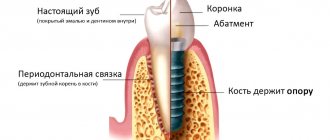
Also watch: Important questions about anesthesia and sedationTeeth extraction under sedationCost of sedationWhat is drug-induced sleep in dentistry
Go straight to:
- What is sedation
- Types of sedation
- Superficial
- Deep
- Treatment of children in their sleep
- Contraindications
Every trip to the dentist, even for advisory purposes, is always associated with pain and negativity. At least, this was the case until recently. Now modern dentistry provides dental treatment and preventive measures in the oral cavity with complete comfort and without any pain. All manipulations are accompanied by preliminary sedation and local anesthesia, and in case of emergency, general anesthesia is used.
The local effect of anesthetics on oral tissue is in most cases accompanied by unpleasant and even painful sensations, especially during their administration. This circumstance causes fear and panic in many patients. People who lead an active lifestyle, filled with worries, stress and little opportunity for rest, are especially susceptible to this. To eliminate emotional stress, ensure comfort and painlessness, doctors began to actively use sedation in dentistry. The method is quite serious, therefore it is used only in licensed departments and the specialists involved are, accordingly, highly qualified, with certain knowledge and skill.
How does treatment work under sedation?
Sedation is the effect on the central nervous system of small doses of drugs that are used in general anesthesia. The effect in this case will be tens of times weaker than with general anesthesia, which allows you to put a person into a state of half-sleep, while maintaining all body functions and the possibility of contact with him. This method is called injection. There is also an oral method of putting a person into medicinal sedative sleep and an inhalation method, which is used in pediatric practice.
The purpose of sedation in dentistry is to achieve the following effects:
- the patient is completely relaxed during a painful or unpleasant procedure;
- performing local anesthesia without fear or discomfort;
- ensuring moral and physical comfort;
- creating ideal conditions for a doctor’s work;
- maintaining the psycho-emotional background in a state of euphoria.
In dentistry, sedation is used only in conjunction with local anesthesia techniques, since it does not provide complete absence of pain. The type and means of this method are determined by the anesthesiologist, individually for each patient who comes to the dental clinic. No preliminary preparation for the procedure is required, other than the usual history taking. Thanks to the use of combo anesthesia, that is, an integrated approach to anesthesia, dental treatment and prosthetics are no longer associated with fear, pain and nervous shock.
We know how to treat without pain!
- complete relaxation: you will have no fear of the dentist, pain or treatment,
- complete relief of pain,
- fast recovery,
- pleasant rehabilitation after, since xenon triggers metabolic processes in the body,
- you are relaxed, which means the doctor does his job without being distracted by your emotions.
With us you will stop being afraid of dentists! Individual selection of drugs, the most modern equipment and certified doctors who professionally work with all types of anesthesia.
Enroll now
Types of sedation
Experts distinguish the following types of sedation:
- superficial
sedation is caused by maximum relaxation of the body and suppression of fear with complete preservation of all body functions and the ability to verbally communicate if necessary; - deep
sedation is characterized by a state close to general anesthesia, that is, consciousness is completely turned off and basic reflexes are somewhat suppressed.
In dentistry, superficial sedation is actively used, which is carried out by introducing certain doses of drugs into the body by injection or orally. The mask method of suppressing consciousness to a state of euphoria is provided by inhaling nitrous oxide vapor. These drugs have a moderate inhibitory effect on the central nervous system and are considered the most optimal and safe in pain relief during the treatment process.
Anesthesia and deep sedation are carried out only in specialized dental surgery departments with experienced anesthesiologists, all the necessary equipment (ventilator) and medications for emergency care (pressure drop, cardiac arrest). In this case, the patient undergoes mandatory training.
Will there be pain during and after the procedure?
No, during the operation you will not feel any discomfort, because you are relaxed, and we additionally applied local anesthesia, which numbs the surgical area.
After the operation there will be slight discomfort - you will feel weak, perhaps slightly dizzy. But there will be no severe pain, even after removing all the teeth and installing a large number of implants. After the anesthesia wears off, the pain may increase, but your doctor will prescribe pain medications for you to take if necessary. These sensations will not be associated with the use of xenon, but with tissue injury in general.
Comfortable treatment without pain! We carry out thorough diagnostics, select medications and dosages strictly individually. It's safe here!
Enroll now
Indications for the use of superficial sedation in dentistry
Modern dentistry uses shallow sedation during every, even minor, manipulation, which ensures that patients subsequently turn to specialists without the slightest fear or worry. This type of mild impact on a person’s consciousness does not require special preparation, except for refusing to eat food, coffee or tea a few hours before the expected procedure.
For comfortable treatment and prosthetics in the adult population, in most cases, an injection or oral method of inducing a state of half-sleep (sedative sleep) and euphoria is used.
Indications for this procedure are the following measures in dentistry:
- treatment of caries, which is accompanied by drilling the tooth, removing nerve endings, and applying medications;
- pulp removal, characterized by severe pain;
- removal of teeth or roots;
- professional cleaning accompanied by severe discomfort;
- canal filling;
- deep cleaning of periodontal pockets;
- preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics;
- mini gum surgery;
- installation of implants.
Sedation is carried out 5-10 minutes before medical procedures, and the dose of drugs is calculated for the corresponding time period in which the planned procedure is performed. After completion, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors until the psycho-emotional background is completely restored, which occurs in approximately 15-30 minutes. In case of an emergency, if any unforeseen situation occurs in the patient’s condition, a dental office that uses sedation and other types of anesthesia in its work is necessarily equipped with all the necessary means to provide emergency care. According to statistics, the likelihood of complications is minimal. Sometimes there is a slight fluctuation in blood pressure numbers, which may be accompanied by slight dizziness.
For patients who have contraindications for intravenous sedation, a mask method is used, which involves inhaling nitrous oxide vapor. In this case, mild euphoria, accompanied by dulling of consciousness, occurs within a few seconds and ends immediately after removing the mask. This method is widely used in pediatric dental practice.
Literature
- Boisson-Bertrand, Ravussin P. 4th meeting of the anesthesia-resuscitation section of the ORL Department. Lausanne//Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim. – 1991.- Vol. 10(1).- 1A-2A.
- Buck M., Blumer J. Opioids and other analgesics: Adverse effects in the intensive care unit // Crit. Care Clin. — 1991.- Vol. 7.- R. 615-637.
- Chollet-Rivier M, Chiolero RL. Anaesthesia for procedures in the intensive care unit. // Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. – 2001 – V. 14(4) – P. 447-51.
- Cohen D., Horiuchi K., Kemper M. et al. Modulating effects of propofol on metabolic and cardiopulmonary responses to stressful intensive care unit procedures // Crit Care Med.- 1996.- Vol. 24.- R.612-617.
- Cohen IL, Abraham E., Dasta JF, Gallagher TJ, Papadakos PJ, Pohlman AS Management of the agitated intensive care unit patient // Crit. Care Med. - 2002. - Vol. 30. – R. 97-123.
- Durbin CGJ Sedation of the agitated, critically ill patient without an artificial airway // Crit. Care Clin. - 1995. - Vol. 11. – R. 913-936.
- Ely E.W. Delirium in Intensive Care Unit: Textbook of Critical Care Fifth Edition MP Fink. E.Abraham, JLVincent, PM Kochanek - Flsevier, 2005.- 2358 p.
- Frye MA, Coudreaut MF, Hakeman SM et al. Continuous droperidol infusion for management of agitated delirium in an intensive care unit // Psychosomatics. - 1995. - Vol. 36. – R. 301-305.
- Harvey M. Managing agitation in critically ill patients // Am. J. Crit. Care - 1996. - Vol. 5. – R. 7-15.
- Kress IP, Lacy M., Pliskin N., Pohlman A. The long term psychological effect of daily sedative interruption in critically ill patients // Am. Respira. With rit. With are Med. - 2001. - Vol. 163. R .954
- Kress JP, Pohlman AS, Hall JB Sedation and Analgesia in the Intensive Care Unit // Am. J. Respira. Crit. Care Med. – 2002.- Vol. 166. – R. 1024-1028.
- Lewis K., Whipple J., Michael K., Quehbeman EJ. Effect of analgesic treatment on the physiological consequences of acute pain // Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. - 1994. –Vol. 51. – R. 1539-1554.
- Liu J., Singh H., White PF Electroencephalographic bispectral index correlates with intra-operative recall and depth of propofol-induced sedation // Anesth. Analg. — 1997. –Vol. 84. – R. 185-189.
- Mehta S. Sedation Strategies in the Critically II // Yearbook of Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine - Edited by JI.Vincent -Elsevier - 2005.- R. 78-
- Milbrandt E.W., Ely E.W. Agitation and delirium. Critical Care. Fifth edition. Finc MR, Abraham E, 2005, chapter 2.
- Park G, Lane M, Rogers S, Bassett P. A comparison of hypnotic and analgesic based sedation in a general intensive care unit. // Br J Anaesth. – 2007. – V.98(1). – P.76-82.
- Rhoney DH, Parker DJ Use of sedative and analgesic agents in neurotrauma patients: effects on cerebral physiology // Neurol. Res. - 2001. –Vol. 23. – R. 237-259.
- Terao Y., Miura K., Saito M., Sekino M., Fukusaki M., Sumikawa K. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between sedation and resting energy expenditure in postoperative patients // Crit. Care Med. — 2003. –Vol. 31(3). - R . 830-833.
- Vinik H. Intravenous anaesthetic drug interactions: practical applications. //Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. Suppl. – 1995. – V.12. –P.13-19.
When is deep sedation indicated?
Deep sedation has an effect on the body akin to general anesthesia, but without complete suppression of vital functions. This type of action aimed at consciousness can only be provided by a highly qualified anesthesiologist with extensive experience. Deep sedation is used in specialized and licensed departments, where there are appropriate specialists and all the necessary equipment. The likelihood of any complications is several times greater than with superficial sedation, therefore the medical institution must be equipped with a ventilator, the required volume of oxygen (cylinders) and emergency medications to restore cardiovascular activity and respiratory function.
The use of deep sedation is indicated in the following situations:
- carrying out an open sinus lift, which is due to numerous manipulations on the gums and bone tissue of the upper jaw (incision, drilling of the bone, implantation of a bone implant);
- operations in the treatment of periodontitis (curettage, flap surgery);
- complex operations on the gums;
- correction of severe forms of malocclusion;
- operations of varying degrees of complexity on the temporomandibular joint;
- restorative operations on the dentition, accompanied by maximum time costs;
- the patient has mental pathologies;
- the patient’s extremely burdened allergic history, which is due to the inability to use any local anesthesia.
To use deep sedation, the patient must undergo thorough preparation. Preparatory measures include a comprehensive examination (clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests, electrocardiogram), premedication and refusal to eat food 3-4 hours before surgery. After all procedures are completed, the patient must remain under medical supervision for another day.
Deep sedation is due to a significant effect on all parts of the central nervous system, but is tolerated much better than general anesthesia and has virtually no consequences. Patients recover well and quickly after this procedure within the first 2-3 hours. Of great importance in the profound impact on consciousness is the professionalism of the anesthesiologist, who first conducts a survey and examination of the patient to select medications and doses that provide the most safe anesthesia and comfort.
Expert opinion
Igor Yurievich Malinovsky
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 11 years
To make a positive decision about treatment under sedation, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis. The patient is prescribed a set of examinations: ECG, biochemical and general blood tests, tests for AIDS, HIV, hepatitis A and B. The latter are necessary if urgent hospitalization is necessary. All tests must have an appropriate statute of limitations.
Adults are recommended to use sedation for the following indications:
- severe fear or panic before the upcoming procedure;
- long-term treatment more than 2 hours;
- complex treatment: removal of wisdom teeth or several teeth in a row, implantation;
- increased gag reflex threshold;
The effect of inhalational sedation wears off as soon as the patient removes the mask. In most cases, sedative anesthesia is mild. However, after deep sedation, some patients may experience nausea, headache, or dizziness.
If there is a possibility and there are no direct indications, then any qualified doctor will advise both children and adults to do without sedation.
Sedation in pediatric dentistry
In dental treatment for children, sedation is very important. By safely influencing the child’s level of consciousness, the doctor ensures the normal state of mind of the little patient, and increases the time range for himself to carry out therapeutic manipulations. Sedation is carried out using a mask placed over the nose, through which the baby inhales nitrous oxide vapor, which provides a state of euphoria, but maintains verbal contact with the doctor, that is, the child responds to the doctor’s requests to open his eyes or mouth, or turn his head. Many dental offices provide cartoons for young patients during treatment procedures accompanied by sedation.
Modern conditions for dental treatment in children provide the following advantages:
- maintaining a healthy psycho-emotional background of the child;
- ensuring calm visual and verbal contact with the doctor during the treatment process;
- the absence in the little patient’s memory of any situations that could provoke the development of a phobia;
- the opportunity for the doctor to fully carry out therapeutic manipulations in the baby’s oral cavity;
- ensuring the child’s calm state at the next appointment in the dental office.
The inhalation method of sedation in pediatric dentistry is considered the most pleasant and safe component in pain relief measures. No preparatory measures are required for this form of sedation.
[slide-anything id=”3470"]
Content
- Indications
- Are there any disadvantages?
- About the dangers of sedation
- Possible complications
Sedation is an opportunity for dental phobes to calm down and carry out dental procedures if the situation is unusual. Mild sedatives, or sleeping pills, allow the patient to avoid stress, especially when it comes to tooth extraction. Are there any negative aspects to dental treatment under sedation?
General anesthesia for dental procedures is usually not used. Only mild sleeping pills. In this case, the patient seems to be sleeping, but is conscious, and can be woken up at any time.
The following methods of sedation are used:
- Inhalation, similar to general anesthesia - the patient falls asleep with a nitric oxide mask, the depth of his state is regulated by devices;
- Oral – as a result of taking medications, the patient’s level of relaxation is assessed as average, he cannot hear the doctor;
- Injection - after the injection, the patient falls asleep, does not hear the doctor’s speech, and cannot fulfill his requests.
After the manipulation, it is not recommended to drive, as the reaction speed will be slowed down.
PROMOTION
Inexpensive dentistry
Prices are 1.5-2 times lower
Contraindications for sedation
Sedation and its types, like any intervention in the body, may have contraindications. Usually, before using any methods of sedation, the dentist or anesthesiologist finds out certain nuances that may interfere with the creation of a comfortable and pleasant state of health during dental treatment.
The following body conditions are considered to be the main contraindications for the introduction of sedatives into the body:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- the age of the child is up to 3-4 years, which is caused by unformed functions for voice contact with the doctor during the treatment process;
- severe form of epilepsy, since with sedation with certain drugs there is a risk of developing an attack;
- a history of severe traumatic brain injury;
- complicated allergy history;
- drinking alcohol on the eve of dental treatment;
- decompensated cardiovascular diseases;
- constant use of potent drugs.
An experienced anesthesiologist will select the necessary means for safe pain relief, even if there are any contraindications, but only in emergency cases of the need for dental intervention and if the appropriate equipment is available in the clinic where the treatment will take place. Modern pharmacology has safe drugs for superficial sedation, one of which is nitrous oxide. Inhaling its vapors can only slightly increase intracranial pressure, and then only with prolonged use.
Sincerely, Levin D.V., chief physician