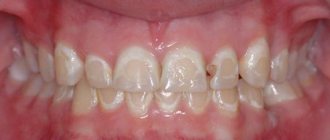
To answer the question: why there is a yellow palate in the mouth (see photo), you should study the subject of attention in more detail.
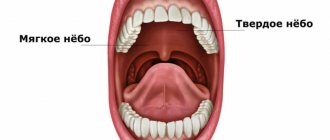
When examining the mouth, in addition to the tongue, gums with teeth and the inner surfaces of the cheeks, a concave dome-shaped surface is also visible, limiting the oral cavity from above.
This palate is a mucous membrane-covered bony structure formed by the palatine processes of the two halves of the upper jaw.
The main purpose of the palate is to be a partition separating the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
The palate performs the following functions:
- prevents saliva and food from entering the area responsible for breathing and smell recognition;
- ensures unhindered movement of inhaled and exhaled air;
- is responsible for the separate participation of the oral and nasal cavities in the function of sound formation.
In addition to the fixed bone (hard) part of the palate, there is also a soft part. This is a duplication of the mucous membrane (a fold that looks like tissue folded in half), moved up and down by a special muscle: when it contracts, the soft palate rises, and when it relaxes, it lowers.
In a calm state, the soft palate hangs down, allowing free passage of the air stream. But when swallowing, straining and blocking access from behind, from the nasopharynx, it absolutely hermetically separates the two largest cranial cavities from each other, preventing food from entering the nasal space.
Why did the sky turn yellow?
The palate area, like all areas of the skin and mucous membranes on and inside the head, has an abundant blood supply due to a dense network of capillaries.
The palate owes its normal color to the color of the blood flowing through them: in hard ones it is pale pink, in soft ones it is also pink, but of a more saturated dark tone. When inflamed, the color may become flaming crimson or bluish with a purplish tint. If the palate turns red and the throat hurts, this is considered normal, but the palate should not be yellow. For what reason does its color change?
The first thing that comes to mind is smoking. Indeed, the resins contained in tobacco and released when it burns stain the oral mucosa, giving it various shades of yellow and cause the formation of plaque on the palate.
But in addition to direct coloring, smoking:
- causes disorders of blood microcirculation in tissues;
- changes the composition and properties of blood.
Blood cells that contain minimal oxygen become paler, as does the area they supply. At the same time, in the region poorly supplied by them, fatigue and aging of cells increase due to chronic oxygen starvation.
And finally, once the transformations begin, they become irreversible, leading to changes in the biochemistry of tissues and the loss of their original color.
Therefore, the palate in a smoker’s mouth becomes covered with yellow spots with red dots and veins - a picture of capillary paresis.
Diagnosis and examination of plaque on the tongue
When examined by a dentist, the condition of the teeth, gums, and oral mucosa is examined. When a plaque is detected on the tongue, its color, location, density, the condition of the mucous membrane under the plaque, the appearance of the taste buds, the presence of cracks or erosions are assessed.
An important diagnostic sign is the onset of appearance, the duration of existence of plaque on the tongue, as well as its connection with any disease.
If it is determined that the cause of plaque formation on the tongue is dental disease, further observation and treatment of the patient is the responsibility of dentists. The first specialist you should contact is a dental hygienist, who will carry out thorough oral hygiene using special equipment and medications and will tell you whether additional help from his colleagues is required.
If the appearance of yellow plaque on the tongue is not related to dental problems, the patient is referred to a therapist to determine the cause of the pathology.
What diseases can there be?
In addition to smoking, the following diseases can cause a yellow palate in the mouth:
- liver;
- kidney;
- gastrointestinal organs.
Or lipid metabolism disorders lead to the same result.
Liver diseases
Disorders of intrahepatic metabolism lead to profound disorders in the biochemistry of all organs and systems of the body and disorders of all types of metabolism:
- protein;
- fat (lipid);
- carbohydrate;
- microelement;
- pigmented.
There is a disruption in the formation of vitamins and hormones, blood parameters change (viscosity, etc.), which leads to tissue hypoxia, which is fraught with biochemical changes on a local scale. In relation to the upper soft and hard palate, this can be either pallor and loosening of the mucous membrane, or a change in its color to yellow.
In case of liver diseases, the appearance of the palate will be particularly diverse, namely:
- yellowish corners of the anterior part of the soft palate with lines in the middle are characteristic of chronic cholecystitis and gallstones;
- Liver cirrhosis is characterized by the appearance of yellow spots in areas of dying tissue;
- viral hepatitis in the icteric phase also leads to staining of the palate.
Kidney diseases
Kidney diseases threaten the body not only with edema and dangerous blood thinning due to impaired water excretion, but also with the accumulation of many toxic substances in the blood: uric acid, creatinine, heavy metal salts and others, which also affect the biochemistry and color of tissues.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A change in the properties of the digestive juice, bile, which has a pronounced yellow color, during inflammation, which occurs in parallel in the liver and pancreas, leads to the deposition of bile salts in the tissues of the skin and mucous membranes. The skin responds to this process not only with itching, but also with a change in color. The same is observed in the mucous membranes lining various cavities.
With pathology characteristic of the liver-pancreas system, a bronze-icteric color appears exclusively on the soft palate.
The palate may turn yellow due to chronic inflammation in the small and large intestines with frequent constipation.
Blood diseases rarely have an independent character; most often they are a reaction to metabolic disorders in the liver or other organ systems. But its properties determine not only the level of tissue chemistry, but also their color.
It is for this reason that the skin of patients not only due to liver diseases (malaria, hepatitis), but also due to anemia-anemia, looks icteric, as well as the mucous membranes. In addition, the phenomenon of hemolysis is inherent in blood, and the transition of the initial “bruises” to yellow is a common thing for hemoglobin.
A yellow color to the body can also be given by “bronze disease” - a pathology of the adrenal glands, also called Addison’s disease.
Associated symptoms
In addition to staining the palate yellow, the diseases that cause it also have other characteristic accompanying symptoms. So, this is when:
- kidney pathologies - swelling and urinary disorders;
- blood diseases - symptoms of insufficient blood supply to organs (up to the development of trophic disorders or enlarged lymph nodes);
- changes in the liver - digestive disorders and all types of metabolism.
But if, with diseases of the digestive system, metabolism also suffers and body weight changes, then Addison's disease is characterized by crises. Caused by acute adrenal and vascular insufficiency, they are expressed:
- sudden sharp pain in the lower back, legs, abdomen;
- a sharp decrease in the ability to move (adynamia);
- severe (hectic) fever;
- intense diarrhea and vomiting, quickly leading to dehydration and shock;
- sharply developing arterial hypotension (drop in blood pressure);
- loss of consciousness occurring after a previous short acute psychosis with confusion or delirium;
- violation of water-salt metabolism due to low levels of adrenal hormones in the blood, detected by laboratory tests.
Considering the formation (due to hemolysis) of brown plaque on the teeth and tongue, there is a very high probability that the first doctor a patient with “bronze disease” will visit will be a dentist.
Causes of yellow sputum
Purulent bronchitis
The acute process is characterized by a frequent wet cough, which is accompanied by expectoration of dirty yellow sputum.
The bronchial discharge is liquid, with an unpleasant odor, and occasionally there are individual yellow-green lumps in it. Coughing increases in the morning after inhalation. Patients experience chest pain, shortness of breath, and increased body temperature. In chronic bronchitis, outside the period of exacerbation, a person occasionally expectors yellow sputum, but the cough mainly ends with the discharge of cloudy mucus. An increase in coughing attacks and an increase in the amount of yellow purulent discharge is observed with exacerbation of inflammation. The symptom is combined with signs of intoxication and decreased performance. With a long history of bronchitis, broncho-obstructive syndrome develops.
Lung abscess
The production of yellow, foul-smelling sputum is characteristic of the second period of the disease—breakthrough of the abscess into the draining bronchus. This happens suddenly: a dry cough gives way to a wet one, then a large volume of liquid purulent discharge is coughed up “with a mouthful.” Taking into account the size of the infected cavity, up to 0.5-1 liters of yellow sputum can be released per day after opening the abscess.
There is a clear connection between the onset of coughing up yellow pus and the general condition of the patient. In the first period, a person suffers from hectic fever, chills, severe chest pain and a painful non-productive cough. After the sputum is discharged, the state of health quickly improves, body temperature normalizes, and signs of intoxication disappear.
Bronchiectasis
The appearance of thick yellow sputum is typical for mild and moderate forms of the pathology, while in severe cases green discharge with a putrid odor is observed. Coughing up yellow pus occurs during an exacerbation of bronchiectasis (1-4 times a year). During the day, a person secretes up to 200 ml of yellow sputum, the main volume of which occurs in the morning - after waking up, pus is coughed up “with a mouth full”.
Throughout the day, coughing attacks occur as secretions accumulate in the bronchi. During paroxysms, a small amount of yellow sputum mixed with mucus is released. When the bronchial capillaries are injured due to a severe coughing attack, streaks of blood are noticeable in the purulent discharge. The patient is concerned about shortness of breath and symptoms of respiratory failure, intoxication, and exhaustion of the body.
Yellow sputum
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
The release of yellowish sputum when coughing indicates an exacerbation of the disease and the addition of a bacterial infection. Patients complain of increased cough paroxysms during the day, after which thick sputum is coughed up. Specific changes in the bronchopulmonary system and ventilation disorders contribute to the proliferation of microorganisms, therefore purulent processes in COPD are observed several times a year.
Pulmonary eosinophilia
The pathognomonic symptom of this group of pathologies is the appearance of bright yellow (canary) sputum, which is caused by an increased content of eosinophils in the mucus. The symptom occurs in diseases of various etiologies: parasitic pulmonary infestations (ascariasis, hookworm disease, strongyloidiasis), aspergillosis, acute and chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Occasionally, yellow sputum is discharged during an attack of atopic bronchial asthma.
Kartagener's syndrome
A congenital anomaly of the structure of the epithelium of the respiratory tract manifests itself in children from the first months of life. Ciliary dyskinesia leads to recurrent bacterial infections accompanied by a purulent yellow discharge. At first, sputum is coughed up only during periods of exacerbation. After 2-3 years of age, the process becomes chronic, so scanty yellow discharge when coughing becomes a common symptom.
Foreign body of the bronchi
Expectoration of yellow sputum is possible when a foreign object remains in the respiratory tract for a long time, which contributes to the development of purulent inflammation around it. The process is sluggish, so when you cough, a meager amount of pus is released. The disease proceeds like chronic pneumonia with alternating periods of exacerbations and remission, when sputum stops being coughed up.
Lungs' cancer
The appearance of yellow purulent discharge is typical of cancerous pneumonia - a serious complication of malignant neoplasia, which is caused by hypoventilation or atelectasis of a section of lung tissue. In addition to chest pain and intoxication syndrome, a person’s temperature rises to febrile levels and a frequent wet cough with yellow sputum is noted. A similar clinical picture is observed with pulmonary metastases.
Diagnostic methods
You should begin studying the problem with a visit to the dental office, because only a dentist is able to conduct the most complete and competent examination of the oral cavity.
When treating a patient, the dentist will pay attention not only to the palate - he will examine and examine the entire oral cavity, including the spaces between the cheeks, gums, and lips and the area under the tongue.
Because it is in these hidden places that something that does not catch the eye at a quick glance can be discovered, for example, the first signs of thrush-candidiasis.
Considering that pigmentation of the palate is rarely an independent condition, in addition to a dental examination, the help of other medical specialists may be required to diagnose the problem:
- therapist;
- ENT doctor;
- oncologist;
- allergist.
A mandatory part of diagnosis is laboratory studies of the internal environment of the body in the form of biological fluids: blood, urine, bile, and feces.
It may be necessary to perform allergy tests and study the body’s immune system using instrumental (ultrasound, MRI, CT, radiography) and laboratory methods.
Diagnostics
If yellow sputum is present, the patient requires the help of a general practitioner or pulmonologist. During a physical examination of the patient, attention is paid to the participation of the chest in breathing, retraction of the intercostal spaces, and local areas of pain on palpation. Auscultation of the lungs provides valuable information - a preliminary diagnosis is made based on the presence of wheezing, harsh or amphoric breathing. The diagnostic scheme includes the following methods:
- X-ray studies.
On a survey X-ray of the chest in two projections, you can see areas of infiltration in the lungs, a round shadow with a horizontal fluid level, and local compaction. To diagnose tumors, a CT scan of the chest is performed. To confirm chronic bronchitis, bronchography is performed. - Endoscopy of the bronchial tree.
Bronchoscopy with visual examination of large and medium-sized bronchi is an informative method for diagnosing chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes and detecting malignant tumors. During the examination, biopsies of suspicious tissue areas are taken for examination under a microscope. - Functional techniques.
In chronic diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, external respiration is impaired. To detect pathology, spirometry is prescribed, with the help of which the forced expiratory volume, vital capacity of the lungs, and other indicators are assessed. For express research, peak flowmetry is indicated. - Sputum tests.
The cytological method is aimed at identifying eosinophils and neutrophils, specific crystals and spirals of mucin in the tracheobronchial secretion. Culture with an antibiogram is used to determine the type of bacterial pathogen that caused the disease.
Additional diagnostic methods include a hemogram, which determines leukocytosis with an increase in ESR, eosinophilia, lymphopenia, as well as a biochemical blood test, which determines acute phase indicators and the ratio of plasma proteins. In chronic bronchopulmonary processes, heart function is often disrupted, so the examination plan includes an ECG and EchoCG.
Sputum analysis
Treatment methods
The data obtained after completing all the necessary studies provides an answer to the question: what is the patient dealing with?
If a therapeutic pathology is detected (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, etc.), treatment is carried out by a general practitioner or a specialist with a narrower profile:
- gastroenterologist;
- urologist:
- nephrologist.
In the case where there is a systemic disease of the category rheumatism, syphilis, HIV, treatment is necessary in a specialized medical institution.
The presence of oncological pathology may require joint treatment by an oncologist, a surgeon and consultant doctors of various profiles: a neurologist, an ophthalmologist and others.
If there is a local microbial-viral nature of the lesion in the oral cavity, antiseptics and antibiotics recommended by the dentist can be used.
After the process subsides or during it, professional cleaning of the oral cavity is often required, without which one cannot count on the success of treatment. It may be necessary to repair or replace existing orthodontic structures in the mouth.
Personal hygiene should be ensured by the patient himself, who is interested in resolving the problem as quickly as possible.
Treatment with traditional methods
The general principles of treatment with traditional methods do not differ from those in medicine and dentistry:
- the use of antiseptics (teas, infusions) for oral hygiene;
- increasing the level of health with the help of traditional, proven means (honey and bee products and the like).
The use of traditional medicine methods should in no way contradict the requirements of official science; proposals to use unstudied or questionable treatment methods should be categorically rejected.
The use of any form of rinse or other treatment method must be approved by the patient's attending physician.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Coughing up yellow sputum indicates serious damage to the respiratory system, so you should not delay a visit to the doctor. To relieve symptoms, the pus should drain unimpeded. To do this, it is recommended to take special drainage positions and massage the chest. It is forbidden to use antitussive drugs that contribute to the stagnation of pathological secretions in the bronchial tree.
Conservative therapy
In most cases, yellow sputum is purulent in nature, so patients need etiotropic antibacterial therapy. Medicines are selected empirically immediately after diagnosis of the disease, and after receiving the results of the antibiogram, the treatment plan is adjusted. Against the background of the destruction of pathogenic bacteria, purulent sputum ceases to be released. For pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment use:
- Expectorants
. They enhance the discharge of thick sputum and thin it, accelerating the sanitation of the bronchial tree. Thanks to the use of mucolytics and secretomotor drugs, recovery occurs faster. - Corticosteroids
. Hormone therapy is justified for eosinophilic lung disease. The drugs quickly stop the inflammatory reaction and reduce allergy symptoms. Glucocorticosteroids are used in the form of aerosols or parenterally. - Bronchodilators
. The production of yellow sputum in bronchiectasis or COPD requires the administration of beta-adrenergic agonists and anticholinergics. They are administered using nebulizers or spacers to ensure targeted delivery of the drug to the bronchi.
Surgery
In case of bronchiectasis and other chronic pathologies, when conservative measures are ineffective, they resort to therapeutic bronchoscopy and sanitation of the bronchial tree. After washing and removing the pus, the patients' condition improves. When lung diseases are complicated by pleurisy, a puncture is performed to remove exudate and targeted administration of medications.
Large abscesses, localized bronchiectasis, and areas of suppuration in the complicated course of Kartagener's syndrome are subject to surgical removal. If lung cancer is diagnosed early, radical surgery is performed in combination with radiation or chemotherapy. To alleviate the condition of cancer patients at stages 3-4, palliative interventions are indicated.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures include the following:
- careful and attentive care of teeth and oral cavity in general;
- visiting the dentist in a timely manner and following his recommendations, and if problems arise, providing professional assistance;
- preventing possible diseases by fully increasing the body’s defenses (maintaining a consciously healthy lifestyle), and in the event of an acute pathology, its timely treatment.
As a conclusion from what has been said: a person needs to be constantly engaged in maintaining health, but if problems arise, be sure to consult a specialist doctor.
Causes of plaque formation on the tongue
Insufficient oral hygiene
If the rules of dental care are not followed, opportunistic bacterial flora is activated in the oral cavity, which begins to multiply rapidly.
As a result, a film is formed on the tongue, consisting of dead epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, food debris and bacterial mass. Gradually the film thickens, turning into a dense yellow coating. We all know that we need to brush our teeth twice a day after eating. However, few people brush their tongue along with their teeth, and there are even special scrapers for this! Regular mechanical removal of plaque will greatly alleviate the problem, no matter what caused it.
Other reasons for the formation of persistent plaque on the tongue:
- Consumption of products containing dyes.
- Smoking.
- Taking medications.
- Dry mouth.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract