Have questions?
Stomatitis is a disease in which the oral mucosa becomes inflamed.
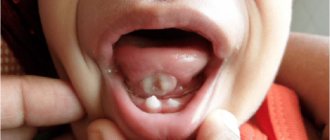
Stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of painful ulcers and wounds in the mouth, which cause significant discomfort to the patient. They are localized on the gums, tonsils, inner lips, cheeks, and under the tongue. The disease is most often bacterial or viral in nature and occurs as a result of poor oral hygiene or microtrauma of the oral cavity, through which microorganisms enter the soft tissues. It may also have an allergic or fungal origin. It mainly affects children, but often occurs in adults.
Causes of stomatitis
The imperfection of local and general defenses of the child’s body makes the mucous membranes of the oral cavity vulnerable to adverse factors. And the healthy curiosity characteristic of every child has made stomatitis one of the most common diseases among children. Sometimes, for the development of an illness, it is enough to taste any less than sterile object. The main causes of the disease include the following:
- insufficiently good oral hygiene;
- minor injuries - cheek biting, scratch, etc.;
- burns, including chemical burns;
- exposure to pathogens from unwashed hands or dirty toys.
Dentists focus on stomatitis associated with biting the inside of the cheek.
This is often associated with recent dental treatment under local anesthesia. For some time after the procedure, there is reduced sensitivity in the area of the lip or cheek, so you need to eat food after treatment very carefully and only after you have waited for the recommended period of time - usually from 1 to 2 hours. The likelihood of developing stomatitis for these reasons increases after infectious diseases, previous interventions, hypothermia and other factors that contribute to a decrease in protective forces.
Types of stomatitis
The treatment regimen for stomatitis in children is based on the type of disease. There are several types of stomatitis:
- bacterial;
- viral, including herpes;
- fungal;
- aphthous;
- angular;
- allergic;
- traumatic.
All types of stomatitis occur in children, but the most common among children under 3 years of age are aphthous, candidal, herpetic and allergic. An increase in the incidence of traumatic stomatitis is usually associated with a period of active growth of primary teeth.
It is important to understand that in some cases, stomatitis is combined with other diseases with similar symptoms and is the first sign of more serious diseases. For example, with cheilitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane and red border of the lips, food allergies, etc.
Sore throat in children: forms and clinical manifestations
Depending on the nature of the change and the degree of damage to the tonsils, several forms of angina are distinguished.
Catarrhal sore throat
A mild form, characterized by enlargement and redness of the tonsils, as well as the absence of purulent lesions. The child feels dry mouth, a whitish coating appears on the tongue, and the cervical lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. In addition to a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing, the child feels a sore and burning sensation. The temperature rises to 38 degrees, children complain of weakness and headache.
Follicular tonsillitis
A serious disease in which the tonsils become covered with purulent pinpoint follicles. On days 2-3, the ulcers open, leaving wounds that heal quickly. There is severe pain in the throat, radiating to the ear, making it difficult to swallow, children refuse to eat and drink. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed lightly. Fever and chills are accompanied by a temperature of up to 40 degrees, vomiting, convulsions and fainting are possible.
Lacunar tonsillitis
In the lacunae, between the lobes of the tonsils, islands of yellow purulent plaque appear, which tend to unite into wide purulent foci. The symptoms are similar to those of purulent follicular tonsillitis, but are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe intoxication of the body. It hurts the child to turn his head, his mouth opens with difficulty, which makes speech slurred.
Viral (herpetic) sore throat
Most often, the development of the disease is facilitated by vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity. The tonsils become covered with red blisters, which burst, leaving small ulcers in their place. In addition to a sore throat, symptoms are acute respiratory in nature: cough, runny nose, abdominal pain, indigestion, as well as stomatitis and conjunctivitis. Lack of timely treatment of herpetic sore throat in children can lead to serous meningitis.
Fungal tonsillitis
A relatively mild form of sore throat that occurs in children under 3 years of age. It is distinguished by a coating of white, curdled flakes on the tonsils and, with proper treatment, goes away within a week.
Symptoms
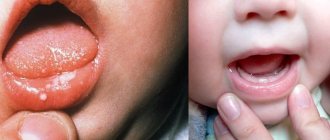
Common symptoms of stomatitis are pain, burning, swelling of the mucous membrane and redness, and bad breath. Salivation also changes - it can be excessive or insufficient, with dry mouth. In some cases, there may be an increase in temperature and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
The types of stomatitis in children and treatment methods differ, as do the specific manifestations. For example, with aphthous stomatitis, only one large ulceration may appear, but with viral stomatitis, inflammation almost always takes the form of numerous elements or a rash merging into one focus.
Candidal stomatitis is characterized by the formation of a white or yellowish cheesy coating. It is easier to recognize traumatic stomatitis because it is preceded by damage or the source of injury is nearby - a chipped tooth or a rough filling.
Diagnostic features
A dentist can detect stomatitis during the first visual examination. But in controversial cases, laboratory tests may be required. Thus, bacterial inflammation may require identification of the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to antibiotics. A scraping and/or virological study will help determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If a combination of several ailments with a similar picture is suspected, as well as if the child’s general well-being deteriorates, laboratory tests of blood and urine and consultations with other specialists may be prescribed.
Sometimes stomatitis can be the first manifestation of systemic diseases, general somatic pathology, for example, diabetes mellitus or malignant neoplasms. Therefore, a timely visit to the doctor is extremely important.
Forms of the disease
According to the ICD, aphthous stomatitis is assigned code K12.0. There are two forms of the disease - acute and chronic. The second is characterized by frequent relapses and may be a consequence of inadequate or untimely treatment of acute inflammation.
An acute disease is characterized by severe symptoms. It begins quickly, severe pain occurs at the site of mucosal damage, and the child may refuse to eat. In some cases, body temperature rises, weakness and lethargy occur.
The chronic form is characterized by a sluggish course; the child’s general well-being does not suffer. The disease can recur up to several times a year.
Features of treatment
As is often the case with diseases that are at the intersection of several areas of medicine, inflammatory lesions of the oral mucosa are one of the least studied areas of dentistry. Therefore, several specialists can be involved in the treatment of stomatitis in children in the mouth: pediatrician, dentist, dermatologist, immunologist-allergist, otolaryngologist, etc. This is especially convenient when you go to a multidisciplinary clinic.
Self-medication of stomatitis is unacceptable, and although it is now easy to find ready-made treatment regimens and folk recipes, it is important not to experiment with the baby’s health.
Conservative treatment is mainly used, which involves treating the underlying cause of the disease. Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- antibacterial drugs (systemic and local in the form of ointments): for bacterial inflammation;
- antiviral agents for herpes and other types of viral stomatitis;
- antifungal drugs for fungal diseases;
- antihistamines - both for allergic origin of stomatitis, and as part of complex therapy to reduce swelling and itching;
- symptomatic drugs - anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis in infants should be carried out with caution. At the same time, it is important to pay attention to your health; sometimes the cause of such a disease can be insufficient breast hygiene during lactation.
Often, only local remedies are sufficient, but make sure that the entire oral cavity is treated with the rinse - inflammatory agents can be found on the entire surface of the mucous membranes. Healing applications can be used to a limited extent, only on areas of inflammation.
Treatment of stomatitis of any kind in children involves strict adherence to a diet. The diet should be gentle, it is important to avoid salty, spicy, sour foods and drinks, serve the child warm meals, and limit the consumption of sweets.
If traumatic stomatitis occurs, the doctor will prescribe medications to speed up healing. However, it is very important to prevent re-injury. If it was caused by sharp edges of a tooth or filling, this cause should be eliminated. The doctor will suggest grinding off the filling or replacing it, and will also choose the appropriate option for restoring the shape of the crown in case of chips and cracks.
Types of stomatitis: symptoms and treatment
Stomatitis is a general name for various inflammations of the mucous membranes in the mouth: on the roof of the mouth, the inner surface of the cheeks, under the tongue, in the throat, on the lips or gums. Therefore, with stomatitis, symptoms and treatment are determined by the causes of the disease and the affected area.
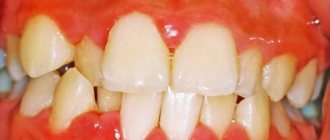
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis)
It manifests itself in bleeding, swelling of the gums and discomfort when pressed. Accompanied by an unpleasant odor from the mouth. Sometimes it leads to tooth mobility. In case of gingivitis, professional hygiene is often carried out, and then the periodontist determines how to treat stomatitis in the mouth and strengthen the gums: he may prescribe rinses, recommend medicated toothpaste and an electric toothbrush with a special attachment.
Stomatitis on the lip (cheilitis)
Symptoms can be different: a “cold” on the lip, severe peeling, inflammation of the lip border, cracks over the entire surface of the lips. How and with what to treat stomatitis on the lip in an adult depends on the nature of the inflammation. An integrated approach is practiced:
- elimination of acute symptoms: for pain, anesthetics are prescribed, for high temperatures - antipyretic drugs;
- local treatment: agents are used that relieve inflammation and promote tissue healing;
- correction of the immune system.
But before treating stomatitis on the lip, it is necessary to determine the cause of this disease, since without eliminating it, there is a high probability that the problem will soon recur. Taking into account the nature of the infection, medications (antibiotics, antivirals, etc.), vitamin therapy and a gentle diet are prescribed.
Inflammation of the tongue (glossitis)
Signs: swelling of the tongue, change in color to burgundy or bright red, the appearance of plaque, the formation of painful ulcers. The general approach to treating stomatitis on the tongue in adult patients involves two directions: relieving local symptoms (antiseptic rinses, applications, etc.) and influencing the main cause of inflammation.
Stomatitis in the throat
Inflammation in the throat is characterized by painful sensations when swallowing, headache; the temperature may rise. To understand how to treat stomatitis in the throat in adults, blood tests, saliva testing (bacterial culture), and cytological smear tests are often prescribed. For treatment, antiseptic sprays and rinses, drugs aimed at eliminating the causative agent of stomatitis, and anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
In addition to following the doctor’s recommendations, for stomatitis in the throat, it is advisable to drink herbal decoctions, avoid overheating (baths, saunas, hot baths) and physical activity.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes virus and usually occurs with fever, vomiting and diarrhea; Bubbles appear on the mucous membranes, turning into ulcers that heal after a few days. When diagnosed with herpetic stomatitis, treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms and immunocorrection.
Fungal stomatitis
Stomatitis caused by candidiasis (fungal infection) is characterized by the appearance of a white coating with a curd consistency, a feeling of dryness and burning in the mouth. During treatment of candidal stomatitis, it is important to maintain hygiene: thoroughly wash your hands and dishes, rinse your mouth before and after eating. The diet should consist of warm food and plenty of fluids; smoked, salty, and spicy foods should be excluded. The oral cavity is treated with antifungal and anti-inflammatory agents.
Drug-induced stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is a consequence of an allergic reaction to antibiotics and other medications. Symptoms include the formation of spots, blisters and ulcers on the mucous membrane, accompanied by pain and bad breath.
Complex treatment of medicinal stomatitis consists of several stages:
- exclusion of the drug that caused stomatitis;
- taking antihistamines;
- diet correction;
- To heal the affected areas, sprays or ointments are used, often containing an anesthetic to relieve pain.
Prevention of stomatitis
You can reduce the risk of developing stomatitis using the following recommendations:
- regular washing of toys, bottles, pacifiers, breast hygiene if the baby is breastfed;
- general strengthening activities: walks, wet cleaning, a balanced diet, moderate hardening, adherence to a daily routine;
- fighting bad habits of biting nails, pencils, etc.;
- regular dental examinations and timely interventions in case of dental injuries.
The dentists of the Family Doctor clinic treat and prevent stomatitis in children.
Advanced equipment allows us to quickly and accurately assess the condition of the oral cavity and perform the necessary studies in a short time. We practice modern approaches to the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and adhere to an individual approach to each small patient. Consultations with a pediatric dentist are available by appointment. To make an appointment, call the single contact center or fill out a special online appointment form with a pediatric dentist on the website, or you can also visit the clinic’s reception in person.