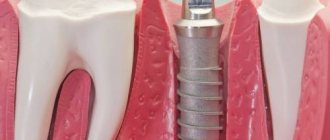
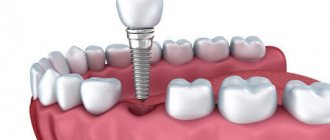
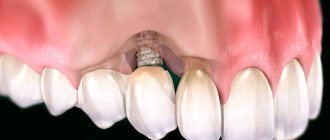
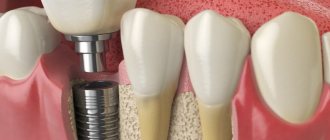
The seventh teeth (second molars according to the dental classification) are located in hard-to-reach places. They are often lost due to poor hygiene. Also in this area there are high chewing loads, which accelerates destruction. To restore missing teeth, implants and dentures are used. When removing sevens, a terminal defect often occurs, since wisdom teeth are often removed at the eruption stage or do not erupt at all. In such cases, implantation is the best solution, since it guarantees reliable fixation, restoration of chewing function, and long service life.
Causes and consequences of losing the seventh teeth
Tooth loss usually occurs due to chronic diseases. Sevens are at risk - they are subject to heavy loads when chewing food, and their location does not allow for high-quality hygiene at home. Together, these factors lead to the rapid development of caries, pulpitis and crown destruction. Following the crown, inflammation moves to the root, periodontitis occurs, the formation of granulomas and cysts. If not treated in a timely manner, the inflammatory process spreads over large areas, which leads to the removal of the source of infection. Other reasons:
- periodontitis;
- jaw injuries;
- bone atrophy due to age-related changes;
- congenital anomalies.
The loss of even one unit of dentition leads to the following consequences:
- malocclusion - voids in the dentition lead to a displacement of neighbors towards the missing unit, while the jaws will no longer close as tightly as before;
- diseases of neighboring teeth - when tilted towards the defect, the necks become exposed, sensitivity and inflammation occur;
- diseases of the digestive system - food is not chewed properly, pathologies of the stomach and pancreas develop;
- bone atrophy - due to root loss, the load on the jaw decreases and it becomes thinner;
- change in appearance - tired appearance due to sunken cheeks and wrinkles.
Where do teeth come from?
Teeth begin to form and develop when the fetus is still inside the womb (at about 6 weeks). They have their source - the epithelial dental plate. Already by 14 weeks, active formation of dental tissues, which are hard, occurs. Initially, this occurs in the area where the crown will be, and later at the root.
Molars, namely their first rudiments, appear by the 5th month of the embryo. They are located higher than the child’s baby teeth or lower. By the time the child is born, the rudiments are already practically formed in the tissues of the jaw.
Teeth that belong to an additional group (have no predecessors) are formed later. This occurs after about 1 year of life. Why? Because the baby's jaw is still very small and there is not enough space for them.
Recovery methods
You can restore sevens by:
- fixation of a dental bridge;
- installation of a removable denture;
- implantation
A bridge in the absence of one tooth consists of three crowns. The outer ones are fixed on the supporting teeth, and the middle one compensates for the lost unit. Since the seventh tooth is usually the end tooth, there is nothing to attach the permanent bridge to. In this case, removable structures are used.
Removable dentures are fixed on the teeth on one side, and glued to the gums with a special gel on the other. This is an inexpensive option, but unreliable - the fixation of the prosthesis is unstable and does not provide functional qualities.
Implants completely imitate the structure of the tooth and are the best solution to the problem. A titanium root is screwed deep into the jaw, and a crown is placed on top. Neighboring units of the dentition are not involved in any way. An artificial tooth is no different from a natural one and takes the same chewing loads.
- Dental bridge
- Removable denture
- Implantation
Differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Permanent and temporary teeth are built in the same way, but still have certain differences between themselves:
- The enamel on baby teeth is whiter. And the enamel on permanent teeth has a yellowish tint;
- the best indicators of density and mineralization are noted behind the molars;
- the pulp of a baby tooth is large in size, and the dense tissues and their walls are thinner;
- permanent teeth are larger in size, here the length is greater than the width;
- The root of baby teeth is short and thin compared to permanent teeth. When the root of temporary teeth is formed, they expand in width. Therefore, the permanent bud has free space to grow.
Implantation stages
Implant installation is carried out using the classical method. Includes stages:
Preparatory
Examination and sanitation of the oral cavity, assessment of the condition of bone tissue, examinations, including x-rays and consultation with a therapist. It takes from one to two days (if no contraindications are identified and no sanitation of the oral cavity is required) to a couple of months (if obstacles to the operation are found).
Bone tissue augmentation
Optional step. It is necessary for long-term absence of a tooth, when the jaw at the site of the defect is atrophied and needs to be restored. The material is planted into the alveolar process and waited until it fuses with the bone. The operation itself lasts 2-3 hours, but the recovery period takes up to six months. In cases of minor bone loss, osteoplasty is performed simultaneously with the installation of an artificial root.
Implant installation
The gum is surgically removed and a hole is made in the bone for an artificial root. After installing the implant, a plug is attached on top, and the mucous membrane is sutured. Engraftment up to 6 months.
Installation of the healing abutment
The gums are opened and a former is placed on the titanium root for 10-14 days to create the contours of the gums for the future crown.
Fixation of permanent prosthesis
The former is replaced with an abutment (an adapter between the crown and the implant). The crown is installed using previously taken impressions.
Groups, tooth numbering
There is no unified identification and classification system. Let's consider the basic principles of dividing teeth into groups and designating each.
Numbering of different groups of teeth.
All elements of the upper and lower jaw are divided into frontal and chewing. The frontal elements are designed for biting food and also play an aesthetic role. Chewable ones allow you to crush pieces of food and prepare them for entry into the digestive tract.
There are notation systems:
- square-digital;
- two-digit;
- universal;
- Haderup system;
- alphanumeric.
Square-digital system
Zsigmond-Palmer numbering is common among dentists. Each jaw is conventionally divided into two identical halves, each of which is numbered from 1 to 8. If we talk about a preschool child, Roman numerals from I to V are used, numbering goes from the middle to the edge. Central incisors are assigned the number 1, lateral incisors - No. 2, canines - No. 3, extreme molars - 8. To identify a tooth, its number, jaw, and side of location (right or left) are indicated. This numbering is simple and convenient.
Two-digit numbering
The International Organization of Dentists has recognized a two-digit system. It is a modification of the previous one, more accurate and functional. The numbering used is the same as in the Zsigmond-Palmer system, but the number of the quadrant of the oral cavity in which the tooth is located is additionally indicated. The following designations are used: 1 - right half of the upper jaw, 2 - left half of the upper jaw, 3 - left half of the lower jaw, 4 - right half of the lower jaw. Accordingly, unit number 43 is the right canine of the lower jaw, 21 is the central left incisor of the upper jaw.
Universal
The universal numbering system is the most understandable. Each tooth is assigned a serial number from 1 to 32. Numbering starts from the rightmost upper molar. He is assigned No. 1. Left upper extreme molar - No. 16. The lower jaw is numbered from left to right. It contains teeth No. 17-32. The letters of the Latin alphabet from A to T are used to designate baby teeth.
Alphanumeric
The alphanumeric system is used primarily to describe the characteristics of the bite, since it does not take into account the location of the teeth on the right or left side of the mouth. According to this numbering, the groups are designated by Latin letters: I - incisors, M - molars, C - canines, P - premolars. In addition to the letter, each unit is assigned a serial number. The designation M1 corresponds to the first molar, and I 2 to the extreme incisor.
Haderup system
These designations are similar to the Zsigmond-Palmer classification, but a “+” or “-“ sign is added to the numbers. The first identifies the upper jaw, and the second identifies the lower jaw. To indicate baby teeth, add “0” before each number, for example +02 - the outermost baby incisor on top. This notation system is rarely used.
Is it possible to use express methods for sevens?
Express implantation can be performed in two ways.
Option 1 - place a crown right away
Implantation Immediate Load - instant loading of a titanium root with a crown. In 3-7 days, the patient completes the full course of treatment and receives a new tooth. But this protocol is not suitable for sevens. Usually there is not enough bone tissue in case of loss of the last tooth. And implantation with an immediate load is carried out only when there is a sufficient amount of bone. In case of atrophy, rapid loading does not provide reliable fixation of the titanium root; it cannot be guaranteed that the implants will last the entire period promised by the manufacturer.
Even in the case of ideal conditions with a sufficient amount of bone tissue, it is not recommended to immediately load the seven implant with a crown. The second molar is actively involved in the chewing process; displacement during chewing is possible.
Option 2 - place an implant immediately after tooth extraction
The implant is installed in the hole immediately after the seven is removed. In this case, the healing stage after extraction is skipped, which saves the patient 4-5 months. For 7 teeth, this method is allowed only if there is an adequate amount of bone tissue, planned rather than emergency tooth extraction, the absence of cysts and granulomas on the root, and gentle extraction without damaging the alveolar process.
Teething order
Typically, all children start teething at about the same time. Teeth emerge from the molar set at the age of 5, and it is the molars (large ones) that emerge. Then the diagram is as follows:
- Initially, the incisors on the lower jaw change, which are located in the center;
- then the central incisors appear on the upper jaw and the incisors on the sides on the lower jaw;
- at about 8-9 years old, the incisors on the top and sides change;
- up to 12 years of age, molars (small) grow;
- at the age of 13, the fangs change;
- after the child turns 14 years old, the second molars (large ones) come in. They were not included in the milk kit;
- and after another 1 year the third molars (large) appear. This is a wisdom tooth. But he may not appear at all.
Price
The cost of installing an implant in our Center is standard. Pricing is formed on a turnkey basis. There are several ready-made treatment options. For example, using Nobel Biocare PMC implants, restoring a seven is 20 thousand cheaper than installing a Nobel Biocare Conical Parallel CC. The first ones are used for weak bones, the second ones - of the new generation, for strong ones.
The operation takes place in two stages. At the first, the price includes the procedure itself, the implant and plug, pain relief, consumables, postoperative X-ray examination and CT scan after eight weeks. The application and removal of sutures are also taken into account when determining the cost.
At the second surgical stage, the price list includes painkillers, antiseptics, opening and removal of implant plugs, fixation of gum formers, and consumables.
In the “implantation” case, the cost of surgical treatment does not include crowns. The price depends on the manufacturing method and type of fixation.
Our Center has its own laboratory, where only all-ceramic crowns are manufactured using the Zirkonzahn Schule method. You can order production at the Swiss PROCERA plant, but you will have to wait longer.
The cost of the case does not include sanitation, sinus lift, osteoplasty and temporary prostheses until the implants are healed.
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
There are certain signs that indicate that permanent teeth will soon begin to erupt:
- The spaces between the teeth increase. The jaw grows and the free space increases;
- baby teeth become loose as the root gradually dissolves. It cannot be firmly fixed in the jaw tissues;
- in case of loss of a temporary tooth. This confirms that the molar will soon come out as it has pushed out the previous one;
- The gums are slightly swollen and red.
When permanent teeth erupt, the child’s general well-being usually remains the same, the temperature does not rise, and there is no pain.
Guarantees
The Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin” has a guarantee program. The patient of the clinic will receive a guarantee for:
- implant;
- surgery;
- sinus lifting and osteoplasty;
- prosthetics.
Only Lifetime on Nobel Biocare issues a lifetime warranty on the implant; other companies usually provide 25 years.
The warranty provides a year of free service for implantation and two years for all types of treatment. The contract is valid subject to systematic medical examinations and proper care.
Possible problems
Permanent teeth have just appeared, but this does not mean that there will not immediately be any problems associated with them. Parents should be aware of possible dental problems:
- lack of molars;
- pain in the molar area;
- crooked position of molars;
- molars fall out;
- injuries.
For any of these problems, it is important to contact a specialist in time to receive qualified help.
Deviations in teething
Minor changes in the timing and sequence of dental growth should not cause alarm. However, significant deviations from the norm in teething are a cause for concern.
- The tooth does not appear for a long time. Reason: genetic predisposition to long eruption or lack of rudiments.
- Too early appearance of teeth. Caused by disruption of the endocrine system.
- Black or brown enamel surface color. Indicates high iron levels, poor salivation, or chronic inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
- Incorrect row position. Bite pathologies indicate a hereditary factor or deformation of the maxillofacial bone.
Why do teeth erupt with irregularities?
The condition of a child’s teeth in the first years of life depends on the health of the mother during pregnancy. The formation of hard dental tissues may be disrupted if a woman:
- suffered from toxicosis at the initial stage of pregnancy;
- experienced severe prolonged stress;
- was treated for kidney disease;
- suffered from rubella.
In addition to maternal diseases, the maturation of teeth and the development of the jaw system can be affected by:
- fetal prematurity or, conversely, delayed birth;
- conflict of Rh factors;
- sepsis suffered by a child in the first month of life;
- frequent colds, pneumonia;
- convulsions;
- toxicosis;
- refusal to breastfeed.
Often, parents, driven by the best intentions, want to alleviate the baby’s suffering by giving him medications. You must understand that any medicine, even if it seems completely safe, cannot be taken without consulting a pediatrician!
Location of teeth by numbers
Despite all the individual characteristics of each person, the location of the teeth and their name are the same for everyone. This is explained by the fact that dental elements begin to form long before birth (approximately 2-3 months of embryogenesis), and at birth the child has all the dental buds located deep in the jaw.
In both adults and children, the dentition is symmetrical - the upper and lower jaws have the same number of teeth of the same name (the reference point is the midline of the face).
The table shows the order of the teeth and their correct name.
| Serial number | Dairy | Permanent |
| 1 | central incisor | central incisor |
| 2 | lateral incisor | lateral incisor |
| 3 | fang | fang |
| 4 | first molar | first (small) premolar |
| 5 | second molar | second (small) premolar) |
| 6 | — | first (large) molar |
| 7 | — | second (large) molar |
| 8 | — | third (large) molar |
As can be seen from the table, only the front teeth (incisors and canines) have the same names and locations in children and adults. The rear (or “root”) have significant differences.
Painful teething: advice for parents
When faced with teething in children, many parents are at a loss. First of all, you need to call an ambulance and determine the reason for the baby’s poor health. If symptoms are confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medications for teething - antipyretics and painkillers.
You can treat your gums yourself with an anesthetic gel with a cooling effect to reduce itching and swelling of the mucous membrane. Ice will also help. To reduce gum irritation, there are special silicone fingertips made of hypoallergenic material.
Folk remedies for teething will effectively relieve painful sensations - a decoction of chamomile, sage, tincture of valerian and honey will soothe inflamed tissues.
Painkillers for teething are contraindicated in children; this can worsen their health.
Important!
Without a doctor's recommendation, antibiotics and other strong teething medications can cause an allergic reaction.