The fact that baby teeth have begun to fall out is an absolutely normal physiological phenomenon. Every child goes through this at the appropriate age.
In place of the fallen temporary canines, molars and incisors, new (now molar) units of the dentition then grow. Here, it would seem, everything is clear and natural. However, this process often raises many questions among parents.
What to do in obscure situations when the replacement of baby teeth in children with permanent ones occurs earlier than the established standards or, conversely, noticeably later? What signs and indicators should be considered normal? Do I need special care for my gums during gum loss? All these issues will be covered in detail in the review below.
Change of teeth in a child. At what age does it happen? Tips for parents (video)
Why do baby teeth fall out?
This question, of course, can be answered with some short phrase from the category “This is how nature intended it.” On the one hand, there is absolutely nothing to add to such a categorical remark, but, on the other hand, there are still many “dark places” left. In the sense that the logic of the natural design taking place is still not clear.
To close some serious information gaps, let's take a closer look. So, let's start with the fact that the primary dentition counts only 20 units, while the permanent dentition reaches a much higher figure - 32.
Baby teeth are always temporary. Why is that? The reason is that as we grow older, the human body in general and the jaws in particular grow. But teeth do not have this feature.
The conclusion is simple: there is no way to do this without an appropriate replacement. Otherwise, as the body grows, the interdental spaces would become larger and larger, acquiring simply catastrophic proportions. And this, as you yourself understand, is ugly and non-functional.
An interesting fact: permanent teeth begin to form as soon as the baby is born. The roots of temporary (milk) units gradually dissolve, resulting in loosening and loss.
And then, as you might guess, comes the eruption of stronger molars. Why doesn't this happen right away? The main reason is that baby teeth act as unique markers for permanent teeth. The latter erupt in exactly the same places and sequence as the former.
About children's teeth (video)
What problems do children and their parents face when replacing baby teeth with molars?
As mentioned above, first the root of the baby tooth is absorbed. In this case, the loss occurs painlessly on its own or under the influence of external signs (constant loosening by the child or eating fairly solid food). But it may also happen that the root of the tooth has not yet been sufficiently absorbed, the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the molar has already begun to grow. If you do not consult a dentist in time to remove a tooth that is interfering with natural growth, a significant malocclusion may occur: a molar may simply grow next to the baby tooth. Such changes in the oral cavity may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature and significant pain.
Another significant problem is teeth falling out too early. It can be caused by various gum diseases or physical trauma. If you do not seek advice from a specialist in time, the gums may become overgrown at the site of tooth loss, which will subsequently prevent the eruption of a molar at this site and the curvature of the dentition. In this case, they usually resort to prosthetics. A structure made of hypoallergenic materials is installed on the damaged area, completely identical in appearance to a natural tooth. It maintains the child’s neighboring teeth in an even state, preventing the formation of an incorrect bite.
Another significant problem is the delay in tooth loss, when the molar is already beginning to erupt, but the milk tooth is still quite firmly “sitting” in its place. This may be due to a lack of nutrients, delays in the development of the body in general and the oral cavity in particular. In this case, you should contact a dentist, who will examine the little patient in detail and prescribe the necessary measures. In most cases, the tooth that is preventing growth is simply removed. In this case, local anesthesia is used, which will make the process of tooth extraction almost painless.
Newly erupted molars are not yet strong enough; their tooth enamel is thinned. Therefore, during the period when baby teeth are replaced by molars, there is an increased risk of acquiring dental diseases. The most significant of them is caries. It can occur due to poor oral hygiene and consumption of large amounts of sweet foods. If caries is not treated in time, complications in the form of pulpitis and other dangerous dental diseases are possible. There is also a possible risk of damage to the oral cavity during this period by various types of infections, which often lead to inflammation of the gums and loss of newly grown teeth.
Replacing baby teeth with molars is a very important process for a child. Parents should do everything possible to make it enjoyable and painless. Therefore, it is very important to visit the pediatric dentist on time.
When does baby teeth start to fall out in children?
It is well known that absolutely everything in nature is interconnected. If the standard period for the appearance of baby teeth coincides with the baby’s readiness to switch to regular adult food (the so-called “complementary feeding”), then the period of their loss occurs just at the beginning of school life. At this time, the baby’s biological maturation occurs, for which medical practice even uses a special designation: “dental age.”
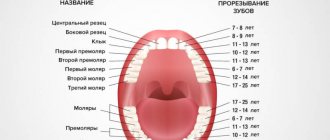
The pattern of loss of baby teeth in children (according to accepted standards) is as follows: this process begins around 6-7 years old, and ends approximately by 12-13 years. In addition, about a year and a half before the first period, previous symptoms appear: unsteadiness, as well as possible painful sensations. This state of affairs is due to the process mentioned above, in which the roots of baby teeth are naturally absorbed.
With regard to the loss of individual units of temporary dentition, the following temporary standards apply:
- upper and lower incisors – the disappearance of the roots begins at the age of 4, ending with loss before entering school;
- lateral incisors - loosening occurs at about 5-6 years, and loss - by 7-8 years;
- premolars - the roots begin to dissolve by the age of 7, and such teeth fall out and are subsequently replaced at 9-11 years;
- fangs are the last to come loose, being completely replaced by the age of 9-12;
- the second premolars complete the process of loss as they approach the 10-year age threshold.
Swelling and gumboils after milk tooth extraction
The surgical dental procedure is quite traumatic. When a baby tooth is extracted, tissue and blood vessels are torn. The child does not feel pain under anesthesia, but almost always experiences stress. Therefore, common consequences include a slight rise in temperature, swelling after the removal of a baby tooth, a small bruise in the projection of the extracted unit, the whims and bad mood of the baby.
In the case of edema, parents should monitor closely. Within normal limits, swelling persists and even increases in the first three days after removal. After this, the swelling should subside. But in some cases the situation begins to worsen. Improper healing, infection or pathology is indicated by:
- high temperature - more than 38 degrees;
- gumboil - a very swollen cheek after a child’s tooth was removed, as well as when the swelling went down to the throat;
- bleeding - repeated or continuous;
- pain - severe, difficult to relieve with medications;
- numbness of the gums - in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth;
- vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Any of the listed symptoms indicates the need to consult a doctor and take urgent measures to eliminate the ailment.
Features of caring for a place with a fallen milk tooth
Immediately after the loss, a dimple appears in the place of the lost unit of the dentition, in which bleeding can be observed. In such a situation, you need to perform the following simple procedures:
- rinsing your mouth with an antiseptic,
- checking the formed hole for the presence of remains of the roots of a baby tooth,
- placing a sterile piece of gauze in the hole, which you then need to bite lightly.
The minimum time after which you can feed the baby is 1 hour. In this case, salty, spicy and sour foods should be eliminated from the diet.
In cases where the bleeding does not stop for 20 minutes or more, or there is residual bone tissue in the gum from a lost tooth, contacting a dentist is mandatory and immediate.
Baby teeth and preserving space in the dentition (video)
In addition, parents should take care of both the physical and psychological condition of the child. You can do this in several ways:
- organize a conversation in a loving family environment on the topic that changing teeth is a completely natural process, indicating growth and maturation, as a result of which there is absolutely nothing to worry about;
- play the role of the Tooth Fairy, inventing a unique ritual of exchanging a “lost pearl” (i.e. a lost tooth) for something pleasant: money, sweets or some other gift that the child will be very happy about;
- completely exclude (even if made out of bright impulses and boundless love) teasers from the category of “toothless”, “ugly”, etc.
Child psychologists advise following the above recommendations every time a child loses a primary canine, incisor or molar.
If the parents correctly followed all the recommendations, then as a reward they receive the most valuable thing: a child with good physical and psychological health.
Problems when changing bites
Sometimes a situation arises that a child “grows a tooth under a tooth” - the permanent one has already appeared above the gum, and the temporary one is firmly held in its place. This happens when the resorption process of one or more milky roots is disrupted. This is also a reason to go to the dentist - after all, no one can say how many days later a loose baby tooth will fall out, and its “stubbornness” leads to the dystopia of a permanent one.
Dental doctors remove even such semi-loose teeth with anesthesia, so as not to cause discomfort to children. Only a specialist can decide what to do when changing the bite. Regular monitoring by the dentist during such an important period will help to avoid the formation of an abnormal relationship of the dentition, which will require further treatment by an orthodontist.
If a child’s baby tooth is loose, then you shouldn’t guess how long it will take for it to fall out; it’s better to consult a doctor without delay for qualified advice.
At the Shifa clinic, children are treated with modern equipment using the latest materials. The center has all the conditions for an accurate diagnosis of the condition of primary and permanent dentition, and this is the key to correct medical tactics. The dentists of the Shifa clinic find an approach to every child and master the most advanced methods of assistance, constantly improving their professionalism in Russia and abroad. Contact the best doctors who will help solve any dental problem!
Why don't baby teeth fall out?
There are several reasons for the delayed (late) loss of dentition units:
- hereditary predisposition,
- gender of the child (according to observations, boys are more predisposed to late shifts),
- past metabolic diseases, various serious infections, as well as rickets, phenylketonuria, and dysfunction of the endocrine system (all this has a significant negative impact on the mineral composition, and, consequently, the quality of tooth enamel),
- pathology during pregnancy, which affects the process of formation and quality characteristics of baby teeth;
- quality of food, water and air (including percentage of oxygen);
- the general state of the environment in the place of residence;
- climatic zone (for example, in cold Murmansk, precipitation may occur somewhat later than in the warmer city of Voronezh).
What are the consequences of delayed loss of primary teeth? The main danger is the high probability of developing a malocclusion. If the child is over 8 years old and there are still no signs of loss, a prompt visit to the pediatric dentistry is mandatory.
Contraindications to tooth extraction at home
Before choosing a method to extract a tooth yourself, it is important to make sure that this manipulation will not cause harm. The presence of the following manifestations is a contraindication for removing thrush at home:
- redness of the gums;
- strong adhesion of the tooth to the jaw;
- thickening of the gums due to swelling;
- the presence of blood or pain when the milkman staggers;
- increased body temperature, signs of acute respiratory viral infection, sore throat;
- the child has severe fear.
When performing a manipulation, you cannot hold the child by force, otherwise the fear of performing procedures in the mouth will remain for life. In all doubtful and complex cases, you should contact a specialized specialist - a pediatric dentist.
Children often experience carious lesions in primary teeth, leading to their partial destruction. Such situations require a mandatory visit to a doctor with subsequent treatment or removal. Even severely damaged carious teeth cannot be pulled out on your own - this will lead to pain and injury to the gums and lips.
The most common dental injuries
Tooth luxation:
- complete luxation (the tooth has fallen out of its socket)
- partial luxation (the tooth has moved but has not fallen out)
- impacted dislocation (the crown part of the tooth is pressed into the gum and bone; the tooth becomes shorter in appearance, and perhaps it is completely invisible).
Tooth fracture:
- chipped piece of enamel
- chipping of the crown within the dentin without damage to the dental pulp
- fracture of the tooth crown with damage to the pulp (blood is visible at the fracture site)
- tooth root fracture
When teeth are injured, soft tissues (lips and gums), the alveolar process (the bone in which the tooth root is located) and the jaw can be damaged. This creates an additional psychological impact on the victim and people providing assistance. Don't panic and stay calm.
Preparing a child for tooth extraction
Before pulling out a child’s tooth, it is important to carry out psychological preparation - explain in a calm voice the essence of the procedure and its purpose, emphasizing that it is not painful and quick. You can come up with a fairytale story about the milkman's journey or tell that mom and dad also had their temporary teeth pulled out.
You also need to ask the child to swing the tooth as much as possible with his tongue - this will make it possible to quickly pull it out of the gums. When the milkman wobbles, its short nerve endings are torn off or pulled out of the canals, so there is no pain syndrome.
TOOTH FRACTURE. What to do?
As we wrote above, the following injuries include tooth fractures:
- chipped piece of enamel
- chipping of the crown within the dentin without damage to the dental pulp
- fracture of the tooth crown with damage to the pulp (blood is visible at the fracture site)
- tooth root fracture
Root fractures can be of more complex types:
In all these cases the recommendation is the same:
- If possible, find all the broken tooth fragments and place them in water
- No emergency visit to the dentist is required; make an appointment this day or the next .
Useful tips for parents
- Monitor your baby's teeth closely. If there are several children in a family, it is better for each of them to have a sign indicating the lost and emerging teeth.
- Teach your child to take care of their teeth. Teach him to brush his teeth twice a day and rinse his mouth after eating. You can use plain water or herbal decoction of chamomile.
- During the teething period, give your child plenty of calcium. Avoid solid foods and feed your baby soft purees, grated fruits and other foods.
- Discuss the upcoming change of teeth with your child so that it does not come as a surprise to him.
If you observe difficulties with the germination of dental units, this is a reason to immediately consult a dentist. Remember that changing teeth is a stressful process for your child. Support him so that this period passes with minimal psychological losses.