Palate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that forms from the mucous membrane of the hard and soft palate. This is a fairly rare disease. It is more common between the ages of 40 and 60 years. Men get sick 4 times more often than women.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern research methods. The oncology clinic is equipped with modern equipment from leading American and European manufacturers, which allows you to quickly establish an accurate diagnosis. To treat malignant tumors of the palate, surgical interventions, chemotherapy drugs and innovative methods of radiation therapy are used.
The most malignant tumor of the palate occurs due to metastases of cancer of the nasopharynx and nose. The neoplasm affects the periosteum of the hard palate, lower and upper jaws, muscles and tissue of the oral cavity, and tongue. Atypical cells spread to the submandibular, mental and cervical lymph nodes.
Classification of palate cancer
Based on location, cancerous tumors are divided into 2 types of malignant tumors of the palate. In case of cancer of the hard palate, the malignant neoplasm is located at the border of the nasopharynx and the oral cavity, affects the bone structures and spreads to all layers of the oral mucosa. In the case of cancer of the soft palate, the tumor is localized in the mucous layer and muscles of the vault of the oral cavity.
Based on the histological structure of the tumor, there are 3 types of malignant neoplasms of the palate:
- Cylinder;
- Adenocarcinoma;
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
Cylindroma (adenocystic carcinoma) is formed from glandular tissue. It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of pathologically altered cells and quickly metastasizes. Adenocarcinoma develops from the epithelium of the oral cavity. The tumor can be localized in all parts of the hard and soft palate. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of oral malignancy. The tumor affects the mucous membrane.
Possible dental diseases
In 90% of cases, swelling of the soft tissues around the tooth appears with the development of periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis or an abscess. Other possible causes are extremely rare.
Periodontitis
With the development of periodontitis, the inflammatory process affects the bone tissue of the jaw. The cause of the pathology is the penetration of infection of the dental root canals and its spread. Swelling of soft tissues during periodontitis is caused by the accumulation of pus. If left untreated, pus may be released through the resulting fistula. The swelling subsides during this period, but the inflammation cannot be eliminated on its own. Treatment is mandatory.
Gingivitis
A distinctive feature of gingivitis from periodontitis is the development of an infectious and inflammatory process in the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. Swelling of the gums with gingivitis mainly occurs during the period of exacerbation. The swelling of the gums can be so severe that the tissue covers the tooth.
Periodontitis
The development of periodontitis occurs against the background of advanced periodontitis. Lack of treatment provokes a purulent process with a localized abscess area. With a periodontal abscess, a cavity forms under the gum in which pus accumulates. Externally, in addition to edema, a pronounced swelling in the form of a semicircle up to 1–2 cm in size appears on the soft tissue. Treatment is carried out surgically.
Causes and risk factors for palate cancer
Malignant tumors of the oral cavity occur under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Irritating effects of aggressive substances contained in cigarettes, alcohol, smoking mixtures;
- Constant consumption of too hot dishes, which burn the mucous layer and change the structure of cells;
- Chronic injury to the palate due to poorly installed dentures.
A tumor in the palate develops against the background of precancerous conditions of the oral cavity - leukoplakia, papillomatosis. They often degenerate into a cancerous tumor under the influence of provoking factors.
Risk factors for the development of malignant neoplasms of the palate include hereditary predisposition, periodic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, vitamin A deficiency, which occurs with poor nutrition or in smokers due to a disruption in the process of its absorption in the body. Palate cancer can be a secondary disease - metastases of malignant neoplasms of the neck and head.
The first signs and symptoms of palate cancer
During the first weeks and months, malignant neoplasms may occur without subjective sensations. In some cases, patients, when touching the palate area with their tongue, notice a small compaction that is surrounded by a cushion. If the patient consults a doctor at this stage of the pathological process, treatment is most effective.
As the cancer progresses, the size of the tumor increases. The tumor invades new areas of the palate and grows deeper. Patients present the following complaints:
- Pain in the oral cavity, which radiates to the ear, temporal region of the head;
- Discomfort while eating, as the process of chewing and swallowing becomes difficult;
- Bad breath;
- Unpleasant taste;
- The change in speech articulation is disrupted due to the fact that the mobility of the tongue changes, and the tumor interferes with the normal movement of air.
- Poor appetite;
- Noticeable weight loss;
- Rapid, unreasonable fatigue.
When examining the oral cavity, plaques, compactions, and ulcers of various shapes and sizes can be seen on the roof of the mouth. In advanced cases of palate cancer, the ulcers bleed and the septum between the nose and throat may collapse. For this reason, pieces of food get into the nose while eating, and speech becomes completely slurred. At the last stage, the cancer tumor destroys all tissue adjacent to the palate.
Why does the mucous membrane of the throat swell?
Mechanical damage
Swelling of the throat mucosa due to injury is observed when damaged by hard objects, pieces of food, or fish bones.
Small foreign bodies can get stuck between the ridges, arches, and tonsils in the posterior parts of the oropharynx. The patient complains of severe local pain, soreness, and the sensation of a foreign object. Upon examination, swelling and hyperemia of the affected area are revealed. With deeply located foreign bodies, there are no obvious visual changes. If the object is located in the hypopharynx, suffocation is possible. Thermal burns of the pharyngeal mucosa are usually superficial. They develop when eating too hot food or inhaling hot steam during inhalation. There is a burning sensation that intensifies when swallowing. Chemical injuries to the throat vary in severity and are accompanied by severe pain and the formation of white or gray scabs. In addition, swelling is observed after operations in the area of the oropharynx and hypopharynx.
Infectious diseases
Acute infections are one of the most common causes of swelling of the throat mucosa. The symptom is detected in the following pathologies:
- ARVI and influenza.
Swelling is insignificant, appears in the initial stages of the disease, is combined with moderate hyperemia, weakness, weakness, fever, and muscle pain. - Measles.
The sign is more pronounced in children, complemented by hyperemia and granularity of the pharynx. Occurs simultaneously with fever. After 3-5 days, the condition improves and a rash appears on the body. - Typhus and typhoid fever.
Not only the throat swells, but also the neck and lower part of the face. Peculiar hemorrhages into the mucous membrane are possible. Significant hyperthermia, severe intoxication, and rash are observed. The condition is serious. - Scarlet fever.
The throat is swollen, bright red (“flaming throat”), areas of necrotic, fibrinous or mucopurulent plaque may form. The cervical lymph nodes become enlarged, and a pinpoint rash appears on the body. - Diphtheria.
Against the background of swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa, a typical plaque forms on the tonsils. In severe cases, plaque spreads to the oropharynx and is combined with swelling of the subcutaneous tissue above the enlarged cervical lymph nodes. In the toxic form, swelling of the throat is so severe that it interferes with breathing.
Swelling and other signs of inflammatory damage to the throat mucosa, reminiscent of local symptoms of ARVI, can be detected at the initial stage of hepatitis A, secondary syphilis, and tuberculosis. There are also signs of intoxication, skin rashes, muscle and joint pain, and other symptoms.
Inflammatory ENT pathologies
Swelling of the mucous membrane is accompanied by the most common acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the pharynx and larynx:
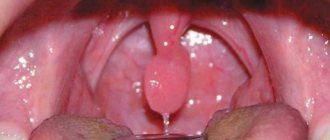
- Tonsillitis.
Swelling and hyperemia of the tonsils, posterior wall of the pharynx, soft and hard palate are determined. Local surface films, loose plaque or purulent foci are formed on the tonsils, reminiscent of a “starry sky” picture. Body temperature is increased. Chronic tonsillitis is manifested by repeated exacerbations, which occur with more sparse symptoms than acute tonsillitis. - Pharyngitis.
In the acute form of the disease, the swelling spreads throughout the entire pharynx; in the chronic form, it covers its upper, middle or lower part. Redness appears. The general condition suffers slightly or remains satisfactory. - Laryngitis.
Swelling of the mucous membrane is localized in the lower parts of the throat and is not visually detectable. There is soreness, scratching, tickling, burning, dry, convulsive cough, and hoarseness. After a few days the cough becomes wet. In chronic laryngitis, the symptoms are smoothed out, the disease proceeds in waves.
Swelling of the throat mucosa
Purulent complications of ENT diseases
Unlike uncomplicated otolaryngological pathologies, which are characterized by diffuse symmetrical damage to the structures of the throat, with purulent complications the symptoms are more often expressed on one side. Upon examination, a local focus is determined; the prevalence of edema depends on the severity of the process. Swelling of the throat is accompanied by the following pathological conditions:
- Peritonsillar abscess.
There is sharp unilateral pain when swallowing; in 10% of cases, bilateral damage is detected. The swelling quickly increases, the pain becomes tearing and radiates to the ear. Due to swelling and accumulation of pus, the tonsil and uvula may deviate to the side. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
Symptoms are determined by location. Along with swelling and sore throat, when the abscess is located in the upper parts of the pharynx, nasal breathing is disrupted. Abscesses of the middle and lower sections are accompanied by hoarseness, deepening of the voice, difficulty breathing, and sometimes suffocation. - Intratonsil abscess
. It is more often observed in adults suffering from chronic tonsillitis and severe somatic diseases. One tonsil becomes sharply painful, enlarges, and takes on a spherical appearance. With cold abscesses due to leukemia, there is no intense pain. - Abscess of the root of the tongue.
Swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa occurs secondarily and is a reaction to the presence of an abscess in nearby tissues. Severe pain, hyperemia in the root zone, and enlarged tongue prevail. - Abscess of the epiglottis.
Severe pain in the lower part of the throat, foreign body sensation, difficulty breathing, and nasal voice predominate. The area of maximum edema is located in the larynx.
In patients with Ludwig's angina, the inflammation is diffuse, beginning in the submandibular space and moving to the floor of the mouth. From there, the swelling spreads to the pharynx, which is accompanied by difficulty swallowing. When the larynx is involved, the voice changes or disappears. Another type of diffuse purulent inflammation is phlegmonous laryngitis. Maximum swelling and pain are observed in the larynx area, loss of speech and acute stenosis of the larynx are possible.
Allergic reactions
Swelling of the throat mucosa is accompanied by many allergic reactions. The symptom appears suddenly, combined with a sore throat, nasal congestion, sneezing, watery eyes, and itchy skin. The most common cause is contact with plant pollen, animals or house dust. This manifestation is especially pronounced in Quincke's edema, which is complemented by swelling of the face and other parts of the body, speech impairment, and wheezing stridor.
Tumors
With benign tumors of the pharynx, the symptom appears in case of trauma to the formations. Pharynx cancer is accompanied by tissue swelling during the disintegration of neoplasia and the development of inflammation of surrounding tissues. Swelling of the mucous membrane of the larynx and pharynx can occur during radiotherapy of the neck organs for oncological lesions of the larynx, pharynx, thyroid gland, and other anatomical formations of this area.
Other reasons
Due to reactive inflammation against the background of reflux of gastric contents, swelling of the throat can be observed with gastroesophageal reflux disease. The symptom is especially often detected in cases of prolonged course of the disease with the development of laryngitis, GERD during pregnancy.
Swelling, soreness, and hyperemia of the throat are typical for some acute poisonings affecting the respiratory system, including berylliosis and toxic pulmonary edema. The symptom appears at the initial stage, then manifestations from the bronchopulmonary system, myalgia, and hyperthermia are added.
Diagnosis of cancer of the soft and hard palate
The resulting cancerous tumor of the palate is difficult to determine independently in the early stages. If the pathological process has affected large areas of the soft or hard palate, a preliminary diagnosis can be made after a visual examination of the oral cavity.
To confirm the diagnosis, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform the following diagnostic procedures:
- X-ray – finds pathological changes in bone tissues adjacent to the oral cavity;
- Biopsy – taking a piece of tissue for histological examination (analysis is necessary to identify altered tumor cells and its type);
- Blood tests - signs of anemia;
- Radioisotope examination - allows you to examine the structure of the neoplasm.
Ultrasound examination is carried out to detect cancer metastases in distant organs. Patients of the Yusupov Hospital can undergo complex diagnostic procedures in partner clinics and receive advice from leading dental oncologists in Moscow.
Treatment of palate cancer
The choice of treatment method for cancer of the hard and soft palate depends on the histological type and stage of the malignant tumor, the extent of the pathological process to nearby tissues. The main method of treating the disease is irradiation of a malignant neoplasm of the palate with X-rays. Radiation therapy can stop the development of cancer cells. If it is started at an early stage, complete destruction of the malignant neoplasm is possible. Radiation is performed before and after surgery.
Surgery for palate cancer involves removing the tumor and the soft tissue and bones located next to it. After surgery, a defect remains on the face, to eliminate which plastic surgery is performed. In advanced cases of cancer, surgery and radiation therapy sessions are performed.
For palate cancer, treatment is carried out with cytostatic drugs. They are administered as droppers or prescribed for oral administration. Chemotherapy for cancer of the soft and hard palate is effective in combination with radiation and surgery. The action of chemotherapeutic drugs is aimed at preventing and eliminating metastatic foci.
Timely diagnosis and selection of a well-designed treatment regimen allow doctors at the oncology clinic to achieve an almost complete cure for 80% of patients. If you experience unpleasant sensations in the oral cavity, contact oncologists and make an appointment by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Prevention
As preventative measures, as well as after an attack, it is recommended:
- strengthen immunity;
- perform moderate physical activity;
- use halotherapy and climatotherapy (stay at sea and in the mountains);
- use air purifiers;
- adhere to a diet excluding highly allergenic foods and products containing preservatives and chemical additives.
If you are concerned about breathing problems of any kind, we are always ready to provide assistance, make the correct diagnosis and begin treatment immediately. Call and make an appointment at the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic!