What is local anesthesia
The main distinguishing feature of local anesthesia is that the person remains conscious during its effect. This type of anesthesia acts on receptors that are located below chest level. In addition to complete anesthesia, local anesthesia eliminates other tactile sensations, including temperature, pressure on tissue, or stretching.
Local anesthesia is possible in the following areas:
- on the surface of the mucous membranes of various organs - trachea, larynx, bladder, bronchi, and so on;
- in the thickness of tissue - bone, muscle or soft;
- in the direction of the nerve root extending beyond the boundaries of the spinal cord membrane.
- in impulse-conducting nerve cells of the spinal cord.
The main goal of local anesthesia is to block the occurrence of impulses and their transmission while maintaining consciousness.
Why is general anesthesia recommended?
Many years of clinical experience are aimed at achieving maximum comfort and safety of procedures. We use the latest anesthesia technologies and drugs that were developed and used not only for cosmetic surgery. They are designed for a smooth course of anesthesia and quick awakening. During this restful sleep you will feel absolutely nothing. This will allow the doctor to be completely focused on the operation. For surgeries lasting more than an hour, our anesthesia requires fewer medications. It is also characterized by rapid awakening and absence of nausea.
Types of local anesthesia
In medicine, there are the following types of anesthesia, differing in some characteristics and scope of application:
- terminal;
- infiltration;
- regional;
- intravascular.
Each type has a list of indications and contraindications that must be taken into account when conducting them.
Terminal anesthesia
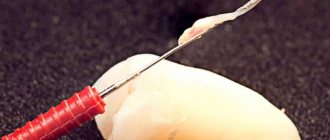
This type is also known as topical or surface anesthesia. The main areas of application are dentistry, gastroenterology and proctology. Terminal local anesthesia (anesthesia) differs from other types in the method of administration: anesthetics in the form of a spray, gel or ointment are applied to the surface of the skin or mucous membranes.
In proctology, local anesthetic gels and sprays (Katetdzhel, Lidochlor, Lidocaine, etc.) are used during proctological examinations and diagnostic procedures: rectal examination, anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy. The examination becomes virtually painless. Also, local anesthesia in proctologists is used during certain medical procedures: latex ligation of hemorrhoids, sclerotherapy of hemorrhoids, infrared coagulation of internal hemorrhoids, as well as biopsy from the rectum.
Infiltration anesthesia
It is used in dentistry and surgery, and involves the introduction of special solutions into soft tissues. The result of the procedure, in addition to a pronounced anesthetic effect, is an increase in pressure in the tissues, and, as a result, a narrowing of the blood vessels in them.
Regional anesthesia
This type involves the introduction of an anesthetic near large nerve fibers and their plexuses, resulting in pain relief in localized areas. It is divided into the following types of local anesthesia:
- conduction, with the introduction of drugs near the trunk of a peripheral nerve or nerve plexus;
- spinal, with the introduction of drugs into the space between the membranes of the spinal cord and “turns off” pain receptors over a large area of the body;
- epidural anesthesia, with the introduction of drugs into the space between the spinal cord and the walls of the spinal canal through a special catheter.
Intravascular anesthesia
It is used mainly for surgical interventions on the extremities. Administration of drugs is possible only with the application of a hemostatic tourniquet. The anesthetic is injected into a blood vessel located near the nerve responsible for the sensitivity of the limb in the area below the injection site.
In recent years, due to the emergence of more effective local anesthetics, the number of proctological operations performed using local anesthetics has increased significantly. In addition, our specialists have developed a method of combined anesthesia - a combination of local anesthesia and intravenous anesthesia. This significantly reduces the toxicity of general anesthesia and reduces the severity of pain in the postoperative period, which allows the patient to recover faster after surgery.
Most often, when performing proctological operations (hemorrhoidectomy, excision of anal fissures, small pararectal fistulas, rectal polyps), pararectal blockade, as well as spinal anesthesia, are used.
How to use drugs to cleanse the intestines
It is necessary to take special products to clean the intestinal lumen at home. Before using any such tool, you should study the instructions. This will avoid the development of side effects and clarify the order of taking the drug.
It is not advisable to eat food directly during bowel cleansing, but it is necessary to consume a lot of water. This is necessary to compensate for the liquid losses that inevitably occur during the cleaning process.
You should start taking medications 2-3 hours after a light breakfast. Some medications must be taken strictly on an empty stomach. The most common means of preparing for a colon examination include:
- Fortrans
. It begins to act 2 hours after administration. Able to effectively cleanse all parts of the intestines. One sachet of the product is designed for dilution in 1 liter of cold water. 1 sachet per 20 kg of patient weight. For a patient weighing 80 kg, 4 sachets will be required. The resulting solution must be divided into 2 parts. Drink half between 18-20 hours, in portions of 0.25 liters every 15 minutes. The second half should be consumed between 6 and 7 am on the day of the study. - Lavacol
. Osmotic colon cleanser. Available in powder form. You need to take it according to the regimen indicated in the instructions. Standard dosage is 15 sachets per procedure. - Endofalk
. macrogol, sodium chloride, potassium chloride and sodium bicarbonate. The medicine is a mixture of different salts and macrogol to obtain a homogeneous isotonic solution. - Picoprep
. It has a complex effect - it helps soften stool, accelerate its excretion, and retains fluid in the intestines. It begins to act 2-3 hours after administration. - Moviprep (recommended)
. The product begins to act 1-2 hours after the first dose. It is necessary to divide the reception into 2 parts, evening and morning! read more here! It retains fluid well in the intestines and is well tolerated by patients due to the small volume of the drug (only 2 liters).
Important to remember
Please note that before using any laxatives, you should consult your doctor. Only a specialist will be able to prescribe the correct remedy and show the exact regimen for its administration.
Preparations for local anesthesia
The following drugs are used to provide local anesthesia:
- Novocaine;
- Dicaine;
- Lidocaine;
- Trimecaine;
- Bupivacaine;
- Naropin;
- Ultracaine.
Each of them is effective when carrying out a certain type of anesthesia. Thus, Novocaine Dicaine and Lidocaine are more often used when it is necessary to anesthetize the skin and mucous membranes, while more powerful drugs, such as Naropin and Bupivacaine, are used for spinal and epidural anesthesia.
What to eat immediately before the procedure
One day before the test, you need to follow a more specialized diet. It is advisable to exclude solid foods; after the middle of the day, do not eat at all; you can take water or clear drinks (non-carbonated).
The nutritional order should be as follows:
- Morning
. Light breakfast of dishes prepared according to the list of permitted products. - Until 13.00
. You can have lunch, it is advisable to take a minimum portion of food. - Dinner
. Only clear liquids; after starting preparation with the drug, you should not eat.
You should also not eat food on the day of the test. You can consume the clear liquid in any quantity. Drinking liquids 1 hour before the procedure is not advisable, but not prohibited.
Indications for local anesthesia
All methods of local anesthesia have the same list of indications, and are used if necessary to numb a specific area for a short time (up to an hour and a half). It is recommended to use them:
- for performing surgical non-abdominal interventions or small abdominal operations, the duration of which does not exceed 60-90 minutes;
- with intolerance to general anesthesia;
- if the patient is in a weakened state;
- if it is necessary to carry out diagnostic procedures against the background of severe pain;
- if the patient refuses general anesthesia;
- in elderly patients;
- when general anesthesia cannot be used.
What foods can you eat?
You need to switch to a special diet at least 3 days before the examination. It is better if this period is 5-6 days. The following products are allowed to be consumed:
- Low-fat cheeses, kefir.
- Eggs.
- Buckwheat porridge.
- Boiled lean meat.
- Boiled fish of low-fat varieties.
- Honey, sugar, jelly.
- Mashed potatoes (small quantities).
If you are having a colonoscopy, you need to pay maximum attention to preparing for the procedure at home. Diet violations should not be allowed; this can lead to the accumulation of gases and feces in the intestines, which will greatly complicate the examination.
Possible complications when using local anesthesia
The use of local anesthetics carries certain risks, which include several types of complications:
- damage to the central nervous system and conduction system of the heart;
- damage to spinal tissue, nerve roots and spinal cord membranes;
- suppuration at the site of anesthetic injection;
- allergic reactions.
In most cases, the listed problems arise when the anesthesia technique is violated, or when the anamnesis is not collected completely.
Why is anesthesia needed?
It would seem that anesthesia is needed for pain relief. However, that's not all. Anesthesia allows not only to relieve a person from unpleasant sensations, but to control his condition during surgery. The fact is that the human body reacts to any such intervention very actively - with heartbeat, increased heart rate, changes in pressure, which is completely undesirable during surgery. Anesthesia blocks such reactions of the body and during the operation a normal heartbeat and a calm state are maintained. In addition, thanks to anesthesia, the person does not seem to remember about the operation. Anesthesia relieves the patient of serious stress. When the patient does not remember either pain or fear, rehabilitation proceeds faster.
Reasons why anesthesia does not take effect
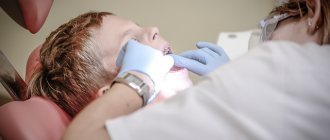
A patient comes to me and says that anesthesia does not work on him and that the last time he had a tooth removed under anesthesia. And now we are supposed to work on tooth extraction. I honestly say that he may well go to the previous clinic, where he had general anesthesia, because... I don’t know the real reasons why the anesthetic didn’t work and why the doctors then switched to general anesthesia. Then the patient decided to remove the tooth from me without general anesthesia, with ordinary anesthesia. And it turned out that the anesthesia worked great and we removed the tooth painlessly.
I want to tell you in what cases anesthesia does not work. You can understand this, you can prepare for it and make sure everything goes well.
- It is not recommended to drink any alcohol in any quantity within 24 hours. Because the anesthesia will not work. How it works? The anesthetic reduces pain sensitivity by acting on the nerve endings going to the tooth. Alcohol also affects the nerves - it relaxes. And, in particular, it relaxes those small branches of nerves that innervate the teeth. And therefore, if you drink a glass of wine or a glass of beer, the nerves from the tooth will also be “relaxed” for about 24 hours: until the alcohol is transformed in the kidneys and liver and is eliminated from the body naturally. Usually, during anesthesia, pain sensitivity goes away immediately, that is, the anesthetic solution is perceived normally by the nerve fiber. And if it doesn’t work, one of the possible reasons is that there was alcohol in the blood, and it could even be one glass of wine!
- When there is a lot of swelling and inflammation inside. Inflammation is an acidic environment, the pH of which inactivates the injected anesthetic solution immediately. Those. the injected anesthetic solution, entering a place next to the tooth, cannot act on the nerve endings, because there is an acidic inflammatory environment there. When does this happen? When a visit to the dentist is postponed until the last minute, to such a state that it becomes more and more difficult to help.
- When your own adrenaline goes off scale from fear and general tension in the body, when the muscles of the neck, shoulder blades, back of the head, and upper shoulder girdle are so tense that the blood simply does not circulate due to tightness and muscle tension. All this does not help the anesthesia work; the substance simply does not reach the recipient. You need to take three deep, slow breaths, relax, relieve muscle tension in your shoulders and try not to concentrate on your images of fear, but to think about the good.
- Good anesthetics of the latest generation are effective. I use Ultracain DS forte in different dosages. I consider other, cheaper anesthetics not very effective. Although many doctors say that they are the same as Ultracain DS forte only one and a half times cheaper. I believe that you cannot skimp on anesthesia. It must be a priori good. No options. Good pain relief means job success and patient peace of mind.
Application in pediatric dentistry
The technique is popular in pediatric dentistry, as it allows you to completely anesthetize any dental procedure, creating a trusting attitude towards doctors in young patients.
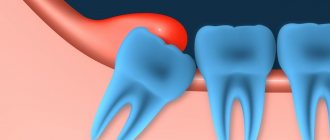
The porous structure of children's primary teeth is especially susceptible to topical anesthesia. The drug easily penetrates tissue, turning off sensitive receptors even in the deep layers of the gums. This allows the method to be used as the main method of pain relief - not only for superficial procedures, but also for the treatment of deep caries of primary teeth.
ATTENTION! In pediatric dentistry, drugs with a low level of toxicity are used. Drugs such as Dicaine are contraindicated for use in patients under 10 years of age.
Indications for use in dentistry
Application anesthesia is indicated for all patients with increased anxiety to create a favorable mood at the dentist’s appointment. However, the direct purpose of this method is to relieve pain from superficial procedures, such as:
- removal and application of sutures;
- injections (intermediate pain relief reduces any discomfort to zero);
- prosthetics (fitting of crowns and bridges);
- taking impressions (if the gag reflex is pronounced, the anesthetic is applied to the basal area of the tongue);
- procedure for cleaning teeth and removing tartar;
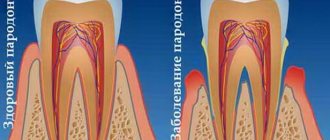
- treatment of periodontal pockets, treatment of periodontitis and gingivitis;
- treatment of uncomplicated caries of superficial and moderate severity;
- any manipulations with increased sensitivity of tooth enamel (preparations are rubbed directly into the tooth enamel and adjacent tissues);
- treatment of pulpitis (for local anesthesia of the inflammatory process, the drug is placed at the bottom of the carious cavity);
- removal of baby teeth or teeth with pathological mobility (for example, with periodontal disease);
- opening of gingival abscesses.
The main contraindication to topical anesthesia is an allergic reaction and hypersensitivity to the drug.
In rare cases, when infiltration anesthesia is strictly contraindicated for a patient, application anesthesia is the only way to somehow reduce pain.