Pan Marianna Yanovna. Dentist-therapist, 25 years of experience in the specialty. For more than 10 years he has been engaged in restoration work, microprosthetics, and is proficient in all manipulations of therapeutic dentistry, including therapeutic periodontology. She has been working at the Dentalika clinic for more than 3 years.
One of the primary questions of interest to patients is whether they have caries ? What is it?
Caries is a pathological process that manifests itself after teething in places where cariogenic (causing the development of caries) dental plaque accumulates, during which demineralization of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs with the subsequent formation of a defect in the form of a cavity.
There are a number of factors influencing the development of caries.
General cariogenic factors
- Poor nutrition.
- Diseases and dysfunction of internal organs.
- Unfavorable genetic code.
- Extreme impacts.
Local cariogenic factors.
- Dental deposits.
- Microflora.
- Violation of the properties and composition of oral fluid.
The diagram below gives a general idea of the causes of tooth decay.
Let's talk in more detail about local factors that have a direct damaging effect on the hard tissues of teeth. The most cariogenic value, both independently and in combination with other factors, is represented by dental deposits: dental plaque and dental plaque.
Scheme of caries development
Soft plaque –> dental plaque (70% composed of microbes) –> acidic environment under the dental plaque –> dissolution of enamel (caries).
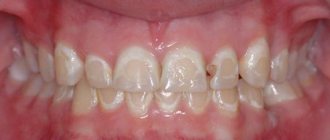
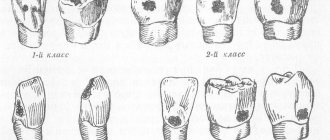
The most favorite places for the localization of caries are the chewing surfaces of the lateral teeth, and in the area of natural grooves (fissures), (Fig. 1-1).
Often caries occurs in the cervical area (Fig. 1-5). The location of carious cavities on the contact surfaces of the teeth is more difficult in terms of treatment (1-2, 1-3).
Often, the patient consults a doctor when he himself discovers a deep cavity, or when painful sensations arise. It is not difficult to diagnose open carious cavities, however, caries often affects contact surfaces hidden from view in the neck of the tooth. At the same time, outwardly the tooth appears undamaged, and pain often does not occur immediately, because there is no direct impact on the damaged surface. When the walls become so thin that the “roof of the tooth” suddenly collapses, it becomes clear that something is happening to the tooth! At the same time, pain may appear. Only for a specialist is it not particularly difficult to identify hidden caries. That is why dentists strongly recommend that you come for an examination periodically, preferably once every 6 months! It is better to identify caries at an early stage and prevent the development of complications that entail suffering and large material costs.
Of course, patients are interested in how much caries treatment costs?
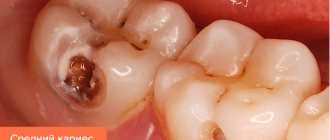
This depends on the depth of the cavity and location. Let's take a look at Figure 2 for a moment.
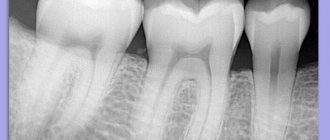
A cavity on the chewing surface, in the area of natural fissures (we already know that this is what the grooves on the surface of the tooth are called), depending on the depth, can be initial ( or , spot stage , Fig. 2-1) caries. A cavity within the enamel is a superficial caries (Fig. 2-2). If the enamel and dentin are affected, this is a medium caries (Fig. 2-3). With deep caries, the destructive process has gone very deep, almost to the boundaries of the cavity where the dental nerve is located. In such cases, you can focus on the prices given in the Dentaliki price list - in positions with the same names.
Now let's return to Figure 1. The greatest difficulty in treatment is presented by the cases illustrated in Fig. 1-2. Because:
- firstly, it is necessary to completely restore the shape of the tooth,
- secondly, each tooth must be separated from the adjacent tooth, at the same time, the edges of the teeth must be close enough to each other to prevent food from getting between them.
- thirdly, the surface of the filling must be perfectly smooth and aesthetically pleasing.
- In such cases, the work is assessed as tooth restoration .
Thanks to the availability of modern composite materials and various devices and instruments, such work is successfully carried out and, of course, this depends on the skill and professionalism of our doctors.
Special mention should be made about caries of the frontal (front) teeth . It is clear that for the lateral group of teeth , of course, first of all, the strength of the filling is important. It’s not for nothing that the side teeth are called chewing teeth! It is known that when chewing, colossal force is developed, and one can imagine what kind of load the teeth, and with them the restored surfaces of these teeth, take on!
The front teeth are not subject to such stress, but here it is more important to maintain an aesthetic appearance , choose the right color, transparency, ideal smoothness, but, at the same time, it is also necessary to properly restore contact between the teeth! Therefore, a slightly different price for the work performed is made here, which is reflected in the corresponding positions in the Dentaliki price list.
As for the materials used in our clinic (I will not dwell on the properties of composites and the requirements for them), preference is given to composite materials. This is a new generation nanocomposite. The material is universal, characterized by high strength and gloss retention after finishing, which makes it possible to use it in any clinical situations.
Diagnosis of caries
It is clear that before starting treatment, a correct diagnosis is necessary, especially if the patient complains of pain. We, therapists and dentists, try to keep the tooth “alive” whenever possible. In cases of superficial and medium caries this is quite possible. If you are concerned about a feeling of discomfort, slight pain when exposed to irritants (sour, sweet, mechanical when eating, or food getting stuck in the cavity), you can assume the presence of superficial or medium caries. It should be noted that some individuals with a reduced sensitivity threshold may not have any complaints. More often this happens with the chronic course of medium and even deep caries! If pain occurs from temperature stimuli - cold or hot (pain from hot may already be a sign of deeper and more serious destruction, most often when there is inflammation of the pulp!), more intense and prolonged, but still passing after the cessation of exposure, it can be assumed about deep acute caries. In some cases of deep caries, for a more accurate diagnosis or for therapeutic purposes, it is necessary to use various therapeutic materials containing calcium hydroxide in the form of temporary linings such as “Calcimol” (Voco), “Life” (Kerr), which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and remineralizing effect (in such cases, treatment usually involves 2 visits), or permanent linings such as “Vitrebond”, “Vitremer”, which release fluoride, used under composite materials, or independently for a long period. If within the time limits established for stopping the inflammatory process in deep caries, the pain does not go away, or a feeling of discomfort remains, it should be assumed that the pulp is inflamed, in this situation the treatment tactics change, we are talking about a complication of caries.
Caries susceptibility of the tooth surface
Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue of the human body. In terms of hardness, it is only slightly inferior to diamond. It consists of 96% minerals, mainly hydroxyapatites, which are very susceptible to acids, so the destruction of enamel begins already at pH 4.5.
The caries susceptibility of the tooth surface depends on many factors:
- Property of the anatomical surface of the tooth: in natural fissures and in the spaces between teeth there are favorable conditions for long-term fixation of dental plaque. Saturation of tooth enamel with fluorine: the resulting fluorapatites are more resistant to acids.
- Oral hygiene: timely removal of plaque prevents further development of caries. This is why it is so important to regularly check with your dentist and carry out professional oral hygiene and dental plaque removal.
- Diet factor: Soft, carbohydrate-rich foods promote plaque formation. The amount of vitamins and microelements also affects the general condition of the body and especially saliva.
- Quality and quantity of saliva: a small amount of viscous saliva promotes the attachment of bacteria to the pellicle and the formation of dental plaque. The buffering properties of saliva (which neutralize acids) and the amount of immunoglobulins and other protective factors in saliva have a very important influence on enamel caries resistance.
- Genetic factor.
- General condition of the body.
Caries as a multiple progressive process. Prevention of caries.
Treatment of dental caries is not always limited to filling carious cavities; it is necessary to stop the carious process. Against the background of pathological changes in the body, a decrease in its reactivity, and immune deficiency, caries often takes on the character of a multiple process with progressive tooth destruction . If such a pathology occurs, you must, first of all, be on your guard: something in your body is malfunctioning!
This requires:
- mandatory identification and elimination of somatic (that is, bodily, from the Greek “soma” - body, there are also mental) diseases (with the involvement of doctors of other specialties)
- carrying out important general strengthening activities aimed at improving the health of the body, including proper nutrition.
The main cariogenic dietary factor is an excess of easily digestible carbohydrates, supplied in the form of refined food, which, moreover, does not promote self-cleaning of the oral cavity, increases the accumulation of soft plaque on the teeth, and reduces the remineralizing ability of saliva. The consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates (and these are foods containing sugar and flour products) must be at least significantly reduced.
The consumption of a sufficient amount of biologically valuable proteins, which contain the required amount of amino acids in products of animal origin - beef, rabbit meat, poultry, fish, is encouraged. Among plant foods, beets contain a large number of essential amino acids.
An important component of nutrition are minerals, especially calcium, phosphorus, and fluorine. The most balanced product in mineral composition for the absorption of calcium is milk and dairy products (preferably fermented milk), including cheeses. Fish, eggs, and some plant products (cereals, peas, beans, legumes) also contain large amounts of minerals.
To absorb these microelements, vitamin D is necessary (butter, milk, egg yolk, caviar, liver and, especially, fish oil). Sufficient amounts of vitamin D are produced from cholesterol in the upper layers of the skin when exposed to ultraviolet rays during sun exposure or ultraviolet lamps.
Phosphorus is part of the mineral components of dental hard tissues (milk, cheese, nuts, fish, meat, egg yolk and some cereals).
Fluoride deficiency is of particular importance for the occurrence of caries . Fluoride is mainly found in drinking water. Increased fluoride content in some mineral waters and in sea fish - mackerel, sardine. A good additional source of fluoride is green tea. To reduce the effects of caffeine, it is recommended to drain the tea leaves after steeping and pour boiling water over the tea again for 20-25 minutes. This simple technique reduces the amount of caffeine in tea by 70-75%, which is especially important in childhood.
With multiple caries and its acute course, the properties of the oral fluid change and the viscosity increases. In this case, it is necessary to increase salivation, stimulating the remineralizing effect of saliva and reducing the formation of dental plaque. Intensive chewing of fairly coarse food promotes natural self-cleaning of the oral cavity and prevents the accumulation of dental plaque (plaque).
Professional oral hygiene is a procedure performed by a doctor to prevent caries. Includes cleaning teeth from hard dental deposits (tartar) using an ultrasonic scaler (scaling). Together with ultrasonic scaling, it is practiced to remove soft plaque and polish the surface of the teeth with an “Air-Flow” type device, or to use various cleansing pastes applied with brushes. You can read more about these procedures on our website in the “Professional teeth cleaning” section. Then fluoridation is performed on all tooth surfaces with a special composition “Bifluorid-12” (Voco). After completing the fluoridation procedure, it is recommended not to eat for 2 hours, eat only soft and liquid foods for 24 hours, and not brush your teeth. It is most effective to carry out professional hygiene 2 times a year. In special cases, every 3 months. The cost of a comprehensive professional hygiene procedure including 3 procedures for the entire oral cavity in our clinic costs the same as 3 for the cost of 2, even slightly cheaper!
Cariogenic factors
Conventionally, they can be divided into two types - general and local. They are equally responsible for the risk of dental caries.
Are common
Because of them, the human body does not receive enough microelements and vitamins necessary for health. They cause a change in the composition of dental tissues, as a result of which the tooth becomes vulnerable to caries.
- malnutrition;
- all kinds of diets;
- poor quality drinking water;
- somatic diseases;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- extreme effects on the human body;
- poor heredity, as a result of which the chemical composition of dental tissues is disrupted.
Fissure sealing
Fissures are natural depressions, pits on the surface of the teeth. The fissures of molars (chewing teeth) are the most common location for caries , a kind of risk zone . An effective method for preventing fissure caries is their isolation from the action of cariogenic factors in the oral cavity.
For this purpose, the fissure sealing method is used. Its essence lies in the fact that anatomical formations are filled with special filling materials that prevent the access of saliva, microspores, and dental plaque. Sealing of an open (accessible for sealing) fissure is carried out without machine processing. If the fissure is closed (hard to access for processing), the stage of grinding it with a diamond bur is added. The use of sealants is an effective method of preventing fissure caries.
It is best to do sealing in childhood.
Recommended timing of sealing:
5-6 years - first permanent molars
9-10 years - first premolars
10-11 years - second premolars
12-13 years - second molars
Teeth treated with sealants (sealants) are 10 to 23 times less than untreated teeth!
Marianna Yanovna Pan doctor - general practitioner - dentist October 2009
Dear Colleagues! When copying information, placing a link to the source site is mandatory!
Caries. Dentist's recommendations.
Caries
is a very common disease. In childhood, it ranks first among chronic diseases. According to various authors, from 80 to 90% of children with primary malocclusion, about 80% of adolescents at the time of graduation have carious cavities, and 95-98% of adults have filled teeth. Statistics show that in equatorial regions (Africa, Asia) caries is less common than in the polar regions (Scandinavia, North America). Developing countries also have higher rates of dental caries.
Currently, the occurrence of dental caries is associated with a local change in pH on the surface of the tooth under dental plaque due to the fermentation of carbohydrates carried out by microorganisms and the formation of organic acids.
The mechanisms of dental caries occurrence reveal a variety of different factors, the interaction of which causes the occurrence of a focus of demineralization: oral microorganisms, nutritional pattern (amount of carbohydrates), diet, quantity and quality of salivation (remineralizing potential of saliva, buffering properties, nonspecific and specific salivary protection factors ), changes in the functional state of the body, the amount of fluoride entering the body, environmental influences, etc. However, the main factors for the occurrence of caries are the following: caries susceptibility of the tooth surface, cariogenic bacteria, fermentable carbohydrates and time.
Time
The frequency with which a tooth is exposed to cariogenic acids affects the likelihood of caries. After each meal that contains sugar, microorganisms begin to produce acids that destroy enamel. Over time, these acids are neutralized by the buffering properties of saliva and partially demineralized enamel. After each period of exposure of tooth enamel to acids, the inorganic mineral components of tooth enamel dissolve and can remain dissolved for 2 hours. If you take carbohydrates periodically throughout the day, the pH will be low for a long time, the buffering properties of saliva will not have time to restore the pH and there is a possibility of irreversible destruction of the enamel surface. As was shown earlier, the speed of the carious process depends on many factors; the process that has begun can slow down if fluoride is used, but on average, caries of contact surfaces in permanent teeth progresses slowly and a cavity can form within 4 years. Since the root of the tooth is covered with softer tissue - cement, root caries develops 2.5 times faster than in the enamel area.
If oral hygiene is extremely unsatisfactory and the diet is rich in sugar, caries can develop literally a few months after tooth eruption.
Deep caries (caries profunda)
With this form of the carious process, there are significant changes in the dentin, which causes complaints. Patients indicate short-term pain from mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli, which disappears after their elimination. Upon examination, a deep carious cavity filled with softened dentin is discovered. Probing the bottom of the cavity is painful. Because dentin is more susceptible to caries, the dentin cavity is usually larger than the enamel entrance. In some cases, signs of pulpitis may appear: aching pain in the tooth after removing the irritant.
Prevention
- elimination of cariogenic situation in the oral cavity;
- increasing caries resistance of dental tissues.
- regular oral care;
- reducing sugar consumption;
- use of fluoride toothpastes;
- compliance with the correct technology for brushing teeth;
- the use of solutions of 0.1-0.2% chlorhexidine for daily rinsing of the mouth or toothpastes with chlorhexidine;
- consumption of xylitol at least 3 times a day after meals in the form of chewing gum containing xylitol;
- preventive examination by a dentist at least 2 times a year.
Cariogenic bacteria
Many bacteria are found in the oral cavity, but in the process of plaque formation and subsequent demineralization of enamel, mainly acid-forming streptococci (Streptococcus mutans, Str. sanguis, Str. mitis, Str. salivarius), which are characterized by anaerobic fermentation and lactobacilli (Lactobacilli), are involved.
Within a few minutes after ingesting carbohydrates, especially sucrose, a decrease in pH from 6 to 4 is noted. In addition to lactic acid, which is directly formed during the fermentation of carbohydrates, formic, butyric, propionic and other organic acids are found in dental plaque.
Fermentable carbohydrates
It is the acids formed during the fermentation of carbohydrates that lead to the destruction of the enamel surface. The presence and activity of fermentation in plaque depends on the quantity and quality of available carbohydrates. Fermentation of sucrose occurs most intensively, while glucose and fructose ferment less intensely. Mannitol, sorbitol and xylitol also penetrate into dental plaque, but due to the low activity of the enzyme that converts them into fructose, they are not dangerous. Starch, which is a polysaccharide, in its pure form is not cariogenic, since its molecules do not penetrate into dental plaque. However, food processing can lead to the destruction of the molecular structure of starch and increase its cariogenicity.
Clinical picture
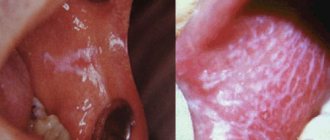
Stain stage (macula cariosa)
Demineralization begins with the loss of the natural shine of the enamel and the appearance of dull, white, light brown and dark brown spots. A white carious spot, depending on the severity of the process, can have 2 development paths:
- the white carious spot (progressive demineralization) subsequently turns into superficial caries due to the violation of the integrity of the surface layer.
- the process slows down, stabilizes, and changes color due to the penetration of organic dyes.
It should be understood that the stabilization is temporary and sooner or later a tissue defect will occur at the site of the pigmented spot. Caries in the spot stage is usually asymptomatic; very rarely, in the acute course of the process (white spot), sensitivity to chemical and thermal irritants may occur. Superficial caries (caries superficialis) / middle caries (caries media) Occurs at the site of a white or pigmented spot as a result of destructive changes in tooth enamel. Superficial and medium caries are characterized by short-term pain from cold and from chemical irritants - sweet, salty, sour. When examining the tooth, a defect (cavity) is discovered. In case of superficial caries, the defect is located within the enamel; in case of average caries, dentin is involved in the process.