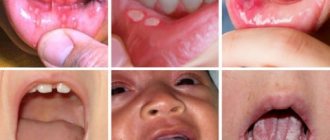
Why can’t stomatitis be treated without the participation of a doctor?
Of course, the use of medicinal ointments and preparations, special lotions and rinses for the oral cavity does not require hospital conditions and strict supervision by doctors. Indeed, you can heal yourself.
However, your decisions and actions should always be in consultation with your healthcare provider. Do not take any action or purchase medications yourself.
One careless mistake can lead to a complicated course of the disease and an increase in the inflammatory process!
Symptoms
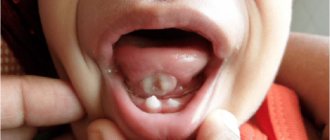
The first manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance of small redness. Subsequently, the affected area swells, swells, pain and itching are noted.
The bacterial form is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with smooth edges. Its center is covered with a thin white film.
Other signs:
- bad breath;
- bleeding gums;
- discomfort and pain in the oral cavity;
- increased salivation.
If the course of the disease is acute, then the body temperature rises and the lymph nodes enlarge. Typically, this clinical picture is typical for children, since their immunity has not yet fully developed. Also, the child may sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and be capricious.
Typical localization of spill elements:
- sky;
- tonsils;
- inner side of lips;
- tongue, sublingual area.
What can cause stomatitis?
One of the main reasons is a decrease in immune functions. Once the immune system weakens, it affects other systems of the body.
Ulcers with stomatitis are a common signal of problems with the immune system. You may need help from different specialists.
Sometimes stomatitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and some other disorders in the endocrine system. Often, ulcers appear after accidental mechanical damage to the mucous membrane (for example, due to careless handling of a toothbrush).
Another possible reason is intoxication of the body associated with poisoning with metal salts. In this case, urgent medical attention is required due to the threat to the patient’s health and life!
Kinds
There are several types of pathology depending on the causes and depth of tissue damage. Each of them has its own characteristics. Here is the classification:
- viral - infection by herpes viruses;
- bacterial - caused by staphylococci and streptococci;
- fungal ─ develops with weak immunity and after antibiotic therapy;
- allergic ─ reaction to plant pollen, food, animal hair and other irritants;
- radiation ─ a consequence of radioactive radiation.
Can stomatitis be a side effect after taking medications?
Rare, but still acceptable causes of stomatitis also include taking certain medications.
Some antibiotics, diuretics, and oral contraceptives affect the condition of the oral mucosa, causing increased dryness and other complications. If your mouth becomes very dry, cracks and ulcers may occur.
Periodontal disease
Dental periodontal disease is a serious disease in which the last stage of gum inflammation occurs. This is often the cause of the development of infectious diseases, gastritis, stomach ulcers or cirrhosis of the liver. Even more often, the patient’s teeth simply fall out, and he cannot lead his usual lifestyle or eat his favorite food.
How to recognize periodontal disease
The signs of this dental disease are unclear and blurred. The patient is most often concerned about:
- exposure of the necks of the teeth;
- presence of tartar;
- burning gums;
- discomfort when eating.
There are 3 stages of periodontal disease:
- Easy. The patient has no complaints; very rarely there is a reaction to cold or hot food. The presence of periodontal disease can be determined during a dental examination. The mild stage of the disease is best treated.
- Average. The roots of the teeth are exposed by an average of 4-6 mm. The patient begins to experience a burning sensation in the mouth, and there is an acute reaction to eating hot, cold or sour foods.
- Heavy. The roots of the teeth are exposed by 8-10 mm. Chewing food causes severe pain.
Treatment methods
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for periodontal disease, the dentist conducts an initial examination, during which he determines the extent of damage to the teeth and gums: which teeth can be restored and which will have to be removed. This is necessary in order to draw up an algorithm for further actions. The patient is then sent to the diagnostic room to take targeted and panoramic X-rays. Using them, the periodontist determines the depth of the pockets and the condition of the bone tissue.
Removing plaque and tartar
Inflammation of the gums, which is always observed with periodontal disease, mainly occurs due to soft plaque, subgingival and supragingival calculus. The main reason for their appearance is poor oral hygiene. Therefore, the specialist’s task is not only to treat the disease, but also to teach the patient proper hygiene.
General and local therapy
To increase immunity, the patient is prescribed a complex of vitamins and anti-inflammatory drugs. If the inflammation is minor, the dentist will prescribe a course of local therapy, which can be done independently at home.
Splinting teeth
An increase in tooth mobility indicates that the jawbone and soft tissue around them have begun to rapidly deteriorate. To prevent the teeth from changing position and falling out (for example, they may fan out), they are held together with fiberglass tape and filling material. This is also necessary before surgical treatment.
Surgical operations
If periodontal pockets reach 5-10 mm, it is impossible to prevent the progression of the disease without surgical intervention. First, the pockets are cleaned of granulations and food deposits. This procedure is called curettage. It comes in two types - open and closed.
Closed is carried out with special instruments, curettes. It is carried out only for periodontal disease at the initial stage (pockets reach 3 mm), when there is slight inflammation of the gums.
Open curettage is necessary in advanced stages of periodontal disease. With its help, all granulations and food deposits are completely removed. This operation is more difficult to perform. To completely clean out the pockets, incisions are made in the gum. Flaps of the mucous membrane are peeled away from the bone and the root surface is cleaned with curettes and an ultrasonic scaler. To restore bone tissue, the periodontist implants synthetic bone.
Next, the patient undergoes flap surgery to prevent receding gums. The doctor removes a 1.5 mm marginal strip of gum, since after prolonged inflammation the gum changes in such a way that it can no longer adhere normally to the tooth. After this, the mucous membrane flaps are pulled to the neck of the tooth.
Timely diagnosis and choosing the right treatment will help stop periodontal disease and maintain healthy teeth!
What remedies are recommended for the treatment of stomatitis?
- Mouth rinses . You can prepare a solution based on boric acid (one teaspoon per 150 ml of water). Another option is a solution with hydrogen peroxide (add one teaspoon to a glass half filled with water).
- Oils for medicinal lotions . Use sea buckthorn oil and propolis tincture. Soak a sterile cotton pad (or gauze) with the product and apply to the ulcer for a few minutes.
- The use of antiseptics to treat ulcers and mucous membranes. Be sure to consult your doctor when choosing a product.
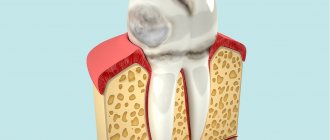
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, which includes the teeth, ligaments, cementum and gums. Periodontitis as a disease is a consequence of gingivitis - a minor inflammation of the gums, the main cause of which is neglect of oral hygiene. If with gingivitis the inflammation spreads exclusively to the soft mucous membranes, then with periodontitis the ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets are affected. This is why in 90% of cases when this disease is diagnosed, tooth mobility is observed, which eventually leads to their loss.
The most common causes of the disease are the following:
1. Improper or irregular oral care
. Dental plaque, which is present on the surface of the teeth and in the spaces between teeth, is not as safe a substance as it might seem at first glance. Soft and easily removed at the beginning, it goes through certain cycles of “development”. The result is the mineralization of plaque and its transformation into hard tartar. This process in most cases is observed in those who do not pay due attention to daily oral care or use an incorrectly selected toothbrush, toothpaste and mouthwash.
2. Poor blood supply to the gums
. Periodontitis is one of the most common problems among smokers. Substances contained in tobacco smoke lead to a narrowing of the blood vessels in the oral mucosa and their fragility, which impairs the blood supply to the gum tissue and supporting apparatus of the teeth. A slowdown in blood circulation and, as a consequence, the development of periodontitis is also facilitated by a lack of chewing load caused by eating habits (for example, the predominance of soft foods in the diet).
3. Nutrient Deficiency
. The lack of fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, a sufficient amount of fish, meat and dairy products in the diet quickly leads to a lack of essential substances in the gum tissue. If poor nutrition is a permanent habit, then over time the metabolic processes in the gums are disrupted, which creates the ground for inflammation and periodontitis. A deficiency of vitamins A, C and group B can lead to negative consequences.
Treatment of periodontitis
Professional teeth cleaning is an integral step in the treatment of periodontitis. This procedure removes physical obstacles (plaque and tartar) that prevent the gums from returning to their previous position and tightly covering the teeth.
Drug treatment - the use of antiseptics for topical use. This need is due to the high risk of spread of inflammation and infection to other tissues.
Surgery
At an advanced stage of periodontitis, when the inflammation has spread deep into the bone tissue, surgical intervention becomes necessary. Such manipulations include partial excision of the gums (gingivectomy), washing of periodontal pockets with medicinal solutions, removal of stones, and flap operations. In some cases, surgical treatment of periodontitis involves the implantation of bone tissue substitutes or the application of collagen or artificial membranes to restore the supporting apparatus of the tooth.
Compliance with oral care rules
Without regularly removing plaque and protecting the oral cavity from bacteria, it is impossible to achieve sustainable results in the treatment of periodontitis. Hygiene procedures twice a day with properly selected products, the use of dental floss and rinses will help make recovery faster.
What should you not do if you have stomatitis?
While you are treating stomatitis, never eat too hot food. Mouth rinse solutions should also be at a moderate warm temperature.
Temporarily avoid ice cream and cold drinks, do not eat spicy, sour, overly salty or sweet foods to avoid increased irritation.
Do not try to remove the ulcer yourself. If necessary, such manipulation will be performed by a doctor on an outpatient basis. If you open an ulcer yourself, you may accidentally introduce an infection into the wound.
Where to take your child
Treatment of stomatitis in children is carried out by a pediatric dentist. In addition to the dentist, children are examined by a pediatrician. The aphthous type of disease in toddlers is severe. This disease requires constant monitoring by a doctor and adjustment of medications. The main thing is that adequate therapy is prescribed and the dose of medication is selected correctly. The age of the patient must be taken into account. If recovery is delayed, the little patient is referred to the following specialists:
- An immunologist to determine the state of the body’s defenses;
- To a hematologist, especially when aphthae appear, as they can occur when hematopoiesis is impaired;
- An infectious disease specialist who can identify the source of infection;
Remember that herpes is a dangerous manifestation. Children's behavior changes dramatically. They become anxious, whiny, restless, and may refuse their favorite food. Such symptoms cannot be ignored. The sooner you see a doctor, the faster your recovery will come.