Korostelev Egor Dmitrievich
Source:
Clinic Doesn’t Hurt!
Enlarge
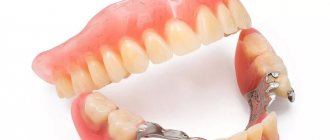
Not all patients who use removable dentures know how to properly care for and clean their dentures. As a result, the removable denture quickly ages, loses its appearance and begins to cause serious problems. Often such patients come to our clinic with typical complaints.
Why do problems occur if you don't clean your removable dentures correctly?
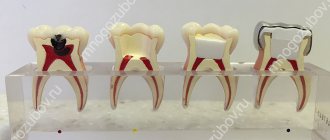
When you eat, food plaque is deposited on your denture, just like on your teeth. The worse a person cleans his dentures, the faster the denture loses its original appearance. Food plaque becomes a breeding ground for the development of microorganisms. The processes of decay and the development of a viral infection cause bad breath and the onset of inflammatory processes on the gums.
In order to avoid the unpleasant consequences of the formation of food plaque and tartar, the removable denture must be cleaned after every meal.
Requirements for cleaning products for orthopedic structures
A product for cleaning artificial crowns and gums must meet the following requirements:
- Efficiency. It is important that the product helps quickly remove all food debris from open and hard-to-reach areas.
- Safety. The composition should not contain toxic substances, foaming agents, or abrasive particles.
- Comfort of use. Good pasta has a pleasant or neutral taste.
Besides these, there are other requirements. For example, paste for dentures should not scratch their surfaces or change color. It is also desirable that after using it, a feeling of freshness appears in the mouth, and all unpleasant odors disappear.
How to properly clean removable dentures?
To clean plaque from a denture, it must be removed from the mouth. The denture is cleaned with a toothbrush or other convenient brush. For good cleaning of dentures, ordinary soap is best suited.
Removable dentures must be cleaned according to certain rules. First, we clean the denture from the outside (from the side of the artificial teeth). After that, be sure to thoroughly clean the inner string (on the side that is adjacent to your gums). Cleaning the inside of the denture is often not given due importance.
Afterwards, the prosthesis is washed well with soap and water.
You should also rinse your mouth thoroughly. And only after this the prosthesis can be put on again.
Medical Internet conferences
The purpose of our study is to review means for fixation of complete dentures.
In this work we set ourselves the following tasks:
-describe the properties and composition of means for fixing complete removable dentures;
- analyze the physical and chemical properties of gels for fixing complete removable dentures;
-conduct a review of the market for means for fixing complete removable dentures presented in pharmacy chains, dental stores and clinics;
- analyze data to assess adhesive strength.
Materials and methods:
— familiarization with the literature on this topic;
— study of experimental data to assess adhesive strength, according to the methodology of S.E. Zholudev.
Results:
The problem of complete removable prosthetics is the quality of fixation of dentures in the oral cavity [5]. If it is impossible to achieve functional suction during the manufacture of complete removable dentures, it is advisable to recommend that patients use additional means to improve the fixation and stabilization of dentures [1]. Adhesive compositions for removable laminar dentures have the following properties:
— reliable and durable fastening of prostheses throughout the day,
- preventing food debris from getting under the prosthesis,
— reducing the risk of developing inflammatory processes.
Most fixing adhesive preparations are made on the basis of water-soluble polymers: natural polysaccharide - sodium algiinate; artificial and synthetic components of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), a mixture of sodium-calcium salts of methyl vinyl ether copolymer of maleic anhydride (MVE/MA); polyglyceryl methacrylate and combinations of the above components with the inclusion of various components with antiseptic, refreshing, aromatizing, analgesic, and antimicrobial effects [10].
The use of fixation agents with appropriate pharmacological preparations makes it possible to treat fungal infections of the tissues of the prosthetic bed if indicated [3]. Prosthetic fixation products are easy to use. The action of these products is based on the universal physical phenomenon of wettability. This can be seen in the following example. If two dry glasses are placed on top of each other, they can be easily separated. Adhesion increases many times if the glass is moistened with water. The same applies if there is a layer of oral fluid (saliva) or adhesive agents between the prosthesis and the mucous membrane [4].
Natural resins, especially Kagaua resin, were used as the first fixing agents [7]. Later, carboxymethyl cellulose was used for these purposes. In 1970, Richardson-Wicke introduced Gantrez and its bivalent salts. Gantrez is a copolymer of vinyl methyl ether with maleic anhydride and has two advantages:
- bioadhesion, causing adhesion to the oral mucosa;
- a strong bond between the copolymer chains, leading to strengthened bonds in the substance itself [9].
There are a large number of means for fixing dentures, presented in pharmacy chains, dental stores and clinics in Saratov. The market includes such companies as ROCS, LACALUTdent, Protefix, Fittydent, PresiDENT, Corega. Creams are very popular. Another common means of securing dentures in the mouth are powders. They, unlike creams, are used for low salivation. Fixing strips are used for abnormal jaw structure [6].
One of the criteria for assessing the quality of orthopedic treatment of patients with complete absence of teeth is good fixation and stabilization of dentures [5].
For a comparative assessment of the adhesive ability of adhesives using laboratory methods, the following technique was used [2].
The degree of adhesion was assessed directly on removable dentures, strengthened with adhesive agents on plaster models reproducing the anatomical shape of the prosthetic bed (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Study of the degree of adhesion on jaw models
The studies were carried out on three different plaster models of jaws; the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the prosthetic bed was treated with adhesive; the area of this surface averaged 29.3 cm2.
To recreate more natural conditions of the prosthetic bed, a plaster model was smeared with a diluted (3%) gelatin solution of the same volume before each experiment and dried for 30 minutes at 100-1200C. Then, a 2 kg weight was used for 5 minutes to ensure a tight fit of the prosthesis. The plaster model was fixed in a tripod and then, when adding a load, the mass was determined at which the prosthesis separated from the prosthetic bed of the model (Fig. 1).
The experiment was repeated until the results converged satisfactorily (the relative error was 7%). Adhesive strength (A) was calculated as the quotient of load in grams (M) per area (S):
A = M / S, g / cm.2
Laboratory methods made it possible to evaluate the adhesive ability of products to improve the fixation of prostheses in relation to the acrylic material of the prosthesis base, as well as to identify the influence of the aqueous environment on adhesive properties over time.
The technique was more consistent with the clinical situation and made it possible to assess the adhesiveness in relation to the prosthetic bed, taking into account the factor of anatomical retention. The adhesive ability of the proposed system (25% propolis) in relation to Pectafix, Lacalutdent, SUPER COREGA Haft-Pulver is initially higher and decreases after 1 hour.
The fixation of complete removable dentures of the upper jaw was assessed directly in the oral cavity in 32 patients. The force of fixation of the prosthesis along line “A” was compared, for which a metal plate was fixed to the prosthesis on self-hardening plastic (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. An upper jaw prosthesis with a metal plate fixed to self-hardening plastic to determine the fixation force.
A nylon thread was tied to the outer tip of the metal plate, passing it through a roller for unhindered sliding. The prosthesis with an adhesive agent applied to its inner surface was introduced into the oral cavity and pressed tightly against the prosthetic bed for five minutes. Then fine metal shot was evenly added to a reservoir specially attached to the thread (Fig. 3).
The weight of the load at which the prosthesis separated from the prosthetic bed was determined on electronic scales. The study was carried out with a minimally open oral cavity of up to 0.8 cm. Four adhesive agents were compared: “PresiDENT Garant”; "Lacalut dent"; "Dentipur"; "Tizol with propolis." The patient's head was oriented so that the nasal line made a right angle with the piece of thread that was directly fixed to the load reservoir. In one visit, the patient was determined by the strength of fixation of the prosthesis without adhesive, and with the application of one adhesive preparation to the prosthesis. To determine the strength of fixation of a removable structure with a different adhesive, the patient was prescribed at least 24 hours later.
Rice. 3. Patient with a prosthesis fixed in the oral cavity and prepared containers for metal shot
It was noted that the following pattern was observed in each patient:
1. Fixation of the prosthesis, compared with the initial value without adhesive, statistically significantly increases after five minutes when using Tizol with propolis by an average of 500 ± 45 g, that is, half the initial fixation force obtained when measured without an adhesive.
2. The fixation force of the adhesive based on Tizol with propolis is on average 285±30 g (from 190 to 380 g) greater than the fixation force of the adhesives compared in the experiment with the exception of “Lacalutdent”.
AB Klychkov (2002) proved that the use of adhesive materials ensures the stability of dentures on edentulous jaws and affects not only the functional and anatomical characteristics of the maxillofacial area, but also the physicochemical and metabolic parameters of the oral fluid [8].
Conclusions:
-described the properties and composition of means for fixing complete removable dentures, on the basis of which we can conclude that they are an integral part when using complete removable dentures;
- analyzed the physicochemical properties of gels for fixing complete removable dentures, from which we can conclude that the most important property of gels is bioadhesion;
-conducted a review of the market for means for fixing complete removable dentures presented in pharmacy chains, dental stores and clinics, and patients give their preference to creams for fixing complete removable dentures;
- analyzed data on assessing adhesive strength and found that fixation of the prosthesis without adhesive is less effective than using adhesive.
Features of caring for removable dentures made of various materials
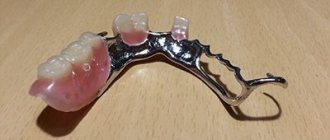
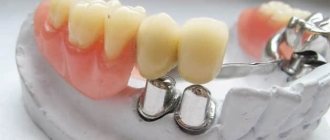
The rules for caring for removable dentures are the same for all types of removable dentures: acrylic plastic, Acre-Free material, clasp and nylon dentures.
Some additional care requirements apply only to nylon dentures.
Nylon removable dentures are more demanding on hygiene. It must be cleaned with special care. A prerequisite for caring for nylon removable dentures is the use of soluble tablets for cleaning removable dentures.
Why does food accumulate on dentures?
With every meal, food particles remain on the prosthesis, and this happens for several reasons:
- Food that falls to the floor of the mouth can become lodged under the lower jaw denture.
- Small pieces of food that move in different directions in the mouth during chewing and swallowing can get into the space between the palate and the upper denture.
- Food sticks to the rough surface of dentures much more easily than to the soft tissues of the oral cavity; Over time, food debris accumulates on artificial teeth.
Dentures take up quite a lot of space in the mouth, and their owners feel the presence of food debris under the denture much better than people with natural teeth, between which food particles can also remain.
Tablets for cleaning dentures
Pharmacies sell special soluble tablets that help remove food and other dyes from removable dentures.
It is known that a person has a lot of food products that can color a removable denture in an unnatural color. For example, coffee, strong tea, berries (blueberries, etc.), vegetables (beets, carrots, etc.), confectionery dyes, etc. If a person smokes, then plaque from smoking strongly eats into the denture and spoils it.
Food coloring deposits or smoking deposits are very difficult to remove with a brush and soap. Dissolvable tablets come to the rescue. The tablets help clean any type of dentures and, as already mentioned, are mandatory for nylon dentures.
Deeper cleaning from germs and plaque
Sometimes patients ask the orthopedic dentist how to clean their dentures to disinfect and remove pigmentation and stains. For this purpose, manufacturers of dental hygiene products offer special tablets that can be purchased at the pharmacy. To carry out deep disinfectant cleaning you need:
- pour 100–200 ml of warm water into a glass;
- throw one tablet into the liquid to clean dental structures;
- Dip the denture into the solution.
This treatment can be done every day, leaving the removable jaw in a glass or container overnight. If you prefer not to remove the denture before going to bed, you can treat it with a special solution once or twice a week, but it is better to do this daily for 10–15 minutes. After cleaning, you need to thoroughly rinse the structure under running water to completely wash away the remnants of a chemical harmful to the mucous membranes.
How to avoid damage and breakdowns?
The removable orthopedic structure is designed for chewing food, so it is made of fairly durable materials. But this does not eliminate the risk of prosthesis breakage if the load is too high. Therefore, when using it you must follow the rules:
- Avoid eating too hard and tough foods, such as dried fruits, nuts, crackers.
- Do not bite off large pieces of hard fruits, but chop them before eating.
- Do not engage in wrestling, boxing or similar sports without a protective mouth guard.
- Do not consume foods with a large temperature difference at the same time.
- Do not allow the structure to fall into a sink, tiled floor or other hard surface.
If cracks or chips appear, you should not try to repair the prosthesis yourself. In such a situation, you should immediately contact an orthopedic dentist.
How to store prosthetic structures?
Stories about “teeth in a glass” are almost a thing of the past. Modern dentures are made from materials that are not in danger of drying out without moisture. Therefore, the rules for storing them have changed:
- After removal from the mouth, the denture should be thoroughly cleaned to remove plaque and food debris.
- Then wrap it in a clean napkin and place it in a special container.
- You can also store it in a disinfectant solution, which is intended for long-term use.
For each type of removable dental structure, specific care rules may be provided. The orthopedic dentist who installed the prosthesis tells the patient about them.