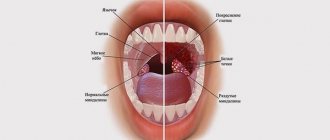
How does uvulitis manifest?
Most often, swelling of the uvula develops suddenly, sometimes even for no apparent reason. You need to react as quickly as possible to prevent complications from developing. Indeed, sometimes the swelling spreads further and leads to asphyxia, that is, a condition when a person cannot breathe. You can tell that the uvula is swollen by the following signs:
- having problems swallowing solid or liquid food;
- a person experiences a sensation of a lump or foreign body in the throat;
- it becomes difficult for him to speak or pronounce individual sounds;
- possible feeling of sore throat;
- saliva production increases;
- false urge to vomit appears;
- and finally, the person begins to suffocate due to lack of air.
If the swelling is minor, the symptoms will be mild. And, conversely, as the disease progresses, it will become increasingly easier for a person to replace its manifestations.
Treatment of uvulitis at home: symptoms, inhalations, antibiotics and medications
Uvulitis is an acute inflammation of the tongue in the throat. The tongue is located in the back of the soft palate, and under normal conditions a person cannot feel it.
The disease occurs suddenly and very acutely, accompanied by pain, especially when swallowing. The patient has difficulty breathing, there is a feeling that there is something in the throat that prevents him from swallowing, like a foreign body.
Coughing only worsens the patient's condition. Against this background, dysphonia and pain in the tongue develop.
Uvulitis is a very unpleasant disease. Most often this occurs after tonsillitis or adenotomy.
The tongue is the last extension of the soft palate, located in the yawning cavity above the root of the tongue. Not only is it a sequel, but the entire soft palate is set on fire. The tongue is rich in blood vessels, so various inflammatory and infectious processes often occur in this part of the throat.
The celestial tongue has a number of important functions:
- provides the correct structure of speech sounds
- produces a cough and gag reflex
- prevents foreign bodies from entering the throat
- separates air flows and gives them direction
- heats the air
Causes of inflammation
Usually the soft palate and tongue are not felt. However, when inflammation occurs, the tongue becomes red, swollen and causes severe pain.
People with tonsils removed are predisposed to pathology.
Uvulitis is believed to be the result of disruption of the venous plexus located in the tongue. This phenomenon can also be caused by vascular ruptures or infections in the mouth.
This happens in the following cases:
- consumption of cold drinks
- hot liquid or food that causes a non-allergic reaction to burn
- chronic angina
- tongue injury caused by severe coughing or sudden sneezing in the nasopharynx
Symptoms of the disease
The disease develops very quickly. At the initial stage, the symptoms of uvulitis are not pronounced. Breathing is not impaired, there is a feeling of a coma in the throat, a change in voice, swallowing and speech disorders. The tongue becomes larger and swells a little.
Moderate to severe uvulitis has more pronounced symptoms:
- dysphonia (voice disorder)
- false vomiting
- increase in body temperature
- hypersalivation (increased salivation)
- Swelling and tender soft palate
- Painful swallowing syndrome
- Feeling of perforation in the throat
The most common signs of uvulitis are observed in the morning, after sleep. The first step is a thorough oral examination. If the tongue becomes bright red and enlarged, then most likely the cause of the discomfort is uvulitis.
If the tongue has increased several times and reached the tongue, then the lumen of the nasopharynx can be completely closed. This can lead to asphyxia and death, so the patient should be treated immediately in this situation.
Particular caution should be exercised in the presence of this disease in young children, since all processes in the body occur much faster in them, so it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnostic features
If the diagnosis requires clarification, the following procedures must be performed:
- Do a clinical blood test. This procedure helps determine the type of infection (viral or bacterial) and the presence of infection in the body. If the disease is contagious, the number of white blood cells increases. If the disease is allergic, then the number of eosinophils increases.
- bacteria from the throat to determine the microflora that caused inflammation of the tongue. The analysis will help determine the type of pathogen and its susceptibility to the main types of antibiotics.
- If an allergy is suspected, allergy tests should be performed.
- Conduct a histological examination of tongue tissue, x-rays and computed tomography to exclude oncology.
Basic treatment methods
First you need to determine the cause of the disease, and then prescribe medications. Therapy should be comprehensive to eliminate symptoms, eliminate discomfort and promptly improve the patient’s condition.
The following recommendations should be followed:
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Regular wet cleaning
- Ventilation of premises
- Air humidification
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Use separate dishes
- Follow a diet, namely, exclude foods that irritate the throat
- Quit smoking and alcohol
Ear, nose and throat specialists treat this condition. If the disease is caused by bacteria, antibiotic therapy is necessary.
Local treatment helps relieve swelling and reduce sore throat. Antiseptic sprays (dernat, kameton, ingalipt) can be used for medical purposes, and rinsing the throat can also be done using a decoction of herbs or a soda solution (1 hour of soda per glass of water).
Antibiotics should be prescribed individually after bacterial test results are available. Antibiotics from macrolides, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones. The most common solutions are azithromycin, moxifloxacin, and ceftazidime.
- Allergic uvulitis is treated with antihistamines (loratodine, cytirizine, rainbow, cetrin), diuretics (mannitol, uregid, furosemide) and glucocorticosteroids for the treatment of respiratory diseases (diprofos, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone).
- The speed of recovery depends on the body's immune system, so it is important to eat a good diet, drink plenty of fluids, take vitamin supplements and pay special attention to vitamin C.
- Surgical interventions are possible only with the development of paratoncillus swallowing abscess and with purulent inflammation in diseases of the dental system.
Solutions for inhalation
One of the most effective therapeutic methods is therapeutic inhalations. It is necessary to prepare a decoction based on thyme, eucalyptus oil and pine buds. Pour 20 grams of buds into a glass of water and boil for 30 minutes.
Then mix 10 grams of thyme with a glass of boiling water and let it boil for 40 minutes. Combine boiling and infusion in a container and add 20 grams of eucalyptus oil.
Place the resulting product in a nebulizer and inhale it at home.
Inhalation edema is also well removed with vasoconstrictor drugs.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of disease
The most commonly used mouthwash is:
- raspberry leaves. Pour boiling water over it and leave for 30 minutes:
- onion peel. Pour 700 ml of boiling water per 1 tablespoon of peel. Leave for about 4 hours.
- Viburnum dried fruit. Pour 1 liter of water per 50 g of fruit and boil for 30 minutes in a bain marie
- garlic infusion. Grind 100 g of garlic and add 150 ml of boiled water. Insist on 5 hours.
Disease prevention
The most important thing is to always treat diseases of the ENT organs in a timely manner. Eliminate all mechanical damage to the oral cavity and, of course, pay attention to oral hygiene. Self-medication is dangerous because it can be fatal.
Most common reasons
There are many reasons why the uvula is swollen. Most often these are not serious illnesses or infections. However, other, rather dangerous options are also possible. Most often, swelling of the uvula is caused by:
- inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx, nasopharynx, mouth, nose or paranasal sinuses;
- injury or irritation;
- allergic reactions;
- burnt by alkalis, acids or other chemical compounds;
- taking certain medications;
- burnt by alcoholic drinks;
- the presence of a tumor in the nasopharynx;
- heredity.
Only a doctor can establish a reliable cause after a thorough examination and examination. Laboratory and instrumental studies help make the correct diagnosis.
Inflammation as a cause of swelling
In most cases, the uvula in the throat is sore and swollen due to inflammation caused by viruses or bacteria. The infectious process develops in the tonsils, nose or throat, then gradually spreads to the uvula, causing swelling and inflammation.
- Sore throat (or tonsillitis) - a streptococcal infection spreads quite quickly to the uvula due to its close location to the tonsils.
- Rhinitis (runny nose) - an infectious process descending into the nasopharynx, and from there to the soft palate.
- Laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia - inflammation of the airways can also cause swelling.
- Caries, periodontitis or other dental diseases.
- Sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis - bacteria that cause the development of infection easily spread to the mucous membrane of the pharynx and soft palate.
Treatment in this case should be aimed at combating the underlying disease. First of all, etiological therapy will be required to help get rid of the cause of the disease. If the inflammation was caused by bacteria, it is necessary to select the most suitable antibiotic. In case of viral infection, antiviral agents and immunomodulators are indicated.
Naturally, carious teeth must be treated immediately by a dentist. And inflammation of the paranasal sinuses requires an urgent visit to an ENT doctor and serious treatment.
What medications are used to treat an inflamed uvula?
When an inflamed tongue swells in the throat, the choice of medications is approached with great caution due to the high risk of complications of the respiratory system. All medicinal tactics are aimed at reducing swelling and relieving inflammation of the uvula.
Complex therapeutic tactics include the use of:
- antiallergic drugs - antihistamines (Lordestin) and glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Triamcinolone);
- decongestant diuretics – Torasemide SZ, Hypothiazide, Furosemide. These medications are considered first aid and prevent the development of asphyxia.
- If the upper uvula is swollen after drinking alcohol, in order to stabilize the condition, Diazolin, Zyrtec or Aleron are prescribed and subsequent alcohol intake is completely avoided.
- When diagnosing a viral or bacterial infection that provoked inflammation of the uvula, antibiotics (Azithromycin, Amoxiclav) or antiviral drugs (Cycloferon, Remantadine, Arbidol) are prescribed.
Complex therapy also includes:
- treatment of the larynx with antiseptic sprays - Hexoral, Kameton;
- taking vitamin complexes (Vitrum, Multi-Tabs and immunomodulators (Immunity, Zdorov).
All medications are taken in a course, in accordance with the doctor’s prescription and under his supervision.
Treatment of respiratory system diseases
There is no doubt that influenza or pneumonia must be treated in a hospital setting. However, a common cold that causes the uvula to swell can be safely treated at home after a visit to the doctor. It is important to follow simple recommendations - and the disease will pass quite quickly.
Drinking regime
In case of ARVI, sore throat or other inflammation, you need to drink as much fluid as possible, because it removes toxic substances formed during metabolism. It is best to drink freshly squeezed juices, decoctions, and herbal teas. They help relieve intoxication and alleviate the patient's condition. Teas are best prepared from chamomile, mint, elecampane, and rose hips.
Vitamins to boost immunity
During illness, you need to eat more citrus fruits - they serve as a source of vitamin C. You should also include other vegetables and fruits in your diet. The vitamins and minerals contained in them will help strengthen the immune system.
It is best to drink tea with raspberries - among other things, they are a natural probiotic, which makes them good for the immune system. You shouldn’t give up kefir, cottage cheese, and yogurt. It is advisable to eat onions and garlic, because they are wonderful immunomodulators.
Injuries and minor damage
Ingestion of rough food, mechanical trauma or other causes can cause irritation and damage to the mucous membrane of the uvula. As a result, inflammation gradually develops in it. In the future, infection may occur. After all, microbes can easily penetrate through the damaged cover.
If the uvula is swollen for this reason, all negative factors that can lead to injury should be excluded. First of all, you need to give up crackers, very hot or cold foods - they are the most harmful in this condition.
Functions of the uvula: what is the essence of the problem?
The uvula is a distant process that is located in the mouth, on the edge of the soft part of the palate, slightly above the tongue, in a healthy state it is small in size and color, identical to the oral mucosa.
It performs important functions for the body:
- protects the nasopharynx from food entering during swallowing movements;
- separates air flows and warms them;
- is a barrier to infection;
- prevents accidental regurgitation of food;
- provokes a throat spasm, preventing a person from choking;
- participates in the formation of some sounds;
- if necessary, provokes vomiting.
When listing the functions of the uvula, it becomes clear why you need to monitor its condition. Inflammation of this organ leads to a failure in the coordinated functioning of the swallowing, respiratory, protective, resonator, and speech systems and makes the entire body vulnerable.
Allergic diseases
If the uvula is swollen for no apparent reason and there are no signs of inflammation, such as fever, wet cough or runny nose, the cause is most likely an allergy. An allergic reaction can be caused by foods with high sensitizing activity (citrus fruits, honey, nuts, eggs), household allergens or certain medications.
Angioedema, a disease characterized by asymmetric swelling of any part of the body, may also be the cause. The most dangerous lesion is the larynx. Most often, angioedema is caused by the following factors:
- insect bites, such as bees;
- pollen of some plants;
- household allergens;
- mites living in house dust;
- chocolate, eggs or other food products;
- medications;
- alcoholic drinks;
- hypothermia or prolonged exposure to the sun.
If the uvula is swollen for one of these reasons, the necessary measures should be taken immediately. It is necessary to eliminate the effect of the provoking factor as quickly as possible. For example, you need to move away from a flowering plant. If it is a food allergy, you need to rinse your stomach immediately.
You should go to the hospital as soon as possible, because laryngeal edema may develop. In this case, the person may die from asphyxia. A sick person can also take a hyposensitizing drug (Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratadine, Claritin or others). Perhaps these remedies will help completely relieve swelling. However, you need to see a doctor in any case.
The essence of pathology
- The uvula is a part of the soft palate, a conical process that performs the following functions:
- – protects the mucous membranes of the pharynx from exposure to cold air;
- – prevents the penetration of pathogenic bacteria;
- – when the need arises, pressing on the palatal tongue provokes a gag reflex;
- – takes over and distributes air and food flows.
Under the influence of external irritating factors (allergens, bacteria, mechanical and thermal damage), the body reacts when this organ increases to such a size that a person’s life is threatened. The process when the uvula becomes inflamed is diagnosed as the development of the disease uvulitis.
Swelling of the uvula contributes to the development of severe complications associated with the functions of breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
Symptoms
- Signs that the tongue in the throat has enlarged are pronounced, manifested in the form of:
- – active secretion of saliva;
- – wheezing and hoarseness;
- – pain (increases during swallowing and talking).
- Swelling of the tongue in the throat, provoked by an allergic reaction, manifests itself in the form of:
- – debilitating cough or sneezing;
- – tearing;
- – sensations of constant tickling of the root of the tongue;
- – a rash may appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
- When your throat hurts and your tongue is swollen due to an infection, the pathology manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- – feeling of weakness;
- – chills or fever;
- – discomfort and pain when swallowing and speaking;
- – sensations of dry mucous membranes of the throat;
- – possible purulent lesions of the oral mucosa.
Causes of pathology
- The causes of swelling of the uvula are varied.
Inflammation can be caused by: - – diseases of an inflammatory nature (the process is activated when the human immune system is unable to fight a large number of bacteria in the growth cavity);
- – chemical, mechanical and thermal damage to mucous membranes;
- – uvulitis as a reaction to contact with an allergen;
- - formations localized in the nasopharynx.
Allergic uvulitis
Prolonged contact with household, chemical, and food allergens is one of the causes of a swollen tongue in the throat. Most often, edema is diagnosed in severe allergic reactions: Quincke's edema or urticaria.
Important: when the first symptoms of an allergy appear, the patient must be immediately taken to a doctor.
Allergies can also cause swelling of the uvula in the throat in asthmatics. Long-term use of medications may cause allergic swelling of the tongue in the throat. Swelling caused by an allergy to medications develops immediately after injections or use of the medicine.
The cause of uvulitis can be an allergy to certain foods: honey, chocolate, citrus fruits. Important: before taking any action to eliminate the swelling of the tongue in the throat, it is important to establish why it is swollen and what (what allergen) causes the disease.
Getting burned
One of the reasons why a small tongue in the throat may swell is a burn. A person swallows large pieces of hot food or suddenly drinks hot liquid, as a result of which blood actively rushes to the tongue and swelling develops. The patient feels very unpleasant pain.
A burn to the mucous membrane and swelling of the tongue in the throat can cause solutions of alkalis or acids to enter the oral cavity. For example, swelling can be caused by rinsing with a strong soda solution or accidentally swallowing vinegar.
Complication of sore throat
Inflammation of the small uvula in the throat as a complication of sore throat is a dangerous condition. Swelling causes the following symptoms:
- - cardiopalmus;
- – difficulty breathing, swallowing and speaking;
- – pain in the throat and ears;
- – wheezing, cough;
- – blue discoloration of the skin (a sign of lack of oxygen).
Ignoring these signs or delaying medical care can cause asphyxia. It is necessary to eliminate swelling in severe sore throat as quickly as possible.
Infectious lesion
Penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the nasopharynx area can provoke inflammation of the uvula in the throat.
The most common cause of swelling of the tongue in the throat is infection:
- Staphylococcus aureus. Provokes a severe inflammatory process of purulent uvulitis. It is difficult to treat with antiseptics and antibiotics.
- Streptococcus. Provokes the development of a mild, sluggish form of uvulitis.
- Herpes virus. Affects the entire body with pathogenic elements. Inflammation of the uvula in the throat is most often provoked by Epstein-Barr infections and cytomegalovirus.
- Chlamydia, gonococci and other pathogenic structures. It provokes uvulitis if there has been sexual intercourse in the recent past.
- Human papillomavirus. More than 500 strains of this virus are known, most of which provoke not just swelling of inflammation, but malignant formations.
Most often, swelling of the uvula is a consequence of damage to the body by infectious diseases, a signal of weakened immunity. As soon as the body's defenses weaken, infections affect the oral cavity, throat (palatal tongue), and provoke an inflammatory process.
Excessive alcohol consumption and frequent smoking
The palatine tongue is covered with multiple small blood vessels, which, irritated by tobacco smoke during active smoking and alcohol due to excessive consumption of alcohol, become inflamed.
Also, abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products reduces the body's resistance to pathogenic bacteria and can cause burns.
What is the danger?
The uvula protects the respiratory organs from food particles entering them, distributes warm air, activates processes provoked by the gag or cough reflex, and participates in spoken speech.
Acute processes of inflammation of the uvula affect the surrounding soft tissues of the oral cavity, which is not just accompanied by unpleasant sensations, but sharply worsens the general physical condition of the patient and provokes breath holding.
Ignoring the pronounced symptoms of the disease can cause asphyxia.
- Swelling of the throat and tongue can provoke a number of negative changes in the body:
- – difficulties in speaking;
- – clogging of the respiratory system with food particles (this case requires an immediate response and can lead to respiratory arrest);
- – damage by infections and bacteria to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- – constant unpleasant feeling of nausea, gag reflex;
- - inflammation of both tonsils.
- Important: swelling of the nasopharynx and palatal tongue is life-threatening and therefore requires prompt medical attention.
Diagnostics
- An ENT specialist conducts diagnostics and determines treatment options (and, if necessary, surgery).
- During the appointment, the ENT doctor:
- Examines the oral cavity for the presence of pathological structure and the presence of foreign objects.
- Collects the patient's medical history.
- Clarifies the location of the pain, the intensity and nature of the pain, the severity of the symptoms.
The doctor can confirm the suspected diagnosis based on the results of the following studies:
- Laboratory blood test.
- Bacterial blood test.
- Immunogram (helps determine the presence of allergies).
- Histological examination of the mucous membranes and tissues of the uvula (recommended if cancer is suspected).
Drug treatment
Only an ENT doctor can determine how to treat pathological processes in the throat. This is due to the high risk of side effects on the respiratory system when taking incorrectly selected medications.
Antihistamines
Treatment of uvulitis caused by an allergic reaction involves eliminating contact with the allergen and taking certain medicinal antihistamines. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following medications: Claritin, Diazolin, Fexofenadine, Suprastin.
- The tongue in the throat can swell under the influence of various allergens, therefore only after the type of allergen has been determined can one decide what to do next.
- Important: in case of severe allergic reactions (for example, angioedema), the doctor may decide to perform a tracheotomy procedure.
Diuretics
Taking diuretics (water medications) helps relieve swelling of the small tongue in the throat. The patient is prescribed: Veroshpiron, Chlorthalidone, Furosemide.
Glucocorticosteroid drugs
Taking glucocorticosteroid drugs: Betamethasone, Hydrocortisone will help prevent the development of breathing and swallowing complications with an enlarged tongue in the throat. These medications contain an anti-inflammatory component, which reduces capillary permeability and stops the development of edema.
Taking antibiotics
The situation when the tongue in the throat has enlarged due to bacterial infection requires taking antibacterial agents: Azithromycin, Timentin, Vilprafen.
Important: antibacterial drugs are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor. Only a specialist can determine exactly the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process and prescribe an antibiotic that is sensitive to this bacterium.
Therapy using traditional recipes
The use of traditional medicine in combination with traditional medications helps speed up the healing process if the tongue in the throat is swollen.
Important: traditional medicine must be taken strictly in combination with the dosage calculated by the doctor.
Herbal decoctions
To quickly relieve inflammation of the tongue in the throat at home, gargling with medicinal herbs will help reduce pain:
- Raspberry decoction. For a liter of water you need two tablespoons of dry raspberry leaves. The raw materials are steamed and left to simmer on the stove for twenty minutes. The prepared broth is cooled, filtered and used as directed at least three times a day.
- Chamomile and sage decoction. To prepare a decoction, you need to take one tablespoon of dry herbs per liter of water. The broth is brewed and left to brew for at least fifteen minutes. After the broth has cooled, filter it and gargle at least three times a day.
- Viburnum decoction. A spoonful of dry berries is poured with boiling water (one liter) and simmered over low heat for half an hour. Afterwards, gargle with a lukewarm decoction. This remedy is good for removing ulcers on the tongue.
Important: before using medicinal plants, you should consult your doctor about possible allergic reactions.
Inhalations
- Carrying out the inhalation procedure will speed up the treatment of laryngeal edema, swollen tongue in the throat, and inflamed tonsils.
- Recipe for decoction for medicinal inhalations:
Mix two tablespoons of pine buds with water. Boil the mixture for half an hour. Separately, boil the dry thyme leaves. Mix the resulting decoctions in a bowl and add a few drops of eucalyptus oil.
Medicinal tinctures
Medicinal tinctures will help to quickly cleanse the mucous membranes of the mouth from pathogenic microorganisms and relieve swelling of the tongue in the throat. Also, taking tinctures is indicated for the purpose of quickly removing toxins from the body and improving the general condition of the patient.
Recipes for the most effective medicinal tinctures:
- Rosehip tincture. Place a few tablespoons of dried rose hips in a thermos and pour half a liter of boiling water. The thermos is tightly closed and left to infuse for at least twelve hours. The tincture is drunk in small sips throughout the day.
- Anise tincture. In a bowl, combine half a glass of crushed anise and water. The mixture is heated and boiled for several minutes. Then add two tablespoons of honey and the same amount of cognac. Infuse the resulting product for twenty-four hours. Afterwards, the tincture is taken one tablespoon, several times a day, before meals.
In combination with traditional drug therapy, taking herbal tinctures can speed up the process of treating an inflamed tongue in the throat.
Preventive recommendations
- The following preventive measures will help prevent inflammation of the tongue in the throat:
- – timely diagnosis and high-quality treatment of ENT pathologies and infections of the mucous membranes of the growth cavity;
- – careful and regular oral hygiene;
- – health control and prevention of injury to the mucous membranes of the growth cavity;
- – giving up bad habits: alcohol and smoking.
Important: if symptoms of uvulitis appear, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. Errors in treatment actions taken can aggravate the course of the pathological process and provoke complications.
Chemical burn
It is very easy to understand that the uvula is swollen due to a chemical burn. This is supported by the consumption of alcohol, any new, unfamiliar drinks or unusual food the day before. In this case, the tongue becomes red, it hurts, there is a burning sensation and discomfort in the throat. It is very difficult to swallow any food.
In this case, it is best to consult a doctor - he will prescribe treatment or the necessary antidote. Usually, if the burn is caused by acid, the mucous membrane is washed with an alkaline solution. And, conversely, the best antidote for an alkali burn is acid.