vitamins, vitamin C, and these can also be vitamin complexes.
- Centrum.
- Multitabs.
- Pikovit.
- Alphabet.
Antibiotics
Often, treatment of sore throat involves taking antibiotics of the amoxicillin group along with clavulanic acid.
- Augmentin.
- Amoxiclav.
- Ecoclave.
- Flemoclav.
- Solutab.
If the baby has an allergic reaction to penicillins, macrolides are prescribed.
- Sumamed.
- Cheromycin.
- Azitrox.
- Macropen.
It is necessary to treat purulent sore throat with antibiotics for at least a week. The doctor may also prescribe topical antibiotics. One of these is the Bioparox spray inhaler. It happens that sulfonamide antimicrobial agents are used, such as Biseptol, Bactrim. They are weak; bacteria do not often react to these drugs. If there is no result on the 3rd day, strong remedies are prescribed.
When treating with antibiotics, it is necessary to use eubiotics.
- Acipol.
- Bifidumbacterin Forte.
- Linux.
- Lactobacterin.
- Biobakton.
- Bifiliz.
- Acylact.
- Bifiform.
Medicines to reduce fever
Often, when you are sick, your body temperature rises. To bring it down, you can use the following medications:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- calpol;
- efferalgan;
- mefenamic acid;
- Nurofen.
In addition to lowering the temperature, these agents have an anti-inflammatory effect.
The use of drugs to lower the temperature is allowed if it rises above 38 degrees. If the level is lower, you should not take them, since the body independently tries to fight the pathogen.
Taking antipyretic drugs should not exceed 3 days.
If you can’t get rid of the temperature with medications, you can try traditional medicine to solve the problem. To do this, you need to undress the child and wrap him in a diaper soaked in cold water. You can grind with an alcohol solution by mixing water and alcohol in equal quantities. You need to drink fluids more often. It can be like water, teas, compotes. The following will help increase sweating and reduce temperature:
- black currant;
- raspberries;
- cranberry;
- cherry.
Traditional methods
If purulent tonsillitis in children has been diagnosed, treatment at home can be carried out using traditional methods, but only with the permission of the pediatrician. Since, even using the well-known chamomile decoction to rinse the throat, it may not fit into the treatment regimen and slow down the patient’s recovery process. The methods used to treat sore throat at home complement the prescribed treatment by the pediatrician, and sometimes relieve signs of the disease.
Basically, treatment involves the use of medicinal herbs for rinsing. You need to drink teas:
- using raspberries;
- honey;
- lemon;
- mint;
- rosehip;
- linden;
- thyme;
- with cumin.
You can drink warm milk, adding honey and butter to it. It is necessary to treat the tonsils with a propolis solution.
Clinical recommendations for disease prevention
The main methods of preventing tonsillitis in children are compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures (avoiding contact with patients and their things, washing hands, using a scarf and hand sanitizers) and strengthening the immune system (hardening, playing sports, etc.).
Tonsillitis is a common disease in children and adults, which without proper treatment can become chronic. If you notice symptoms of illness in your child, immediately contact the children's medical department.
Sources:
- HELL. Vetrova. Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan. Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2021 Sep; 10(9): e3343.
- T.V. Spichak. Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How common is pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis, like a common ARVI (viral infection), occurs quite often. The incidence rate increases during the season from September to May, with a peak in February and March. A decrease in the incidence of pharyngitis by 3-5 times is observed in the summer months.10,11
Acute pharyngitis occurs more often in childhood than in adults. Children under 5 years of age suffer viral infections, including pharyngitis, 6-8 times a year.8,9
In the first year of visiting a preschool institution, the incidence of the disease is 10-15% higher than in children at home. But, unfortunately, “home” children subsequently get sick more often at school age.
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis can be determined by patient complaints and examination of the oropharynx (pharyngoscopy).
Objective symptoms of pharyngitis, which are assessed by a doctor when examining the throat:
- swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the pharyngeal mucosa
- purulent or mucopurulent plaque on the walls of the pharyngeal mucosa
- the presence of inflammation in the arches, tonsils, orifices of the auditory tubes
- the presence of bright red tubercles on the back surface of the pharynx and on the side - hypertrophied (enlarged) lymphoid follicles
- thinning of the mucosa with areas of exfoliating epithelium, crusts and viscous mucus (atrophic pharyngitis)
Based on this, the doctor can make not only a diagnosis of pharyngitis, but also suggest its cause (viral inflammation, fungal infection, etc.).
Despite the fact that 70% of acute pharyngitis is a viral disease, sometimes it is necessary to exclude a bacterial cause. This is very important for further treatment tactics and prevention of complications. To do this, you should conduct a rapid test to exclude the streptococcal nature of pharyngitis.
In some cases, with fever, long-term complaints, or a temperature exceeding 3 days, it is also necessary to take a general blood test to understand the cause of acute pharyngitis.
Prevention of pharyngitis
To prevent pharyngitis, it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia and dress appropriately for the weather
- avoid contact with tobacco and chemical irritants
- carry out frequent ventilation of working and living spaces
- walk outdoors more often. Walking will help strengthen the body's defenses in the fight against pharyngitis.
- don't drink ice water
- do not share food and cutlery, cups
- avoid crowded places and, if possible, stay in them for as little time as possible
- use disinfectants, including in public places,
- transport, etc.
- wash your hands often
Complications of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis usually responds well to treatment. The prognosis for viral pharyngitis is recovery.
Bacterial (streptococcal pharyngitis) can be complicated by the formation of a retropharyngeal abscess, and subsequently have a negative effect on the heart and kidneys, causing endocarditis and glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of pharyngitis can persist even with proper treatment, if the true cause of pharyngitis is not eliminated. For example, if gastroesophageal reflux disease (damage to the gastrointestinal tract) is not treated, then pharyngitis will constantly remind itself.
Acute pharyngitis can become chronic.