Navigation:
- Definition goals
- Determination methods
A differential examination of the condition of periodontal tissues is carried out by a dental hygienist or periodontist.
Modern medicine uses clinical, instrumental, and technological diagnostic methods. determination of periodontal indices in dentistry in St. Petersburg is an important tool for collecting information and forecasting. Information! Periodontium is a functional set of hard and soft tissues that surround the tooth and hold it in the alveolus (socket).
The examination begins with studying the mucous membrane and assessing its condition. The doctor pays special attention to the consistency (elasticity) of the gums, color and width. The severity of the periodontal groove, interdental papillae, and the presence (absence) of morphological signs of damage are noted. Bluishness, hyperemia, and swelling can signal the destruction of the periodontal attachment - the pocket.
The formula will help determine the condition of the mouth
To determine the condition of the oral cavity in medicine, there are about 80 different hygiene indices, based on the principle of staining the enamel with a special solution and identifying dental plaque.
According to the parameters they define, indices can be classified into 4 groups, assessing:
- area affected by plaque;
- thickness of plaque on teeth;
- mass of plaque;
- other parameters of dental plaque (chemical, physical and microbiological).
conclusions
Periodontal indices provide information about the hygienic state of the periodontal tissue, the intensity and prevalence of inflammation and destruction in periodontal tissues.
Examinations allow a preliminary assessment of the general condition of the periodontium and make a conclusion about the effectiveness of therapeutic and hygiene products.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags gums treatment periodontal indices periodontal disease
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
The subtleties of returning the original shade to a tooth using intracanal whitening
Next article
Features of teeth whitening with Double White products
CPU in dentistry
Dentists should use these calculations during the initial examination of the patient. So, for example, the average values of the indices KPU, kp. KPU+KP of teeth and cavities in dentistry allows you to determine the intensity of carious lesions. These abbreviations contain the following meanings:
- K – carious permanent teeth;
- P – permanent teeth in which a filling is installed;
- U – extracted molars;
- j – temporary teeth affected by caries;
- p – filled temporary teeth.
- According to the World Health Organization, the average CP index for children 12 years old should be from 2.7 to 4.4, and for citizens aged 35-44 years 6.3-12.7.
Definition goals
To reliably assess the dental status of periodontal diseases, our center uses a set of objective tests. Periodontal indices in dentistry are a rational comparison of the results of studying the disease over time. The mathematical scoring system is used for the following purposes:
- identifying and eliminating causative predisposing factors;
- taking measures to prescribe therapeutic and preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of a pathological process;
- timely diagnosis of deterioration of periodontal condition;
- monitoring changes in the condition of the mucous membrane;
- control of the treatment process.
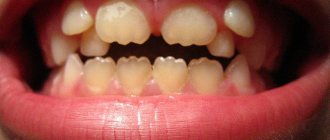
Periodontitis is one of the most common forms of dental diseases, regardless of a person’s age and social status. Inflammations can be acute or chronic. They are divided into reversible, irreversible, complicated.
Simplified index (IGR-U)
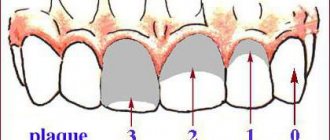
The Green Vermillion Hygiene Index measures plaque and tartar on the surfaces of the 2 upper first molars, 2 lower first molars and 2 upper incisors.
Ratings are given as follows:
- 0 – no plaque;
- 1 – no more than 1/3 of the tooth surface is covered with plaque;
- 2 – plaque affects from 1/3 to 2/3 of the tooth;
- 3 – dental plaque covers more than 2/3 of the surface.
The simplified hygienic index is calculated by adding the plaque index and tartar index on 6 teeth.
General overview
Periodontal indices are a quantitative (in percentage or coefficients) expression of pathological processes occurring in the periodontium.
In comparison with clinical diagnostic methods, the index assessment is relative and does not claim absolute accuracy.
However, it has a number of advantages that clinical diagnostics lack. With its help it is convenient:
- conduct epidemiological studies for any segment of the population;
- monitor the dynamics of pathological processes;
- compare the results of different studies;
- evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and prevention.
PMA – papillary-alveolar-marginal index
When calculating the PMA index, a solution of iodine or Lugol is used, which is applied to the gums and the degree of tissue inflammation is determined by the reaction to the irritant.
The evaluation criteria are:
- 1 – if the papilla (P) is inflamed;
- 2 – in case of inflammation of the marginal edge (M);
- 3 – inflammation of the alveolar part of the gum (A).
Formula RMA = Sum of points/n*3 (in percentage), where n is the number of teeth (up to 6 years – 20 teeth; 6–12 years – 24 teeth; 12-14 years – 28 teeth; over 15 years – 30 teeth) .
If the value is less than 30%, then the degree of damage is mild, 31-60% is moderate, 61% or more is severe.
Index of need for periodontal disease treatment - CPITN
To assess the prevalence and intensity of periodontal diseases, almost all countries use the index of need for the treatment of periodontal diseases - CPITN . This index was proposed by specialists of the WHO working group to assess the condition of periodontal tissues during epidemiological surveys of the population.
Currently, the scope of the index has expanded, and it is used to plan and evaluate the effectiveness of prevention programs, as well as calculate the required number of dental personnel. In addition, the CPITN index is currently used in clinical practice to examine and monitor the periodontal condition of individual patients.
In this regard, the CPITN index can be considered a screening test at both the population and individual levels.
This index registers only those clinical signs that may undergo reverse development: inflammatory changes in the gums, which are judged by bleeding, tartar. The index does not record irreversible changes (gingival recession, tooth mobility, loss of epithelial attachment), does not indicate the activity of the process and cannot be used to plan specific clinical treatment in patients with developed periodontitis.
The main advantages of the CPITN index are the simplicity and speed of its determination, information content and the ability to compare results.
To determine the CPITN index, the dentition is conventionally divided into 6 parts (sextants), including the following teeth: 17/16, 11, 26/27, 36/37, 31, 46/47.
The periodontium is examined in each sextant, and for epidemiological purposes only in the area of the so-called “index” teeth. When using the index for clinical practice, the periodontium is examined in the area of all teeth and the most severe lesion is identified.
It should be remembered that a sextant is examined if it contains two or more teeth that cannot be removed. If only one tooth remains in the sextant, it is included in the adjacent sextant, and this sextant is excluded from the examination.
In the adult population, starting from 20 years of age and older, 10 index teeth are examined, which are identified as the most informative:
When examining each pair of molars, only one code characterizing the worst condition is taken into account and recorded.
For persons under 20 years of age, 6 index teeth are examined during the epidemiological survey: 16, 11, 26, 36, 31, 46.
CODE 1: bleeding observed during or after probing.
Note: bleeding may appear immediately or after 10-30 seconds. after probing.
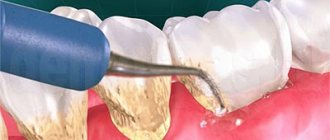
CODE 2: tartar or other plaque-retaining factors (overhanging edges of fillings, etc.) are visible or felt during probing.
CODE 3: pathological pocket 4 or 5 mm (the edge of the gum is in the black area of the probe or the 3.5 mm mark is hidden).
CODE 4: pathological pocket 6 mm deep or more (with the 5.5 mm mark or black area of the probe hidden in the pocket).
CODE X: When only one or no teeth are present in the sextant (third molars are excluded unless they are in place of second molars).
To determine the need for periodontal disease treatment, population groups or individual patients can be categorized based on the following criteria.
0: CODE 0 (healthy) or X (excluded) for all 6 sextants means that there is no need for treatment for this patient.
1: A CODE of 1 or higher indicates that this patient needs to improve his oral hygiene status.
2: a) CODE 2 or higher indicates the need for professional hygiene and the elimination of factors that contribute to plaque retention. In addition, the patient needs training in oral hygiene.
b) CODE 3 indicates the need for oral hygiene and curettage, which usually reduces inflammation and reduces pocket depth to values equal to or less than 3 mm.
3: Sextant with CODE 4 can sometimes be successfully treated with deep curettage and adequate oral hygiene. In other cases, this treatment does not help, and then complex treatment is required, which includes deep curettage.
The prevalence and intensity of periodontal disease in the population is assessed based on the results of a survey of 15-year-old adolescents.
Prevalence of signs of periodontal damage (adolescents 15 years old)
Prevalence Bleeding gums Tartar
low 0 – 50% 0 – 20%
average 51 – 80% 21 – 50%
high 81 – 100% 51 – 100%
Level of intensity of signs of periodontal damage (adolescents 15 years old)
INTENSITY LEVEL BLEEDING GUMS CALCULUS
LOW 0.0 - 0.5 sextants 0.0 - 1.5 sextants
AVERAGE 0.6 - 1.5 sextants 1.6 - 2.5 sextants
HIGH < 1.6 sextants < 2.6 sextants
Php Index
Scientists Podszadlej and Haley developed an oral hygiene performance index. First, a dye solution is applied to the teeth, then the patient rinses his mouth with water, and 6 teeth are examined. In this case, their surface is divided into 5 sections: medial, distal, mid-occlusal, central, mid-cervical. The absence of staining is determined by zero, and the presence - by one.
When calculating, use the formula: IG = ZN/n, where ZN is the sum of codes for all teeth; n – number of teeth examined. With a value of 0, the condition of the oral cavity is considered excellent, and with a value of 1.7 or more, it is considered unsatisfactory.
Iodine index of enamel remineralization.
The active permeability of iodine in tooth tissue is known. Remineralization index (RI), which characterizes the effectiveness of the remineralization therapy used. It is assessed using a four-point system:
1 point – no staining of the tooth area;
2 points - light yellow coloration of the tooth area;
3 points - light brown or yellow staining of the tooth area;
4 points - dark brown staining of the tooth area.
The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
IR = IRNP x number of teeth with hypersensitivity / n,
where IR is the remineralization index;
RRI—remineralization index of one non-carious lesion;
n is the number of teeth being examined.
Dark brown and light brown staining indicates demineralization of the tooth area with non-carious lesions; light yellow - indicates a certain level of remineralization processes in this area of the tooth, and the absence of staining or its slightly yellow color demonstrates a good level of the remineralization process of a particular non-carious tooth lesion.
CPITN (periodontal disease treatment need index)
This method covers 10 teeth, allowing the dentist to see the condition of the gums of the upper and lower jaws. Grades are given as follows:
- 0 – no disease symptoms;
- 1 – gums are bleeding;
- 2 – tartar was found above and below the gum;
- 3 – gum pocket 4-5 mm deep;
- 4 – gum pocket more than 6 mm.
It may come as a surprise to many that the condition of teeth can be determined using a formula, but this is the truth. Therefore, do not neglect maintaining oral hygiene, so as not to be a poor student in this calculation.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!
Determination methods
There are over 10 variants of disease classifications, which are based on diagnosis based on clinical manifestations. In the practice of our clinic, we use the most developed methods that take into account the key symptoms of the disease, which have objectively proven their informative value in prevention and treatment.
Periodontal risk indexes for systemic infection (PIRI)
Modern technology for periodontal screening, eliminating the possibility of subjective errors in diagnosis. The PIRI analysis evaluates periodontitis as a biological disease that can lead to systemic pathology. This approach more accurately integrates the relationship between oral tissue damage and the risk of transfer of pathogens and toxins to other organs. The basis of the method is the diagnosis of ulcerated areas open to infectious bacterial load and clarification of the degree of risk of periodontal-systemic complications.
When calculating, the following are measured:
- Number, depth of periodontal pockets.
- Amount, degree of bone loss (furcation lesion).
The examination is painless and quick. All measurements are recorded and calculated automatically. A printout of the results can be given to the patient or sent to a personal mailbox. The risk of systemic infection is assessed as low to severe.
Russell periodontal index
It is carried out taking into account the gingivitis index according to Silnes Low. The severity of periodontal destruction - gingivitis, the depth of the true periodontal pocket, mobility is taken into account:
- no symptoms identified
- mild segmental gingivitis
- inflammation of the free gum around the crown
- gingivitis, resorption of bone interdental septa is planned
- IG 2.0, pathological pocket, tooth displacement is not diagnosed
- Destruction of mucous and connective tissues, intraosseous pocket, resorption, pathological mobility
The calculation formula is standard: the total score is divided by the number of examinations. The degree of diagnosis ranges from mild to severe. Clinical norm index 0-0.2.
Complex periodontal index PI
Studying the severity of destructive changes in the periodontium that appear due to inflammatory processes. The diagnostic method is visual and instrumental. The presence of hard dental deposits, the level of bleeding of the gingival groove, subgingival calculus, breaks in the epithelial attachment, and pathology of tooth mobility are assessed. The detected signal is recorded with a digital code for each tooth examined. When indexing, the patient's age is taken into account.
The summed total is divided by the number of probed units.
During the study, the individual and average CPI index is determined, and the assessment of the degree of likelihood of the disease or its complications is clarified.