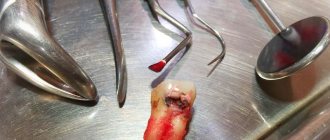
Local swelling of the root zone, compactions of various sizes, throbbing pain, sensitivity to temperature when eating, enlarged lymph nodes may indicate an acute inflammatory process of infectious etiology. In dentistry, there are several types of diseases, among them periapical abscess. It can be caused by advanced caries, chipping of an element of the dental system, overheating of the pulp due to tooth preparation and various pathologies. This can also happen due to poor-quality root canal treatment.
A periapical tooth abscess is an accumulation of pus between the molar and the gums. Purulent exudate can accumulate both in the inner and outer surfaces of the alveolar process of the lower or upper jaw. It most often begins in a tooth with a non-viable pulp, when the nerve dies, causing infection and progressive inflammation. The infection may gradually spread to surrounding tissue. Clinical symptoms are in many ways similar to acute periodontitis. The patient experiences increased sensitivity, acute pain, the mucous membrane may have swelling, there is active hyperemia, and overflow of blood in the vessels of the circulatory system.
Symptoms
- Intense dull throbbing pain.
- Discomfort when chewing food.
- Swelling in this area.
- Painful sensations when swallowing.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unpleasant sensations when opening the mouth.
- Change in molar color.
Other symptoms also include malaise, fever, weakness, and bleeding. It should be noted that in some cases the inflammatory process can be practically asymptomatic; activation can occur periodically, for example in the case of hypothermia. In this case, immediate assistance from a dentist is required so that he can quickly and accurately diagnose and establish a treatment regimen for effective recovery.
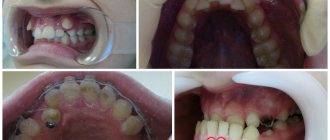
After tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a dental operation during which the gums are injured. If antiseptic rules have been violated or the patient does not provide the necessary postoperative care, infection can enter the wound. Bacteria will multiply quickly. Suppuration forms. If there is no treatment, the abscess affects the soft tissue.
Suppuration as a result of medical error after removal is rare. At the ARDC clinic, dentists use modern equipment, consumables, and medications. You can be confident in the quality of the procedure and compliance with the treatment protocol.
Improper postoperative care is a more common cause of abscess after removal. After the operation, the dentist must give recommendations on how to care for the wound. Careful adherence to all these rules will reduce the risk of suppuration at the site of the extracted tooth.
Causes of abscess
Complications associated with the inflammatory-destructive process can occur due to the following reasons:
- Poor quality endodontic treatment.
- Carious formations.
- Injuries to elements of the dentition.
- Unqualified prosthetics.
- Infectious diseases in the maxillofacial area, such as sinusitis.
Treatment of a periapical abscess without a fistula may be required in case of violation of the endodontic therapy protocol or incomplete obturation of the canal system. Provoking factors can be serious infectious diseases, hypothermia, and a reduced level of the body's immune defense. Leukocyte infiltration also often causes the formation of an abscess and microabscess.
Is it really that dangerous if left untreated?
☣️ You can endure the pain, but the abscess will not go away so easily. As the purulent abscess develops, it provokes pathological processes in the gums:
- secondary lesions with pus appear;
- the breakdown of red blood cells in the blood plasma begins (intravascular hemolysis);
- the body is poisoned (toxemia);
- blood clots form (DIC syndrome);
- blood pressure decreases;
- infectious-toxic shock occurs.
As a result, the abscess destroys the structures of the periosteum and periodontium. The bone tissue of the jaw decreases, the tooth at the site of the abscess becomes loose. The pus will begin to spread through the blood and lymph unless a fistula is formed or the abscess is opened surgically. If the course is prolonged, the risk of losing a tooth or implant increases.