The treatment tactics for caries depend on the cause of the pathological process and its neglect. This is the most common dental disease, characterized by gradual tooth decay. The pathology goes through several successive stages; at first, the patient may not feel anything; in complex cases, complete loss of dental units is possible.
It is not difficult to detect the disease, because most of the symptoms are quite obvious. However, it is better to prevent the occurrence of carious lesions by following preventive recommendations, and then a snow-white smile will delight you for many years.
Caries - what is it?
More than 95% of the inhabitants of our planet face the disease. Thus, it can be called the most common dental problem. At the very beginning, the pathological process affects only the enamel, and in the absence of therapy it penetrates into the deep hard layers. Then the soft tissues with nerve fibers and blood vessels become inflamed.
The disease is insidious because in the earliest stages it does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient begins to sound the alarm only when acute pain and a large hole appear that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods.
Choosing a filling
Previously, mainly mineral cements, acrylic and epoxy, and amalgams were used to make fillings. Today, outdated fillings, which were imperfect in terms of fixation and aesthetics, have been replaced by modern inlays. They improve the adhesion strength to the tooth surface, do not require labor-intensive installation, and are biocompatible with the human body. Among them, the most used are: composites, glass ionomer cements, ormocers, compomers. Materials can be combined to achieve the desired effect.
Causes of caries development
Oral disease develops under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that multiply in a favorable environment. Dentists are of the opinion that the disease occurs due to changes in the acid-base balance on tooth surfaces. Fermentation of carbohydrates caused by pathogenic bacteria releases destructive amounts of organic acids.
The main factors that contribute to the formation of carious cavities:
- improper hygiene care;
- eating problems;
- systemic chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced concentration of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- hereditary predisposition, etc.
Bacterial plaque and tartar
Streptococci are microorganisms that live in organic acids, leading to the destruction of enamel and dentin. During brushing, soft structures are easily removed, but hardened structures cannot be removed. They also contain pathogens that cause destructive phenomena.
Poor nutrition
Every person knows from an early age that you can’t eat a lot of sweets. However, adults often ignore this rule and consume large amounts of carbohydrates, sugar, baked goods, and starchy foods. The enamel layer becomes thinner and more susceptible to external factors. Bacteria multiply better in a carbohydrate environment.
Decreased salivation
During the day, a person secretes about 2 liters of saliva. The secretion washes away food debris from dental surfaces and protects them from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora. If the salivary glands do not function well enough, a lot of food particles settle on the crowns, which the microbes feed on.
Violation of the mineral composition of enamel
This factor is directly related to diet. Demineralization is observed with a meager, monotonous menu, lack of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine. Seeds, cottage cheese, cheese, red beans, and buckwheat are rich in such microelements.
Genetic predisposition also influences mineralization. This means that the disease can be inherited from parents and other relatives.
The problem occurs in pregnant women at different gestational stages. The fetus takes all the useful minerals, and the expectant mother experiences a lack of them. Subsequent intervention is complicated by the inability to use anesthesia.
General diseases of the body
Systemic pathologies (especially chronic ones with periodic exacerbations) affect metabolic processes and, as a result, the proper absorption of vitamins and minerals. This applies to disorders such as hypoplasia and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, and hormonal imbalance. The body does not receive enough essential components, which contributes to the deterioration of the condition of hard tissues.
Poor environmental situation
This is not the main reason for the formation and development of caries in adults. However, there are cases when the patient is absolutely not predisposed to diseases of the oral cavity, leads a healthy lifestyle, eats right, regularly sees the dentist, but when moving to a locality with unfavorable conditions, he discovers deep damage to the dentition. This problem is typical for regions with hazardous production enterprises that emit heavy metal salts, acids, and alkaline vapors into the atmosphere.
Prevention
To avoid the development of caries and its complications, experts advise following a few simple rules for preventing the disease:
- brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss and mouthwash regularly;
- eat right - include foods rich in vitamins, calcium and phosphorus in your diet;
- give up bad habits - smoking, alcohol abuse;
- monitor the general condition of the body - periodically undergo tests at the clinic, undergo preventive examinations at least twice a year at the dentist.
In order not to lead to the development of complications of caries (pulpitis), in which it is necessary to remove the tooth pulp, fill the canals and restore most of the unit, pay attention to any unpleasant symptoms from the oral cavity. If you notice signs of tooth decay, contact your dentist immediately.
Author: Elena Kopylova Dentist-endodontist. Work experience more than 12 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Varieties
Depending on the symptoms and causes of dental caries, localization, systemicity, frequency of relapses, as well as other characteristics, the disease is divided into types.
Classification by intensity of spread:
- single (not accompanied by additional symptoms);
- multiple (systemic) – affects the entire series, new foci quickly appear, the body’s immune defense is weakened.
Types according to developmental complexity.
- Uncomplicated. Additional disorders have not been diagnosed, and there are no negative consequences with timely dental intervention.
- Complicated. Pulpitis and periodontitis appear. Therapy takes a long time and is difficult.
By stage of the process
Depending on the degree of neglect of the pathological condition, the disease is divided into successive stages.
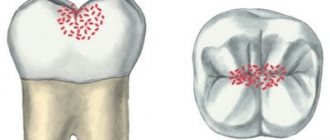
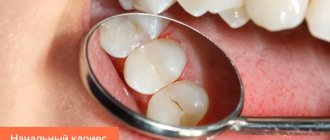
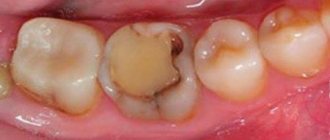
- Spot. Pale whitish or dark formations and stripes are visible on the surface. The patient is not in pain, he may not even notice any external changes when examining the oral cavity.
- Superficial lesion. The black or brown holes increase in size. Sensitivity occurs when consuming hot, cold, sour and sweet foods and drinks.
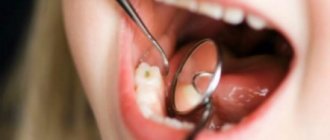
- Average caries. Dentin is destroyed. A person is in pain, unpleasant sensations are constantly present and do not depend on the time of day. Only installing a filling will help.
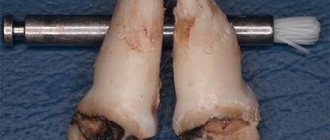
- Deep destruction. All layers rot, the pulp is affected. Experienced doctors can save the tooth by resorting to depulpation. It is often necessary to remove diseased units and subsequently install prostheses or implants.
By localization
This is a popular classification according to Black, according to which the disease is divided into classes depending on the location of the lesion and its depth.
- First. Erosion of the enamel occurs, the process reaches the dentin. At first, nothing is visible on the surfaces, but over time, slight pigmentation is visualized. In this case, you can do without preparation.
- Second. Chewing molars and premolars on both jaws are affected. The shade of the outer layer changes.
- Third. The front incisors and canines suffer. This problem is typical for those with a sweet tooth.
- Fourth. Dentin tissues are subject to severe destruction. Urgent medical intervention is required.
- Fifth. The most severe degree. All rows in the area of contact with the gums are affected. This is dangerous because the integrity of the dentin near the roots is compromised.
By frequency of occurrence
The disease may be detected for the first time. In some cases, an infectious process may develop directly under the filling material.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Types of the disease, officially established:
- carious lesions of enamel;
- bacterial destruction of dentin;
- infection of the root system;
- suspended form;
- odontoclasia;
- other caries.
Clinical researches
Asept toothpastes are distinguished by their clinically proven effectiveness - the products have been repeatedly tested. As part of the tests, it was found that:
- regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33% (research);
- Regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%. (study);
- regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION after 4 weeks improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% (study);
- Regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA GENTLE WHITENING for a month allows you to lighten tooth enamel by 1.5 tones, increases anti-caries effectiveness by 3.4 times and increases enamel remineralization by 2.6 times (research).
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Symptoms
The rate of growth of signs primarily depends on why caries occurs, holes are formed, and the inflammatory process develops in the neurovascular bundle. The most common symptoms of carious lesions:
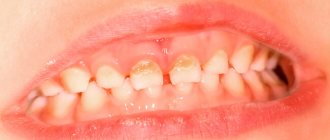
- darkening of the enamel, the appearance of dots or stripes of a white or dark shade on it (typical of the initial stage);
- increased sensitivity when consuming certain categories of foods (sour, sweet, hot, cold, hard); pain when pressing on the diseased area or in the absence of mechanical action;
- deep black holes, cracks in hard tissues;
- bad breath;
- headache, shooting sensation in the ears.
Diagnosis of dental caries
In some cases, the patient can independently diagnose himself, based on characteristic signs such as the presence of black holes and pain. However, there are situations when only a competent specialist can detect a lesion. This applies to the initial stage of the pathology in the absence of severe symptoms. At later stages, a thorough examination is also important in order to correctly differentiate the pathological process from other disorders.
The main methods used in dentistry:
- visual inspection using a mirror and other tools;
- computer images (panoramic, radiovisiography, CT, 3D study);
- functional diagnostics;
- thermal test;
- probing.
Dentik uses modern X-ray machines with safe radiation exposure and other equipment. We examine adult patients, women during pregnancy and lactation, and small children.
Main stages of the procedure
If for caries in the stain stage, treatment comes down to brushing the teeth with a special brush, applying a remineralizing composition and taking medications to strengthen the enamel, then in later stages it is necessary to remove the affected tissue and fill the cavity. In this scenario, the principle of caries treatment is as follows:
- anesthesia;
- preparation of a carious cavity;
- removal of infected tissue;
- cavity treatment;
- tooth filling.
Caries treatment and filling are carried out in one appointment. If, during the treatment of caries, damage to the dental pulp is detected, it may require its removal.
Methods of treating the disease
If the doctor was able to determine why a person has dental caries, he will be able to develop therapeutic tactics and help him recover quickly. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated non-invasively, that is, without the use of a drill. If the lesions are deep, drilling and medical treatment cannot be avoided.
Traditional methods will not help in the fight against the disease. But home recipes show an excellent effect as part of complex therapy to consolidate the results and prevent relapses.
Conservative treatment without preparation
At the initial stage of infection, the dentist will not drill crowns. The doctor will carefully remove plaque and tartar, and then apply a special composition to mineralize the enamel. The procedure lasts about an hour. Procedure:
- visual inspection;
- gum isolation;
- removal of deposits;
- application of remineralizing solutions.
If all manipulations were carried out according to the rules, the pathological process will stop. No additional methods are required.
Treatment with preparation of hard tooth tissues
Severely affected dental units can only be cured by mechanical removal of the diseased areas. The stages of intervention depend on the stage of the disease, usually as follows:
- use of anesthesia or other pain relief option;
- drilling;
- application of medications (antibacterial, etc.);
- installation of a protective gasket;
- restoring the integrity of the crown (filling);
- correction of the shape of the filling;
- grinding and polishing.
With deep lesions, the risk of pulp involvement increases. It is better to take a targeted photograph of the dental unit and make sure that there is no or no inflammation.
In severe cases, depulpation (extraction of the nerve and cleaning of the canals) and extraction (tooth removal) are indicated. These are extreme measures that are resorted to at the very last moment.
Modern dentistry – does it hurt?
Today it is logical to position the patient’s comfort on the same level as the results of therapy. Proper use of anesthesia in a dental clinic allows you to achieve the best results even in the most difficult cases.
Today's best method of pain relief in dentistry is the introduction of formulations based on articaine, a component that has minimal effects on the human vascular system and has a long-lasting effect.
In practice, there are several techniques for pain relief:
- applique. The doctor does not use a syringe or needle; the drug is applied to the mucous membrane in the form of a spray or using a gel-soaked tampon. This method of pain relief is used for relatively painless manipulations, for example, when giving injections to children;
- infiltration The doctor injects an anesthetic into the upper part of the tooth root. This anesthesia allows a person to be relieved of pain when treating deep caries of one tooth. The only condition for ensuring maximum effectiveness of the procedure is the introduction of the drug into the root of the upper tooth (due to the anatomical features of the jaw structure);
- conductor. The doctor injects the drug into the nerve or near the nerve trunk. The patient loses sensitivity in the local area for 2-3 hours;
- intraligamentary. Otherwise, the technique is called intraligamentous. The dentist injects an anesthetic with a special thin needle into the periodontium itself. This anesthesia allows you to “freeze” half of the jaw and lasts about 40 minutes. The method is most common in pediatric dentistry.