Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Caries is a disease that affects all people, regardless of their gender, age and place of residence. Caries is caused by bacteria that settle in the oral cavity due to poor nutrition and poor oral hygiene.
Definition of the concept in dentistry
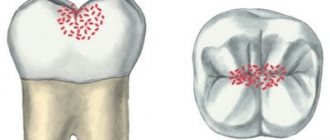
Deep caries is the last stage of the carious process occurring in the tooth, which is characterized by extensive damage not only to hard tissues, but also to the deep layers of dentin. In general, the concept of “deep caries” reflects the depth of the lesion.
Caries can be:
- primary - a consequence of untreated secondary caries;
- secondary (recurrent) - the occurrence of a carious process under a filling in a previously treated tooth.
Based on the sensation of pain and clinical examination, the disease is divided into 3 forms:
- Acute form. It is determined by the narrow entrance opening of the carious cavity and the wide base (during examination), as well as by descriptions of the patient’s sensations - reaction to food temperature and chemical irritants.
- Chronic form. It is characterized by a wide (funnel-shaped) inlet and a narrow base. The patient feels pain when the “hollow” is clogged with food and during examination with a probe by the dentist.
- Deep cervical caries. It is characterized by the development of demineralization of enamel tissue and the carious process in the cervical area of the tooth (near the gums).
According to the clinical course, caries is also divided into several forms:
- compensated,
- subcompensated,
- decompensated.
Why can't you try to get rid of caries yourself?
Only a dentist knows how to treat caries. Under no circumstances should you try to get rid of it yourself. Unfortunately, there are often cases when patients come to the dental clinic who tried to scrape off caries themselves and thereby only worsened the condition of their oral cavity.
Among these “barbaric” methods:
- removing carious stains or tartar using a file or sandpaper, which will cause severe damage to the enamel and will only accelerate the development of caries;
- cleaning the carious area with a needle: even if it is possible to remove the darkened area in this way, this will not stop the process of tooth decay;
- whitening dark carious spots using bleach or other bleaches: this can not only damage the tooth, but also cause a burn to the mucous membrane;
- whitening with vinegar: you can not only worsen the condition of damaged enamel, but also burn your gums and the inside of your cheeks.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which include:
- external inspection using a mirror;
- instrumental examination using a probe;
- voicing symptoms (complaints) by the patient;
- thermal diagnostics (checking the reaction to cold and hot);
- electroodontic diagnostics (testing the reaction to exposure to current);
- radiography (performed if the presence of secondary deep caries is suspected or to exclude it).
If upon examination significant damage (destruction) of the tooth crown is detected, expressed by the presence of a deep carious cavity and accompanied by pain during probing, then this confirms the presence of deep caries in the patient.
In the acute form, the carious cavity is filled with light, softened dentin. In chronic deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with a layer of dense pigmented dentin (from brown to black). Percussion of the tooth is not accompanied by pain.
What is fluoride varnish and how does it work?
The composition of fluoride varnish includes:
- shellac,
- sodium fluoride,
- fir or cedar balsam,
- chloroform,
- ethanol.
It is a viscous dark brown composition with a pine smell. Coating teeth with fluoride varnish creates a protective film that remains on the enamel for a long time. In doing so, it operates as follows:
- affects microorganisms on the surface of the tooth, preventing them from absorbing glucose and releasing acid that destroys enamel;
- interacts with the enamel, forming a hard layer that serves as a kind of shield for the teeth;
- absorbs calcium contained in saliva, restoring the mineral structure of the enamel, saturating it with necessary elements;
- has a positive effect on the gums, making them more elastic and stronger.
Thus, the use of fluoride varnish allows you to avoid many diseases associated with teeth, including caries and periodontitis. Applying varnish increases the service life of fillings and also reduces tooth sensitivity.
What are the differences from other forms of the disease?
Deep caries is very similar to some forms of the disease, but there are still visible and invisible differences.
Difference from pulpitis
Pulpitis is a complication of advanced caries. The forms of the disease can be distinguished from each other by their characteristic symptoms:
- Defeat. With pulpitis, the nerve is affected; with caries, the nerve remains unharmed.
- Feelings of pain. With pulpitis, pain can occur spontaneously, even without exposure to irritants on the tooth. With caries, pain disappears along with the disappearance of irritants.
- Night sleep. With pulpitis, sleep can be disturbed due to severe pain; with caries, the tooth does not hurt at night.
Difference from average caries
The similarity between the two forms of the disease is that the patient in both forms feels pain from cold, sour or sweet foods. However, with average caries they go away within 1-2 minutes, with deep caries they last longer.
Medium caries is characterized by the fact that in this form the carious lesion does not affect the tooth pulp and does not cause inflammation of the nerve, as in deep caries.
Varieties
Depending on the symptoms and causes of dental caries, localization, systemicity, frequency of relapses, as well as other characteristics, the disease is divided into types.
Classification by intensity of spread:
- single (not accompanied by additional symptoms);
- multiple (systemic) – affects the entire series, new foci quickly appear, the body’s immune defense is weakened.
Types according to developmental complexity.
- Uncomplicated. Additional disorders have not been diagnosed, and there are no negative consequences with timely dental intervention.
- Complicated. Pulpitis and periodontitis appear. Therapy takes a long time and is difficult.
By stage of the process
Depending on the degree of neglect of the pathological condition, the disease is divided into successive stages.
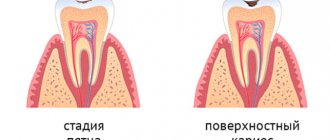
- Spot. Pale whitish or dark formations and stripes are visible on the surface. The patient is not in pain, he may not even notice any external changes when examining the oral cavity.
- Superficial lesion. The black or brown holes increase in size. Sensitivity occurs when consuming hot, cold, sour and sweet foods and drinks.
- Average caries. Dentin is destroyed. A person is in pain, unpleasant sensations are constantly present and do not depend on the time of day. Only installing a filling will help.
- Deep destruction. All layers rot, the pulp is affected. Experienced doctors can save the tooth by resorting to depulpation. It is often necessary to remove diseased units and subsequently install prostheses or implants.
By localization
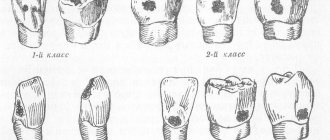
This is a popular classification according to Black, according to which the disease is divided into classes depending on the location of the lesion and its depth.
- First. Erosion of the enamel occurs, the process reaches the dentin. At first, nothing is visible on the surfaces, but over time, slight pigmentation is visualized. In this case, you can do without preparation.
- Second. Chewing molars and premolars on both jaws are affected. The shade of the outer layer changes.
- Third. The front incisors and canines suffer. This problem is typical for those with a sweet tooth.
- Fourth. Dentin tissues are subject to severe destruction. Urgent medical intervention is required.
- Fifth. The most severe degree. All rows in the area of contact with the gums are affected. This is dangerous because the integrity of the dentin near the roots is compromised.
By frequency of occurrence
The disease may be detected for the first time. In some cases, an infectious process may develop directly under the filling material.
International Classification of Diseases (ICD)
Types of the disease, officially established:
- carious lesions of enamel;
- bacterial destruction of dentin;
- infection of the root system;
- suspended form;
- odontoclasia;
- other caries.
Stages of treatment
Treatment of deep caries is impossible without anesthesia (pain relief) and it takes place in several stages.
- Anesthesia. It is carried out using injection (infiltration or conduction) administration of an anesthetic substance.
- Drilling out a carious cavity using a drill. In this way, the specialist can reach and remove all affected areas of dentin, which is very important to prevent relapse under the filling.
- Treatment (disinfection) of the walls of the tooth and the bottom of the cavity.
- Installation of a therapeutic insulating pad and temporary or permanent filling.
- The final stage involves grinding and polishing the filling.
The following factors influence whether a filling will be installed - temporary or permanent:
- at what distance from the pulp is the carious cavity located;
- parameters of dentin, which separates the pulp from the tooth cavity;
- degree of pain.
If there is a high probability of inflammation developing in the pulp area, the dentist will place a temporary filling. And only if there are no complaints of pain and discomfort for several days, the patient will have the temporary filling replaced with a permanent one.
Causes of caries development
Oral disease develops under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that multiply in a favorable environment. Dentists are of the opinion that the disease occurs due to changes in the acid-base balance on tooth surfaces. Fermentation of carbohydrates caused by pathogenic bacteria releases destructive amounts of organic acids.
The main factors that contribute to the formation of carious cavities:
- improper hygiene care;
- eating problems;
- systemic chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced concentration of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- hereditary predisposition, etc.
Bacterial plaque and tartar
Streptococci are microorganisms that live in organic acids, leading to the destruction of enamel and dentin. During brushing, soft structures are easily removed, but hardened structures cannot be removed. They also contain pathogens that cause destructive phenomena.
Poor nutrition
Every person knows from an early age that you can’t eat a lot of sweets. However, adults often ignore this rule and consume large amounts of carbohydrates, sugar, baked goods, and starchy foods. The enamel layer becomes thinner and more susceptible to external factors. Bacteria multiply better in a carbohydrate environment.
Decreased salivation
During the day, a person secretes about 2 liters of saliva. The secretion washes away food debris from dental surfaces and protects them from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora. If the salivary glands do not function well enough, a lot of food particles settle on the crowns, which the microbes feed on.
Violation of the mineral composition of enamel
This factor is directly related to diet. Demineralization is observed with a meager, monotonous menu, lack of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine. Seeds, cottage cheese, cheese, red beans, and buckwheat are rich in such microelements.
Genetic predisposition also influences mineralization. This means that the disease can be inherited from parents and other relatives.
The problem occurs in pregnant women at different gestational stages. The fetus takes all the useful minerals, and the expectant mother experiences a lack of them. Subsequent intervention is complicated by the inability to use anesthesia.
General diseases of the body
Systemic pathologies (especially chronic ones with periodic exacerbations) affect metabolic processes and, as a result, the proper absorption of vitamins and minerals. This applies to disorders such as hypoplasia and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers, and hormonal imbalance. The body does not receive enough essential components, which contributes to the deterioration of the condition of hard tissues.
Poor environmental situation
This is not the main reason for the formation and development of caries in adults. However, there are cases when the patient is absolutely not predisposed to diseases of the oral cavity, leads a healthy lifestyle, eats right, regularly sees the dentist, but when moving to a locality with unfavorable conditions, he discovers deep damage to the dentition. This problem is typical for regions with hazardous production enterprises that emit heavy metal salts, acids, and alkaline vapors into the atmosphere.
Deep caries of the front teeth. What are the differences in treatment?
Deep caries of the front teeth should be treated as carefully as possible so as not to burn the pulp. The main difficulty in treatment is:
- minimum thickness of all tooth tissues;
- inconvenient location of the cavity, if we are talking about caries located in the interdental space.
When infection penetrates into the pulp, pulpitis develops rapidly. A few hours is enough. The disease is accompanied by increasing pain. It needs to be treated immediately.
Indications for applying fluoride varnish
The range of indications for coating teeth with varnish is quite wide and includes many points. Therefore, almost everyone can use fluoride varnish. Most often, the procedure is performed in the following cases:
- with increased tooth sensitivity,
- for the prevention of caries,
- if there are areas of demineralization on the enamel,
- after ultrasonic teeth cleaning,
- before installing crowns,
- in case of injury.
This procedure has virtually no contraindications. These include only increased sensitivity to components and an excess of fluoride in the body. Teeth can be coated with fluoride varnish as early as 6 years of age. Allergic reactions to the composition of the varnish are extremely rare.
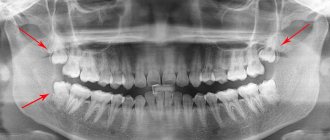
Is it possible to treat deep caries of a wisdom tooth?
The patient can make the decision to remove a wisdom tooth if pain occurs on his own. But only a highly qualified dentist can make a verdict on its treatment.
Treatment of a carious "eight" is considered rational if it has a partial covering in the form of a hood of gum, as well as an antagonist - the third molar located on the opposite side.
Removal shown:
- with a horizontal tooth position;
- presence or absence of 1st and 2nd molars;
- impossibility of treatment due to incomplete opening of the mouth;
- displacement of teeth in a row due to wisdom teeth.
Prevention of caries
What should you do to avoid caries?
- Regularly brush your teeth with high-quality toothpastes, for example, from the Asepta series. They ensure a sufficient supply of minerals to the enamel, break down plaque, and gently whiten.
- Limit the amount of sweets.
- Avoid eating sweets and starchy foods as a snack, before bed or immediately after brushing your teeth.
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year.
- Take care of your gum health.
- Follow the principles of proper nutrition.
- Choose the right oral and dental care products, and change your toothbrush regularly.
- Take vitamins and, if necessary, calcium, fluorine and phosphorus supplements.
- Eat solid foods regularly, such as apples and carrots, but at the same time avoid frequent consumption of seeds and nuts.
- Try to rinse your mouth after every meal, and if this is not possible, then at least chew sugar-free gum.
Fluoridation of teeth for children: benefit or harm?
The child’s baby teeth are not yet strong: they have fragile enamel, followed by a thin dentin layer, and at the base there is a soft pulp chamber with nerve endings and blood vessels. Therefore, children's teeth are more easily damaged; caries often forms on them, which can quickly develop into complications. It seems like just yesterday there was a small dark spot on the enamel, and today your child is complaining of severe toothache and refuses to eat.
To reduce the risk of tooth decay, baby teeth need to be cleaned regularly and properly, and strengthened. How can you help your children maintain a beautiful smile and protect them from toothache? With the appearance of the first teeth, bring your child to the dentist for a preventive examination 2-3 times a year. The pediatric dentist will promptly identify possible problems, teach in a playful manner the correct technique for brushing teeth, and also carry out fluoridation that is beneficial for the enamel.
Simple fluoridation of teeth
The most common way to strengthen teeth. It is used to prevent caries. A special composition is applied to the enamel, which forms a thin protective film. What kind of composition is this? Fluoride varnish, fluorine-containing varnish, fluoride varnish or simply enamel restoration varnish - the strengthening agent has several names, but the result is the same. Your teeth are reliably protected, and the effect lasts up to six months.
What can cause caries
There are several suggestions, for example, that tooth decay is transmitted genetically or that lack of hygiene contributes to the development of the disease. All this is true, but does not give the complete picture.
Where a person lives can also influence the occurrence of caries, namely the quality of water in that area.
Nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of caries. There are scientific studies confirming that eating fresh vegetables, greens and foods rich in proteins helps prevent tooth decay. That is, those people who like to chew raw carrots are less susceptible to dental diseases. That's why you should eat meat and a lot of raw vegetables - this is not only smart advice from nutritionists, but sound prevention in the fight against the development of dental caries.
Memo for patients during the treatment of caries.
- Do not drink alcohol before your appointment - this will reduce the effect of anesthesia.
- After the appointment, until the anesthesia wears off, you should not talk much - you can injure the numb tissue.
- You should not eat food within 2 hours after treatment, especially hot food for the same reason.
- After taking it, increased sensitivity may persist for several days, and bleeding gums may occur.
- If after taking it you feel discomfort when biting or pain, consult a doctor immediately.
What happens in the oral cavity when a diseased tooth is not treated:
- Caries spreads to healthy teeth and you can lose your entire dentition
- This is accompanied by inflammatory processes in the body
- The stomach and cardiovascular system suffers
- A cyst forms, which can lead to blood poisoning or cancer
Along with serious problems for patients, bad breath is inevitable, psychological problems arise (a person feels insecure, he is tense, he is susceptible to stress), which are caused by the unaesthetic appearance of the dentition. This is why it is necessary to treat teeth, even if they do not hurt or cause discomfort.
If it is not possible to prevent or avoid caries, it is necessary to treat it when the first signs appear, without delaying a visit to a specialist. In addition, thanks to modern dentistry, painless dental treatment is available. How? In modern dentistry, drug sedation is used. All procedures are supervised by an anesthesiologist, and you will not experience any pain, fear or discomfort.
Why is it better to treat caries at the Medikastom dental clinic?
- Many years of experience. The dental clinic has been operating since 2000, successfully providing care to patients even with complex illnesses.
- Highly qualified staff who treat each patient with care and sensitivity.
- First-class equipment and modern drugs.
- Using the latest developments and treatment methods.
- Affordable cost of caries treatment.
- Maximum comfortable conditions for the patient.
- Caries treatment 24/7. Our clinic works for you around the clock, without holidays and weekends, providing qualified assistance when it is most needed.
You can get detailed information on caries treatment by calling us at +7(499) 283-71-58.
Call and sign up for a free consultation right now!
We are waiting for you!
How is caries treated with laser?
Laser treatment of caries is a modern non-contact method. The laser beam passes into the dental tissue to the depth required for treatment. It removes affected tissue, disinfects, and reduces the likelihood of bleeding. At the same time, the laser does not damage healthy tissue.
The advantages of laser treatment of dental caries are the minimal risk of complications, the ability to control the intensity and depth of the effect. With all its advantages, the laser is effective in the early stages of caries, like other non-invasive methods.