Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
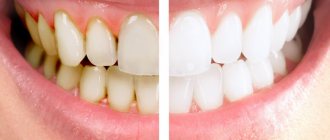
With periodontal disease, the gums “move away” from the teeth, their necks are exposed, and constant itching is felt in the oral cavity. If you notice bleeding or inflammation of your gums, this is a reason to seek advice from a dentist in order to prevent the development of periodontal disease.
Why are gum injections used in dentistry?
Any surgical intervention (amputation of teeth, removal of nerve endings in the root of a tooth, placement of a filling) causes an unpleasant painful sensation of varying degrees. Due to fear of pain, patients often postpone visiting the dentist, which leads to deterioration of the condition of their teeth. Local injections are made to numb the gums.
Another reason for injections into the gums is the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics in the treatment of gingivitis and periodontal disease. The question arises about intramuscular injections, since such manipulations also reduce inflammation and pain sensitivity.
Dentists administer local anesthesia for greater effectiveness and speed of reaction. If the anesthetic is administered intramuscularly, its effect will occur over a longer period of time.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of an anesthetic injection into the gums, there are many absolute and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications to local anesthesia and anti-inflammatory injections on the gums:
- children under 3 years old;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- increased sensitivity to drugs;
- patients with malignant arterial hypertension;
- a history of diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
Relative contraindications to manipulation will be:
- children under 7 years old;
- presence of problems with the liver and kidneys;
- oncological diseases (refers to antibiotic therapy);
- reduced immunity;
- gastrointestinal disease.
Effectiveness of the procedure
Using this technique you can eliminate:
- tooth mobility;
- bleeding gums;
- discolored periodontal tissue;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- the risk of rejection of installed implants is reduced;
- pain and inflammation.
As a rule, plasma lifting is required every 3 months until a positive effect is achieved. The first results will be noticeable within 2 weeks. Despite the complete safety of plasma lifting, after the procedure you may notice swelling and bruising. You should not be afraid of these phenomena, since they will completely disappear within a few days. If other reactions occur, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Reviews about gum plasma lifting are only positive and you can see this for yourself.
Pre-registration is available at our center ☎ +7 (862) 246-35-56 or +7 (988) 400-5-666. You can also get any additional advice over the phone.
Does it hurt to give an injection in the gum?
The painful process of needle penetration into the gum is insignificant, since dentists use small-diameter needles, damaging a small area of tissue of the oral mucosa.
Whether it hurts to give an injection in the gum is a question of the patient’s psychological state and his mood for treatment. Before performing the puncture, the doctor reassures the patient, reminding him that the injection is painless, since this manipulation is short-lived.
If the patient refuses anesthesia, the dentist warns about the increased likelihood of unbearable pain during surgical interventions, and any movements in the dental chair can lead to errors in treatment or complete ineffectiveness of the treatment measures taken.
People who have a high threshold for pain sensitivity are recommended to use anesthetic gels and sedatives (glycine, valerian, etc.) before going to the dental clinic (or before an injection while in line to see a doctor).
Folk remedies for strengthening gums
One of the most common folk ways to strengthen gums is the use of decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants. Commonly used are chamomile, sage, calendula, St. John's wort, yarrow, juniper, lingonberry and tricolor violet leaves. Decoctions of oak bark and linden blossom are very helpful in treating and strengthening gums.
Massage is also quite effective for strengthening gums. It can be done simply with your fingers. This will improve blood circulation and strengthen your gums.
To remove plaque from teeth at home, you can add sea or table salt to your toothpaste. You can also use a special toothpaste for bleeding gums. This paste contains not only a large number of medicinal herbs, but also fluoride, which helps prevent inflammation, strengthen tooth enamel and protect teeth from caries.
In addition, special gels and ointments are used in the treatment of gums. They heal foci of inflammation, forming an indelible protective film.
To keep your teeth and gums healthy, you need to consume various vitamins. If the body does not have enough vitamin A, it can lead to loose teeth. For the proper exchange of calcium and phosphorus, vitamin D is necessary. It helps the absorption and proper assimilation of these elements. Thanks to vitamin C, calcium is absorbed in the bone cells of the teeth. Vitamin B6 is prescribed in the form of medications or intramuscular injections for periodontal diseases.
A lack of calcium in the body can lead to various diseases of the teeth and gums. Therefore, it is better to take it in the form of dietary supplements.
How to perform the manipulation
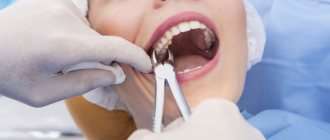
Anesthesia is administered depending on the area of the surgical intervention on the gums. For minor manipulations, the dentist uses a 2% lidocaine spray, sprinkling it on the injection site or applying an analgesic strip (Dentinox, Kalgel), waiting for the first manifestations of the analgesic.
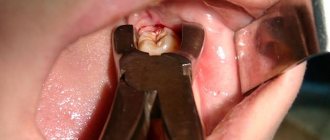
If there are no undesirable reactions (allergic, inflammatory), the doctor proceeds to pierce the already numb gums. The injection site should be as close as possible to the diseased tooth to minimize damage to nearby healthy tissue (the development of gingivitis or periodontitis in the future).
Having opened the ampoules with the contents (analgesic), the medical specialist draws several syringes and injects the medicine into the gums layer by layer, starting from the outer layers.
Types of local anesthesia:
- Infiltration anesthesia – used in the treatment of caries, during the removal of dental nerves.
- Conduction anesthesia is when a nerve bundle is blocked during the treatment of several teeth located close to each other.
- Intraligamentous anesthesia - injection of the drug into the peribuccal fold of the mucous membrane (in the treatment of painters and pre-painters).
- Injection of the drug into the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Performed when implants are implanted or molars are removed, in particular wisdom teeth.
- Involvement of the nerve trunk - anesthesia for large-scale dental procedures. It is carried out with the support of an anesthesiologist in a hospital setting.
The main causes of pain after injection into the gums
The main cause of pain after an injection is damage to the gums by the needle. Pain appears when the action of the analgesic subsides. Normally, the patient is in pain for 2-3 days, and after surgery (more damage - several injections) up to 14-15 days.
If the pain does not subside, but on the contrary, it begins to hurt more severely, you need to consult a doctor again. Such manifestations indicate the presence of acute inflammation, edema, infection or manifestations of postoperative complications (cyst, abscess).
Possible causes of prolonged pain after surgery may be: injuries during surgery; inadequate analgesia (without calculating how long an anesthetic injection lasts or the wrong combination of drugs).
Nerve trunk injury
Damage to the nerve trunk often occurs during conduction or trunk anesthesia, when the anesthetic enters the nerve fiber and kills some of the cells. Due to the death of brainstem neurons, the sensitivity of the innervated area decreases. Restoration of receptor function will occur without medical assistance.
Formation of hematoma on the gum
Since the gums are well supplied with blood, there is a high risk of hematoma formation during injections. Damage to small capillaries will not lead to the formation of large hematomas. But if you give an injection and get the syringe needle into a vessel of a larger diameter, the released blood will accumulate in the gum faster and to a greater extent. This forms a hematoma, causing discomfort and pain to the patient.
If a large hematoma is detected in the oral cavity, it is necessary to consult a dentist in order to reduce the risks of possible complications.
Allergy to anesthetic
Before the injection, doctors ask patients about the presence of allergic reactions to any drugs and review the patient’s medical record for allergies.
Considering these data, the medical specialist begins to administer anesthesia. An allergic reaction occurs instantly at the time of drug administration and is characterized by an increase in the characteristic clinical picture:
- the mucous membrane of the oral cavity swells;
- cheek swells;
- shortness of breath occurs;
- general excitement of the patient appears.
Therapeutic measures to eliminate allergies are carried out by a doctor in the dental chair: antihistamines and decongestants are administered, and the administration of the anesthetic or antibiotic that led to the body’s allergic response is stopped.
Necrotization of soft tissues
If anesthesia is inadequate (injection of a large amount of anesthetic) or an allergic reaction occurs at the time of drug administration, a complication such as necrosis of gum tissue may occur.
The necrotic area of the gum is dead cells that are no longer able to recover. If such a tissue area is insignificant, then the damaged area will be restored by neighboring healthy cells, while with large necrosis, scar formation occurs (replacement of cells with connective tissue).
Another cause of necrosis can be infection in the gum tissue and its rapid progression. If the next day a white spot appears at the injection site, surrounded by an inflammatory cushion, and the patient self-medicates without consulting a doctor again, irreversible tissue death may occur.
Clinical picture of gum necrosis:
- the appearance of plaque or blackening of the gums;
- formation of ulcers;
- bad breath;
- soreness around the lesion;
- increased body temperature;
- general malaise and chills.
Development of an infectious focus
Infection during medical procedures is possible due to poor sterilization of instruments or as a complication of improper postoperative care for the patient.
Contamination of the wound at the injection site causes a local response from the immune system - the formation of an inflammatory zone around the site. If you ignore the growing clinical picture or self-medicate, intoxication syndrome appears (febrile temperature, weakness, loss of appetite).
Treatment in a dental clinic will be aimed at eliminating the causative agent of infection (antibiotic therapy) together with the use of antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Possible complications in the treatment of periodontal disease
Injections into periodontal tissues can lead to unwanted complications. When giving an injection with a non-sterile instrument, an abscess may form. In this case, the resulting inflammation is opened and sanitized. Rinse with disinfectant solutions is prescribed.
If the needle touches the facial or trigeminal nerve, neuralgia may develop, a disease manifested by sharp pain in the areas of innervation of the corresponding nerves. In severe cases, novocaine injections may be prescribed to relieve pain.
Sometimes injury to soft tissues with a needle causes pain that does not go away for a long time. In this case, dentists recommend applying Solcoseryl gel to the gums.
How to get rid of pain after anesthesia
If the pain does not subside within a week after the manipulation, but, on the contrary, intensifies, becoming pulsating, you should consult a doctor. You should not self-medicate, since ordinary inflammation, which causes pain, can be complicated by the addition of an infection, and treatment will become more protracted and difficult.
At first, when the pain is still severe, strong non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help:
- Xefocam;
- Nurofen;
- Nimesulide;
- Ketanov.
It is important to take into account their harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract and avoid overdoses.
Precautions after anesthesia
In order for the rehabilitation period to proceed safely, some points should be taken into account:
- Eliminate hot, spicy, salty foods from your diet.
- Do not take solid food for the first 3 days.
- Maintain oral hygiene (temporarily eliminate the toothbrush and replace with mouthwash).
- Give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Keep records of changes in the general condition of the body (body temperature, general well-being).
- Avoid emotional disturbance.
Taking all these points into account, the patient significantly reduces the risk of complications during the rehabilitation period. The pain that arose after the treatment should not worry the patient on the first day. If your gums hurt for a long period after an anesthesia injection, this is a reason to seek medical help from a dentist again.
Category Miscellaneous Published by kosmetik-dent
Contraindications to injections for periodontal disease
For effective treatment, the doctor prescribes a set of drugs, each of which has contraindications for use. Therefore, it is important to undergo examination and identify possible diseases before starting therapy. For example, in case of autoimmune diseases (diabetes mellitus, glomerulonephritis, multiple sclerosis), immunomodulators are strictly prohibited. Cardiac decompensation and pulmonary failure are contraindications to the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment is not started in the presence of foci of inflammation in the body or in the acute stage of any disease. During pregnancy and lactation, injections are prescribed with caution; if possible, opt for non-drug treatment (massage, rinsing).