Do you have a sharp sore throat, painful swallowing and a fever? This may be tonsillitis, which can occur in acute or chronic form. Often, in the absence of adequate treatment, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic. And chronic, in turn, can occur with periods of exacerbation and remission.
With tonsillitis, the main immune barrier of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, the palatine tonsils, is primarily affected. Their main function is to protect against foreign viruses and bacteria entering the body.
Causes of bacterial sore throat in children
Among the pathogenic bacteria, it is necessary to highlight pneumococcus, Escherichia coli, streptococcus, and staphylococcus. In young patients, sore throat is caused by mycoplasma, chlamydia and ureaplasma. Slightly less frequently, bacterial tonsillitis occurs with opportunistic microflora that are constantly present in the body. The proliferation of microbes occurs against the background of weakened immunity, exacerbation of chronic infections (for example, sinusitis, sinusitis, caries), hypothermia, vitamin deficiency. Sore throat in children develops when the soft tissues of the mouth are injured and bacteria multiply after contact with dirty objects, toys, dishes, etc.
The pathogen enters the body after bodily contact or through airborne droplets. The peak of the disease occurs in the autumn-winter period and ends in mid-spring.
Classification
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) or primary inflammation can occur in catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, and less often necrotic form. Secondary acute inflammation of the palatine tonsils most often occurs against the background of existing inflammatory or infectious diseases - scarlet fever, diphtheria, typhoid fever, mononucleosis, as well as leukemia,
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammatory process in the tonsils, with rare or constant relapses of the disease. Exacerbations can be caused by viruses or bacteria, or against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, or a general decrease in immunity.
Symptoms of bacterial sore throat in children
Babies under one year old are very difficult to tolerate the disease. Parents notice the following signs of illness:
- Drowsiness, decreased or lack of appetite, crying and moodiness.
- Refusing the bottle.
- Vomiting after eating.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Increased salivation.
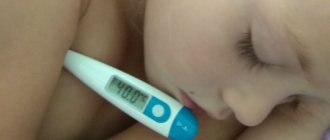
- Temperature rises to 40°C.
Older children experience the same symptoms as adults. They complain of discomfort in the throat and pain when eating, so they eat practically nothing. Outdoor games give way to sleep. The voice becomes hoarse, and sometimes the pain in the throat radiates to the ears.
Prevention of tonsillitis
In order to prevent tonsillitis in a child, parents should adhere to the following rules:
- Gradually harden the child's body.
- Provide your child with a balanced, healthy diet containing all the nutrients necessary for childhood.
- From a very early age, introduce the child to sanitary standards - the rules of washing hands, brushing teeth, etc.
- Promptly eliminate any inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and pharynx.
- Avoid crowded places during epidemic periods.
- Do not self-medicate!
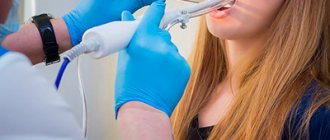
At the SM-Doctor clinic for children and adolescents, tonsillitis is diagnosed and treated by specialists with many years of experience in otolaryngology. The use of modern high-tech equipment allows our doctors to achieve high results in the treatment of ENT diseases. Sign up for a consultation with qualified pediatric otolaryngologists!
Treatment of bacterial sore throat in children
After the examination, the ENT doctor gives a referral to donate blood for a general analysis, culture to determine the microflora and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Only based on the results of the examination, treatment tactics are selected and specific drugs of different dosages are prescribed.
The basic treatment regimen is as follows:
- Taking antibacterial agents. Bacterial sore throat cannot be avoided without taking antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed penicillin antibiotics and aminoglycosides in tablet form. Macrolides are prescribed for children. Streptococci are sensitive to these groups of antibiotics, so the proliferation of bacteria quickly stops. Local broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of a spray relieve inflammation.
- Taking probiotics and eubiotics. They normalize the intestinal microflora after antibiotics.
- Taking antipyretic drugs. If the temperature is above 38°C, then paracetamol-based drugs are prescribed. At temperatures below 38°C, the body fights on its own.
- Rinse with antiseptics to combat pathogenic microflora and wash out pus.
- Taking local medications to relieve sore throat. Dissolving lozenges, tablets, and using a spray relieves local symptoms.
- Vitamin therapy. Vitamin B and C complexes strengthen the body's defenses, helping to recover faster.
- Taking antihistamines. Prescribed for severe swelling of the soft tissues of the throat.
In addition to drug therapy, strict bed rest must be observed. During the first three days, the likelihood of infecting other family members is highest, so you need to provide the patient with a separate sleeping place and household items.
Due to a sore throat, the usual diet is disrupted. The patient eats only liquid and pureed food in small portions, but often. You should drink 2.5-3 liters of clean water to relieve symptoms of intoxication, but you should not drink hot or cold water.
As a rule, improvement after the start of treatment therapy is recorded within 2-3 days. The general course of treatment does not exceed 10 days. If there is a noticeable deterioration in the condition, then this is a reason for hospitalization.
Important to remember! It is strictly forbidden to make compresses, warm the throat and legs, or do inhalations. Such manipulations will increase the proliferation of bacteria.
Diagnostic methods
During the consultation, the doctor will examine the patient’s throat and palpate the lymph nodes. The examination should be carried out by a pediatrician and pediatric ENT specialist. In case of decompensation of the chronic form, the child requires consultation with a pediatric cardiologist, rheumatologist, nephrologist, because tonsillitis can cause concomitant diseases. To rule out pockets of infection in the oral cavity, the child should be examined by a dentist. Laboratory and instrumental studies are also prescribed:
- blood and urine tests;
- pharyngoscopy;
- blood test to determine C-reactive protein;
- definition of ASL-O;
- bacterial culture from the pharynx for flora.
If there are difficulties in making a diagnosis, additional studies may be required - ECG, x-ray of the sinuses, etc.
Surgery in the treatment of bacterial tonsillitis
Often, due to a weakened immune system, tonsillitis worsens frequently (more than three times a year). The tonsils become covered with purulent contents, causing pain and discomfort.
To prevent relapse, some otolaryngologists recommend surgical treatment - tonsillectomy. Surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia and involves excision (removal) of the tonsils.
The operation is also prescribed for complications, when inflammation of the tonsils has caused a soft tissue abscess (peritonsillar abscess).
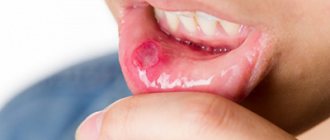
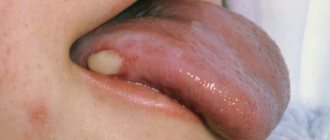
Pus plugs in the tonsils
“Congestion in the tonsils” is a separate problem, mostly hygienic, causing bad breath, sometimes also a feeling of pressure or a foreign body.
What is tonsillitis? It is a cast of food that has fallen into a lacuna (a kind of pocket) of the tonsil, tonsil epithelium and bacteria (most often fusobacterium nucelatum, the main bacterium of dental plaque). But this is not pus, since there are no dead leukocytes and bacteria underdigested by leukocytes.
The conditions for the formation of “plugs” are usually dry mucous membranes of the tonsils, which occurs when nasal breathing is impaired and/or air with low humidity.
Often, if you solve the problem with nasal breathing and the humidity of the inhaled air, then the “traffic jams” disappear by themselves.
What's the moral? If there are “traffic jams”, but no sore throat, then you should pay attention to the state of nasal breathing. And only if the problem persists even with a well-breathing nose, should you look for a solution in the palatine tonsils themselves.
Specific features of bacterial sore throat
It is often difficult for parents to distinguish bacterial tonsillitis from other types of acute tonsillitis. Because of this, the patient’s condition often worsens.
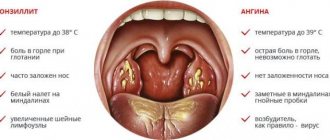
- A sore throat caused by bacteria can be recognized by the following clinical picture:
- The lymph nodes in the neck and lower jaw become inflamed. On palpation they are sharply painful.
- There is no mucus or redness on the back of the throat.
- Pus accumulates on the tonsils in the form of white or gray-green dots, but it does not extend beyond them. With a viral sore throat, pus spreads over the entire surface of the throat and surface of the mouth.
Sore throat caused by bacteria differs from other types of acute tonsillitis in that the runny nose and cough are mild, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and indigestion are absent.
Causes of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an infectious disease that occurs as a result of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection.
Most often, the disease is caused by bacteria - streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci and hemophilus influenzae. Viral tonsillitis can be caused by herpes, influenza and parainfluenza viruses, as well as enterovirus and adenovirus infections. In rare cases, the cause of the disease is fungi, mycoplasma and chlamydia. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the child's respiratory tract through airborne droplets, transmitted from person to person. A healthy body is able to overcome an infection on its own; infection occurs only if there are factors that contribute to a decrease in the child’s body’s defenses, for example:
- hypothermia;
- avitaminosis;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity and pharynx - caries, stomatitis, pharyngitis, etc.;
- frequent contact with sick people;
- poor environmental conditions, dusty air;
- exposure to external irritants and allergens.
In addition, tonsillitis often occurs in children with peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the lymphoid apparatus of the nasopharynx - deep and narrow lacunae of the tonsils, multiple slit-like passages and adhesions, which complicate the process of emptying the lacunae.
Complications of bacterial tonsillitis
Depending on what causative agent of sore throat is identified and how long the treatment is delayed, the risk of complications increases. Thus, staphylococcal tonsillitis is dangerous due to the development of a pharyngeal abscess due to the spread of inflammation inside. Streptococcal tonsillitis threatens to damage the heart, kidneys and liver and can provoke rheumatism or glomerulonephritis, lower back pain.
The likelihood of complications with bacterial tonsillitis is higher than with viral tonsillitis, so you need to seek medical help in a timely manner and not attempt treatment on your own.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, otorhinolaryngologists will quickly conduct an examination, identify the pathogen and prescribe treatment. Our specialists regularly undergo training and improve their skills; they use modern physiotherapeutic techniques and drug therapy regimens in treatment.
A sore throat
Sore throat occurs for various reasons, but most often it is associated with the word “sore throat.”
The word “angina” means an inflammation in the throat that is caused by bacteria (most often streptococcus) and this sore requires the prescription of an antibiotic to prevent the development of all sorts of nasty things with the heart, kidneys and joints afterwards. “Sore throat” occurs in 15-30% of cases, and the trick is that it cannot be distinguished from a viral inflammation in the throat (which does not require the prescription of an antibiotic). Here Streptatest comes to our aid: 10 minutes and we have the answer whether there is streptococcus or not. And if there is, then this is a reason to take an antibiotic so that later it will not be excruciatingly painful.
Inflammation of the tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa: tonsillitis (tonsillitis), pharyngitis - the main cause of sore throat.
The causative agents of sore throat are bacteria, viruses, fungi, and so on.
- The most common pathogens are viruses:
- no antibiotics needed
- goes away on its own
- complications are rare
- the most common cause of sore throat in children under 3 years of age
- Among bacterial pathogens, the leading ones are streptococci, namely group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS):
- more often in children 5-15 years old (peak - primary school)
- almost never occurs in children under 3 years of age
- Antibacterial therapy (ABT) is mandatory, as serious complications may develop:
- acute rheumatic fever, chronic rheumatic heart disease, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, arthritis, etc.
Viruses that can cause sore throat:
- Adenovirus (angina is accompanied by a runny nose, swelling of the face and eyelids, conjunctivitis with mucous discharge, redness of the eyes, cough and others)
- Epstein-Barr virus and Cytomegalovirus (accompanied by enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes, liver, spleen, swelling around the eyes, and rarely - a rash on the body)
- Enterovirus
- Flu
- Human immunodeficiency virus, parainfluenza, RS virus and others.
Symptoms are the same for viral and bacterial sore throat:
- A sore throat
- Plaques on the tonsils and/or back of the throat
- Increased body temperature
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
- General weakness, headache
In favor of viral sore throat they will say:
- age up to 3 years
- conjunctivitis
- rhinitis
- cough
- diarrhea
- hoarseness of voice
- stomatitis
- skin rash
In favor of streptococcal sore throat he says:
- acute onset of illness
- sore throat worsens when swallowing
- purulent plaque on the tonsils
You can make the correct diagnosis using:
- a smear taken from the surface of both tonsils and the back of the throat
- and/or a rapid test (for example, Streptatest, sold in pharmacies), allowing within 5 minutes. determine the presence of group A Streptococcus
- if the rapid test result is positive, ABT is prescribed
- if the rapid test is negative, but with a clinical picture of streptococcal infection - take a smear for culture and still - prescribe ABT
- if the smear result is negative for streptococcus, ABT is stopped
- it is not possible to take tests, but the clinical picture is clear: ABT is prescribed
- A blood test for Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO) for acute streptococcal sore throat is not informative.