What is an abscess
People who do not pay attention to oral hygiene and proper gum care will sooner or later find out what a tooth abscess is. This is an acute inflammatory dental disease, which is often a complication of other pathologies.
There is an accumulation of pus under the tooth in the gum or hole left after extraction. A dense rounded bulge is formed. This is a fistula - a channel through which pus comes out of the tooth. Sometimes it opens and the contents leak out. But this does not mean that the pathology has passed, because its cause has not been eliminated. If bacteria continue to multiply, pus will again accumulate in the dental canal.
Without timely treatment, it is dangerous to health. An extensive abscess of the jaw may appear, the infection will penetrate into the bone or spread through the blood throughout the body. This threatens the development of osteomyelitis, inflammation of the bone marrow, and sepsis.
Granuloma on the root of the tooth - causes of appearance
There are only 2 main reasons for the occurrence of granulomas at the apexes of tooth roots. These reasons occur in 98% of cases, and we have described them in detail below. Much less often, granulomas are formed as a result of poor-quality orthodontic treatment, or mechanical trauma to the tooth (after an impact).
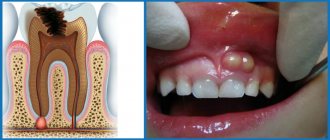
- As a consequence of untreated pulpitis (Fig. 4) - when the carious cavity of the tooth becomes deep enough - cariogenic microorganisms penetrate into the dental pulp, causing inflammation in it (it is called pulpitis). This is accompanied by sharp or aching pain. If the tooth is not treated at this stage, the nerve in the tooth dies and the pain temporarily stops.
After the death of the nerve, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate through the root canals and openings at the apex of the roots - beyond the boundaries of the tooth. This leads to the formation of foci of inflammation at the apexes of the roots (24stoma.ru). This disease is called periodontitis. There are several types of this disease, in one of which granulomas form at the tops of the roots.Keep in mind that in this case the tooth does not necessarily have to have a carious cavity, because Inflammation of the nerve in a tooth can also occur in a tooth previously treated for caries. This happens if the doctor has not completely removed the tissue affected by caries, leaving a small fragment of it under the filling (Fig. 5). In this case, caries develops under the filling and leads to the development of first pulpitis, and then periodontitis with granuloma.
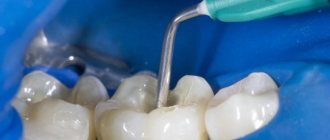
- Poor-quality root canal filling - if a granuloma has formed on the root of a tooth in which root canals were previously filled (for example, during the treatment of pulpitis), then there is only one reason for its formation!
This reason is poor-quality filling of the canals, or more precisely, the fact that the root canals were not filled to the apex of the root (Fig. 6). If your doctor says that the canals are sealed well, and he does not know why a granuloma appeared after treatment, then such a doctor is lying. “The tooth is filled well, take antibiotics” - this is a standard excuse from doctors who do not want to admit to poor-quality work and, at the same time, treat the tooth for free.
Types and forms of abscess
Depending on where the pus accumulates, there are three types of pathology:
- gum abscess or gumboil affects only the gums;
- periodontal develops in the periodontal pocket;
- periapical appears with severe destruction of the pulp and other dental tissues.
This pathology often occurs in an acute form and requires immediate dental treatment. But sometimes the fistula opens on its own. The pus comes out and the patient feels relief. If complex therapy is not carried out, the pathology can become chronic.
Classification of abscess in dentistry
Doctors say there are three types of tooth abscess:
- Desnev. Only the soft tissues of the mouth are damaged. But, if the disease is started, the periodontal ligaments and periosteum will be drawn into the inflammatory process. Then flux develops.
- Periapical. The pulp is affected. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, you will have to perform depulpation or, even worse, tear out the affected unit. More often, this type of disease is diagnosed in children with primary occlusion, which is why dentists have to remove a preschooler’s incisors, canines and molars without waiting for their natural replacement by molars.
- Periodontal. The abscess has a destructive effect on the root, so the tooth becomes loose and falls out prematurely.
The main danger of a purulent tooth abscess is that the pus that has accumulated inside the tumor can penetrate into the blood. Then a general intoxication of the human body will occur. Internal organs, bones, and brain come under attack. A person who ignores the presence of an abscess may develop meningitis, sepsis, and even die.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a tooth abscess is pain. It is localized in one place and intensifies when pressed or chewed. The tooth becomes sensitive to cold, hot or sour foods. If the tumor appears in the upper jaw, pain spreads along the trigeminal nerve.
The following manifestations of pathology are also common:
- malaise, weakness, headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the appearance of greenish discharge;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- if there is pus in the mouth, an unpleasant odor and bitter taste appear.
Signs of illness
It is almost impossible not to notice the presence of pathology - the symptoms are always very clear. Anyone, even those far from the medical field, can understand that something is wrong with their gums.
- First there is an acute toothache. It becomes more pronounced if you press on the unit, touch it, or knock on it. It intensifies if the patient drinks or eats something hot or cold.
- Soon the gums swell. Even the cheek may swell. This indicates that the inflammation is spreading quickly.
- A bulge forms on the gum. At first it is red or with a bluish tint. But it also happens that it is not there, and pus simply begins to ooze from the gums.
Due to the purulent masses, the patient has an unpleasant taste and a foul odor appears from the mouth. It is not possible to remove it using standard hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste, since pus continues to actively form after brushing your teeth.
An advanced abscess contributes to an increase in body temperature, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. In many patients, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged.
Causes of abscess
The main cause of tooth abscess is the penetration of bacteria. This can happen if hygiene rules are not followed, enamel or gums are injured. Pus often accumulates in the tooth in the presence of large carious cavities, pulpitis, gingivitis, and periodontitis.
Sometimes a tooth abscess develops after it is removed. The reason may be failure to follow the extraction technique or the use of poorly sterilized instruments. If removal is difficult, a fragment or piece of root may remain in the hole. But even if the dentist did everything correctly, a gum abscess may develop if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
Less commonly, the cause is common infectious diseases. It could be otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia. The infection is carried into the gums through the bloodstream. At risk are people who eat a lot of sweets, people with diabetes, and people with reduced immunity.
How to treat a tooth abscess
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at eliminating the infectious process and relieving pain. A comprehensive program may include the following activities:
- Opening and draining the lesion. An incision is made on the gum, a drainage is installed through which the pus can freely come out. The drainage system is installed for several days. During this period, the patient is prescribed rinses with antiseptics and saline solutions.
- Endodontic treatment. It involves removing the pulp, treating the root canals with medications and filling them.
- Excision of the root apex. Surgical intervention is performed when the source of infection is located in the periapical area. The surgeon cuts the gum and removes the abscess along with the affected part of the root. The segment itself is preserved.
- Removing a unit. The need for tooth extraction occurs when there is significant destruction of the tooth.
- Therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Restoration of the coronal part with a filling or orthopedic construction.
Treatment methods
Pathology sometimes does not cause pain at the initial stage, so not everyone goes to the doctor on time. But usually the inflammatory process develops quickly, and within a day a noticeable tumor forms. You definitely need to see a dentist. Only a doctor after an examination can determine how to treat a tooth abscess.
Home remedies such as rinsing the mouth with saline solution or herbal decoctions, as well as taking painkillers, may provide temporary relief, but will not eliminate the cause of the pathology. They can be used if it is not possible to immediately get to the dentist.
Treatment prescribed by a doctor must be comprehensive. Its purpose is to remove pus and destroy infection. The following methods can be used for this:
- drainage of pus;
- cleaning dental canals or sockets after extraction;
- treatment of caries, pulpitis and filling;
- use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Opening a tooth abscess is often performed surgically. Some clinics use low-intensity laser. It allows you to painlessly clean the cavity from pus and disinfect it.
If inflammation has developed on a healthy tooth, it can be saved if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Removal is a last resort; doctors resort to it only in advanced cases. But this is the main method of treatment if an abscess has developed in a baby tooth or wisdom tooth in an adult, as well as in cases where the dental tissue is severely destroyed.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms
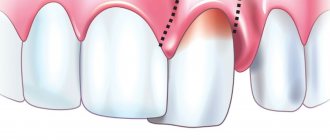
The diagnosis of “apical granuloma of the tooth” can only be made by an x-ray, on which a slight rounded darkening will be visible at the apex of the tooth root (Fig. 1). Darkening at the apex of the tooth root on an x-ray always indicates the presence of a chronic focus of inflammation and the presence of bone tissue resorption. As for the patient's complaints and other symptoms, in most cases they are not pronounced or may even be absent.
Most of the time, the tooth may not bother you at all, or periodically there may be pain when biting on the tooth or aching pain from hot foods. Those. These symptoms are standard symptoms of chronic apical periodontitis, one of the forms of which is tooth root granuloma. However, periodically (during periods of decreased immunity) an exacerbation of chronic, low-grade inflammation may occur.
An exacerbation is usually accompanied by acute pain, especially pronounced when biting on a tooth. In addition, the gums in the projection of the root apex may swell at such moments and be painful when touched. An exacerbation of the process may spontaneously subside (return to a chronic course), but can also lead to the development of severe purulent inflammation, which is popularly called gumboil. Regardless of the outcome of acute inflammation, you will ultimately need the help of a dentist to save your tooth.
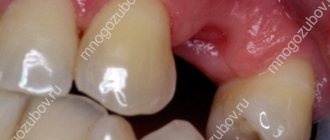
What does granuloma/cystogranuloma look like on the root of an extracted tooth:
Disease prevention
The occurrence of such inflammation can be prevented.
To do this, you need to follow preventive measures:
- brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day using not only a brush, but also dental floss;
- change the brush to a new one every 2-3 months;
- eat a balanced diet, limit your consumption of sweets;
- take multivitamins;
- visit the dentist annually for a preventive examination;
- carry out dental treatment in a timely manner and remove tartar.
An abscess is a serious pathology that, without treatment, can lead to dangerous consequences. To avoid this, you should immediately contact your dentist if you experience any problems or discomfort. Simple rules of prevention will help maintain health.