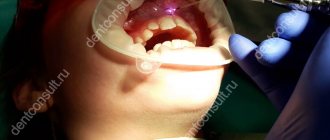
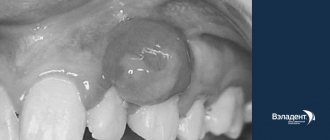
The development of inflammatory pathologies of the palatine tonsils is often accompanied by the formation of purulent-caseous plugs in the recesses of accumulations of lymphoid tissue. As the disease progresses, the cheesy deposits thicken, enlarge and begin to cause discomfort. Rinsing the lacunae of the tonsils is the optimal method of conservative treatment that removes plugs
.
Why do you need to rinse your tonsils?
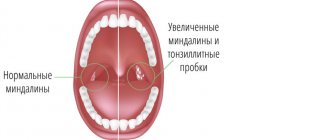
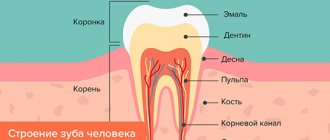
The palatine tonsils are an organ of the human immune system. They are located at the very entrance to the pharynx on both sides. Outwardly, they resemble almonds. This similarity gave this organ its name. The tonsils consist of a large number of winding canals - crypts. On the surface of the tonsils there are small depressions - lacunae. It is in them that tonsillitis plugs accumulate, which are removed by washing.
Our tonsils act like a filter. They filter everything that enters the oral cavity from outside. And if infectious flora gets on the surface of the tonsils, they begin to produce lymphocytes - cells of the immune system that begin to fight the “enemy”.
If the body's defenses are not enough to cope with viruses and bacteria, an inflammatory process (chronic tonsillitis) starts in the palatine tonsils. In the gaps, pathogenic microflora is activated, the remains of bacterial activity and dead leukocytes accumulate. This entire “mixture” is compressed and turns into white-yellow plugs on the tonsils, which are noticeable upon examination and emit an unpleasant odor. These plugs do not allow inflammation to subside, so sanitation of the tonsils is an important part of the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Often, rinsing is the only way to preserve the tonsils and avoid their removal.
Features of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis occurs with exacerbations, during which the same symptoms appear as with angina2,3.
During the quiet period3:
- discomfort in the throat bothers almost 98% of patients;
- putrid odor from the mouth is noted by up to 88% of patients;
- Doctors detect plugs and purulent plaque on the tonsils in almost 84% of cases;
- adhesions between the tonsils and arches are detected in approximately 60% of patients;
- enlargement and pain when palpating the cervical lymph nodes are diagnosed in 62% of cases;
- joint pain bothers every third patient;
- low-grade fever (up to 380C) is noted by 18% of patients;
- pain in the heart – about 8% of patients with chronic tonsillitis3.
Depending on the stage of development, the disease can occur in the following forms2,3:
- The simple form, in fact, is the initial stage of the disease, in which the pathological process is limited mainly to the tonsils2,3.
- Toxic-allergic form:
- Stage I: signs of general intoxication appear, such as low-grade fever, weakness, fatigue, as well as aching joints and heart pain associated with functional disorders.
- Stage II: complications of tonsillitis, such as peritonsillar abscess, sepsis, rheumatism, heart defects, etc., are added to general intoxication2,3. In this case, the picture of tonsillitis is complemented by the symptoms of these diseases.
Up to contents
Contraindications to the procedure
Properly performed sanitation of the tonsils is a highly effective procedure for chronic tonsillitis. But in some cases, the patient may be refused to undergo lavage. Contraindications to manipulation are:
- an infectious disease in the acute stage (here we are talking not only about inflammation of the tonsils, but about any inflammatory processes in the oropharynx. Even carious teeth can cause refusal to carry out the procedure, since during manipulation the infection can get to healthy tissues);
- oncological diseases;
- retinal diseases;
- first and last trimesters of pregnancy;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- high blood pressure;
- children under three years old;
- individual intolerance to the solutions used for washing.
In other cases, washing the palatine tonsils, carried out by a competent ENT doctor, gives an excellent result and allows you to achieve long-term remission when the symptoms of the disease do not bother you. The procedure is safe and well tolerated by patients. And most importantly, a high-quality procedure allows you to save the tonsils and avoid surgery to remove them.
There are several methods for carrying out the procedure: sanitation using a syringe and the vacuum method of washing the tonsils.
Schemes for preparing antiseptic solutions
Self-production of Furacilin, medicinal decoctions, saline solution and a number of other disinfecting liquids is allowed. Cooking methods are listed in the table below.
| Solution | Way | Proportions |
| Saline | Sea or table salt is combined with warm water. | 1 teaspoon of substance per 200 ml of liquid |
| Furacilin | The drug tablet dissolves in boiled water; the solution is infused for up to half an hour. | 2 pills per glass of water |
| Chlorophylliptate | The medicine is mixed with water. | 1 part drug to 5 parts liquid |
| From propolis | The alcohol (aqueous) tincture is diluted with water. | Alcohol: 1 tsp. medical product for half a glass of liquid. Water: 1:3 |
| From medicinal herbs | Medicinal infusions (oak bark, sage, chamomile, calendula) are poured with boiling water, infused for 30 minutes, and filtered. | 1 tablespoon per 200 ml of boiling water. |
When using solutions for the treatment procedure, you must remember the main rule: if you have an individual intolerance to the components of the product (this is often manifested by allergic reactions), the use of disinfectant liquids is prohibited.
Syringe method
This is the most common and accessible method of performing the procedure. And most likely, when you go to the district clinic, you will be offered exactly this.
To carry out the procedure, a needle-free syringe with a curved cannula attached to it is used. An antiseptic solution, for example, a furatsilin solution, is drawn into the syringe. The syringe directs a stream of solution directly into the lacuna. The jet “breaks” the tonsillitis plug. Purulent masses, washed out of the lacunae by the solution, enter the mouth. At this moment, the patient must spit the washing solution into a special tray along with the washed purulent contents. As soon as the manipulation is completed, the surface of the tonsils is lubricated with Lugol's solution.
This method is referred to as the old, “grandfather” methods. Yes, this method is inexpensive, but it cannot be called very effective either. With this technique it is impossible to completely rinse the tonsils and remove deeply located caseous masses. Also, such sanitation requires good professional training from the otolaryngologist. An inexperienced ENT doctor can injure the surface of the tonsils with a syringe, which will lead to the spread of infection to healthy tissue, which will only worsen the situation.
The apparent simplicity of performing such a flush convinces patients to buy a syringe at a pharmacy and try to carry out the procedure at home. But only a few manage to cope. Firstly, we should not forget about the traumatic nature of the method, and secondly, it is not possible to maintain the proper level of sterility at home.
Sanitation with a syringe is an inexpensive and accessible method. But it is much more effective to carry out vacuum rinsing using the Tonzillor apparatus.
Literature
- S. Ya. Kosyakov, I. B. Angotoeva. Modern ideas about tonsillopharyngitis. Medical Council, No. 17, 2015, pp. 32-36.
- T. S. Polyakova, E. P. Polyakova. Chronic tonsillitis: diagnosis, treatment, prevention. Russian Medical Journal, No. 2, 2004, pp. 65-68.
- G. R. Kaspranskaya, A. S. Lopatin. Chronic tonsillitis: different views on an old problem. Medical Council, No. 5–6, 2013, pp. 69-71.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®TABS.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®CLASSIC.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®TABS EXTRA.
Vacuum method
To carry out the manipulation, an ultrasonic device “Tonsillor” is used. As standard, the device comes with a vacuum nozzle for washing gland lacunae. At the beginning of the manipulation, the ENT doctor performs topical anesthesia of the palatine tonsils with a solution of Lidocaine. The patient sits comfortably in a chair and opens his mouth.
The vacuum nozzle is brought to the surface of the tonsils and attached to it. The washing solution is fed through a nozzle, passes through the gaps and, under pressure, washes out all the pathogenic contents from them. Antiseptic or saline solutions are used as flushing solutions. The solution passes through the thickness of the tonsil once and is not reused, since after washing it is removed into a special suction.
Since the waste solution goes directly into the suction, infection of healthy tissues during the manipulation is excluded.
The procedure is carried out under the influence of ultrasonic vibrations, which allows the medicine to penetrate deeper layers of tissue, and this contributes to a rapid recovery.
In general, the procedure on the Tonsillor apparatus resembles the principle of operation of a vacuum cleaner. This vacuum sanitation allows you to effectively clean the lacunae of the tonsils and get rid of purulent accumulations.
On average, five to ten sessions are required to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect.
At this point we could put a full stop and end the article. But there is another way to carry out vacuum rinsing - using a modified attachment of the Tonsillor device, which is used only in the ENT Clinic of Doctor Zaitsev.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Practically not used in modern otorhinolaryngology. For acute bacterial sinusitis, systemic broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are indicated, which successfully cope with the bacterial process without punctures and “cuckoos”.
Punctures for a bacterial process in the maxillary sinuses are mainly indicated if culture of the sinus contents is needed - usually when 1-2 courses of antibacterial therapy are ineffective.
Very rarely, such punctures are performed for diagnostic purposes, when it is not possible to perform radiography or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses. Another indication is severe pain associated with the pressure of the contents on the walls of the sinus. The puncture is done once during the main treatment. Several punctures are indicated only in the case of a persistent bacterial process with two or more courses of antibiotics, and there is no possibility of performing endoscopic surgery on the sinuses.
It has been proven that puncture of the maxillary sinus does not speed up the healing process.
It is important to know : puncture, like any invasive method, can have complications, including trauma to the medial wall of the orbit, nasolacrimal duct, soft tissues of the cheek, and nosebleeds.
Inflammation in the tonsils
The inflammatory process occurring in the palatine tonsils is called tonsillitis. Tonsillitis is a disease that affects children quite often. It has two forms: acute and chronic. The causative agents of the disease are staphylococci, streptococci and other viruses. The disease spreads primarily through airborne droplets, and the peak incidence occurs in autumn and winter. The first signs of acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) are:
- high body temperature up to 39°C
- severe sore throat, pain when swallowing
- the whole body is aching
- lethargy, weakness, adynamia
- headache
- vomiting, in the youngest - abdominal pain
- redness of the throat, rashes appearing on the back of the throat
Under favorable conditions, the disease goes away within a week. In the absence of proper treatment, the acute form can become chronic.
Methods for washing gaps
Cleaning tonsil lacunae is not a surgical intervention, but it should only be performed by an experienced otolaryngologist in an ENT clinic or medical center. You cannot clean it yourself. It is not recommended to ask relatives for help. Manipulation has a clear algorithm of sequential actions. Self-removal of plugs can lead to crushing of the tissues of the palatine tonsil, which will lead to inflammation of the peritonsillar tissue surrounding the tonsil. Also, inept actions can lead to damage to the soft and hard palate, the surface of the tonsils themselves and stomatitis. There are two ways to wash the tonsils for children: washing the lacunae with a syringe and washing the lacunae with the TONZILLOR apparatus. Let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Endolaryngeal infusions
Recommended for acute laryngitis, along with nebulizers, mucolytics and much more.
The cause of acute laryngitis in most cases is a viral infection. Therefore, the main treatment here is time. The use of antibiotics is not indicated even for mild bacterial infections in the larynx, which are much less common than viral ones.
With endolaryngeal infusion, the solution enters directly onto the vocal folds at the time of phonation, which means there is a very high risk of it entering the lower respiratory tract. In cases where the larynx is poorly visible and the procedure technique is not followed, the doctor pours the solution into the esophagus, the patient swallows it, and there is no positive effect after the procedure, even temporary. At the same time, such a “blind” infusion of the solution increases the risk of aspiration (entry into the respiratory tract).
Antibiotics are used for infusions into the larynx, which, when applied topically, do not have a bactericidal effect. Oil solutions can be used, the positive effect of which is easily replaced by a home humidifier and ventilation. The effect of using hormonal agents (dexamethasone or hydrocortisone) is very short-lived. Moreover, in emergency situations, for example, for singers before a concert, preference should be given to the systemic use of hormonal therapy. The use of hormones leads to the rapid disappearance of inflammation of the vocal folds and improvement of voice quality, but one has to put up with the possible side effects of this group of drugs, so in standard situations the potential risk of their use outweighs the possible benefits.
A number of studies have shown that the voice is restored in equal time - when treated with antibiotics and when taking a placebo.
Important to know : viral laryngitis usually lasts 7-10 days and goes away on its own.
Who's at risk
The following are primarily susceptible to the disease:
- Children are carriers of pathogenic microflora. As soon as favorable conditions for the disease occur (for example, during hypothermia), the bacteria are activated. An inflammatory process occurs. The main causative agent of sore throat is considered to be β-hemolytic streptococcus of group A or B.
- Malnourished children. An unbalanced diet, lack of essential vitamins in the diet, and, as a consequence, low body weight - all this inevitably leads to a weakening of the children's immune system.
- Children with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency conditions, when the body is not able to produce the required number of immune cells to fight viruses.
- Children experiencing frequent hypothermia. Low temperatures are always stressful for the body, especially for children. In such tense conditions, he cannot work fully. As a result, the smallest amount of bacteria becomes enough to cause disease.
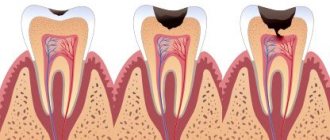
- Children with existing chronic diseases of the oro- and nasopharynx: caries, stomatitis, sinusitis, etc.
- Children with allergies