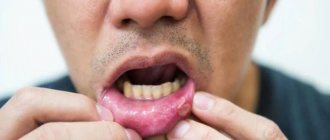
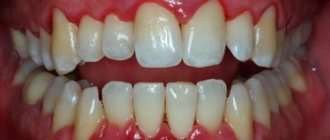
Xerostomia is a feeling of constant dryness in the mouth caused by insufficient salivation. It is also accompanied by a burning sensation and dryness of the tongue and throat, problems with chewing and swallowing food, a metallic taste in the mouth and difficulty speaking.
Xerostomia can be either a symptom of an underlying serious illness (HIV, diabetes mellitus, Parkinson's disease, cancer), or a consequence of previous surgical procedures (for example, removal of the salivary glands), drug therapy, radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
Saliva is a lubricant that facilitates the grinding and processing of food, and also has an anti-inflammatory effect, it remineralizes tooth enamel and neutralizes the negative effects of acids contained in food on the surface of the teeth. That is why xerostomia is a serious problem that requires comprehensive and immediate treatment.
What can cause salivary gland hypotension?
The causes of the disease are different, but most often it acts as a concomitant factor of another ailment, including in the oral cavity:
Constant dry mouth is often experienced by older people who take a large number of medications, especially their combinations. In this case, the disease acts as a side factor.
Dry mouth often plagues hypertensive patients, diabetics, and people with anemia associated with iron deficiency. It accompanies HIV infection, arthritis, and cystic fibrosis. The disease also develops against the background of autoimmune dysfunction in Shane's syndrome. Any virus (infectious mumps, for example) that enters the bloodstream or innervation system can become a catalyst for the development of xerostomia.
It is short-term in nature during moments of dehydration (fever, serious burns, significant blood loss, uncontrollable vomiting, diarrhea). Symptoms are pronounced in oncological diseases of the head and neck during radiation procedures.
Often, salivary dystonia occurs due to various intoxications of the central nervous system, brain injuries or tabes dorsalis.
After surgical removal of the salivary gland, the disease becomes irreversibly chronic. Therefore, the oral cavity requires constant additional hydration with special means.
With senile muscle weakness, when the lower jaw rises with difficulty, sleeping with the mouth open leads to xerostomia up to complete atrophy of the salivary gland.
In healthy people, symptoms may occur with problems associated with the nasal septum or the presence of polyps on the nasal mucosa. Frequent rinsing, especially with aggressive ingredients, will also result in a deficiency of saliva.
Xerostomia
Xerostomia (ICD code 10 - K 11.7) is pathological dryness in the oral cavity, caused by a decrease or complete cessation of salivation. The name of the concept in Latin, Xerostomia, comes from the Greek xero- (dryness) + -stoma (mouth). This is not a separate disease, but a symptom associated with another pathological process. Xerostomia is manifested by perversion of taste sensitivity and distortion of sensations in the oral cavity.
Specialists from the Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk branches of the West Dental family dentistry clinic will help identify the cause of this symptom and determine the specific treatment for all signs and pathological conditions. To do this, doctors have all the necessary high-tech equipment and sterilized instruments.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Prevention
A standard preventative measure is to drink more fluid; for an adult, the norm is 1.5-2 liters per day.
- It is necessary to stimulate constant salivation. You can suck on lollipops, chewing gum and sugar-free sweets;
- Elimination of bad habits. Minimize the consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking. Complete refusal is preferable;
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables. They prevent dryness and bitterness in the mouth;
- Rinse your mouth in the morning and evening with alcohol-free solutions;
- Avoiding dehydrated foods that are high in salt.
What symptoms haunt a patient with xerostomia?
The symptoms of the disease are extensive:
- the appearance of fungus in the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- modified taste and decrease in its brightness;
- constant thirst;
- difficulty swallowing;
- teeth damaged by caries;
- foul odor from the mouth;
- dry nose;
- speech disorders.
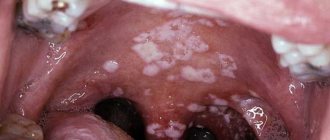
The disease is characterized by three stages. At an early stage, the “saliva factory” has difficulty coping with its functions, but with overwork or prolonged conversational stress, there is a shortage of it, and the mouth dries out. Distonated saliva foams more. At the next stage, complete salivary decompensation does not occur, and its secretion becomes irregular. During this period, problems with speech and swallowing food begin. More severe dryness is noted, the mucous membrane becomes pale pink and shiny. At the last stage, the function of the gland is seriously depressed. The manifestations of the disease become sharp: pain appears, lips dry out and peel. They may develop crusting and cracks in the corners. Ulcers appear on the inner surface of the mouth, and the likelihood of developing glossitis and stomatitis increases. The mucous membrane becomes noticeably red, and the tongue may swell.
Classification
There are 3 stages:
- The mildest stage, in which the submandibular and parotid salivary glands function, and saliva is secreted normally. Xerostomia appears as a symptom of overwork or after a long conversation. Upon visual examination, the saliva is foamy and the mucous membrane is moist.
- The normal functioning of the salivary glands is disrupted and dryness becomes constant, diction becomes difficult. A person has difficulty eating dry food. On examination, the mucous membrane is slightly moisturized, pale and has some shine.
- At this stage, the salivary glands stop functioning. Patients pay attention to severe dryness and painful sensations of the mucous membrane. Erosive and ulcerative surfaces form in the mouth, all aggravated by stomatitis, glossitis, generalized caries and flaky lips.
Treatment of xerostomia
The Implantmaster clinic will determine the exact nature of the disease. You can defeat xerostomia only by eliminating the factors that cause it. With therapeutic intervention, the disease recedes, but insidiously it can recur with new outbreaks. And only a set of systematic measures and accurate diagnostics give a productive result. The temporary form is completely cured. In a chronic course, competent therapy minimizes relapse history.
Treatment of xerostomia comes down to a set of activities in which the patient takes an active part.
The doctor will suggest:
- carefully observe oral hygiene;
- drink water often;
- do not eat salty, spicy, sweet foods;
- give up alcohol and smoking;
- use special rinses that replace saliva.
Folk remedies will also not hurt: decoctions of rose hips and lingonberry juice. Drinking cranberries combats dehydration. Rinsing with infusions of chamomile, sage or calendula helps.
Author:
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis is an important step in further eliminating symptoms and curing the pathological condition. The doctor begins by collecting anamnesis and understanding what medications the patient is taking. Then an ultrasound of the salivary glands and sialography are performed. If the underlying cause of xerostomia is associated with taking a large variety of medications, then its treatment will be simple. However, after courses of radiation, it is difficult, and sometimes impossible, to fully recover. Because this technique maximally suppresses the functioning of the gland and salivation.
From drought
But if the issue is exclusively age-related problems, then only symptomatic treatment is indicated. Will help:
- Diet – since atrophy of the salivary glands can occur because a person is not chewing enough, it is helpful to replace pureed, soft foods with harder foods (including fresh vegetables and fruits). Avoid eating salty and dry foods (crackers, crackers), as well as sugary drinks and sweets in general;
- water regime - increase fluid intake, but drink not in one gulp, but little by little and often. And not coffee and tea, but water with lemon or cranberry juice (these drinks provoke salivation);
- quitting smoking - cigarettes dry out the mucous membranes;
Article on the topicJust a piece of cake! What does a saliva test tell you?
- eating chewing gum and sugar-free candies - they increase the flow of saliva;
- regular use of special rinses (without alcohol) containing extracts of medicinal plants and essential oils (for example, rosemary, chamomile, horsetail, sage, nettle). These ingredients not only freshen breath, but also activate metabolic processes in the gum tissue, which contributes to their better nutrition and regeneration. They also have an anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, soothing effect on the oral cavity, help remove plaque from teeth and strengthen gums;
- eating hot peppers – they contain the alkaloid capsaicin, which enhances the secretion of saliva. But pepper is allowed only if there are no stomach problems and only in small quantities;
- air humidification - if there are no humidifiers, at least place bowls of water near the radiator;
- massage the gums and inner surface of the cheeks with your tongue - you can also simply suck on a plum pit or something hard, this will increase the flow of saliva.
Not a small thing at all
If there is not enough saliva, then a person not only regularly suffers from thirst, problems with swallowing and bad breath, chapped lips, but can also bring many other troubles. Among them:
- poor digestion - without a sufficient amount of saliva, food is poorly moistened and poorly absorbed, hence the lack of vitamins and minerals, as well as many gastrointestinal diseases;
- poor oral hygiene – a lack of saliva impairs the remineralization of tooth enamel, causing teeth to lose strength and tooth enamel erosion may develop. In addition, saliva itself has antibacterial properties. The less it is, the stronger the growth of pathogenic microflora, which, in combination with a violation of local immunity and deterioration of the blood supply to the gums, leads to their inflammation - gingivitis. If this condition is neglected, it is not far from periodontitis and tooth loss;
- risk of injury to the oral mucosa - due to dryness, damage and ulcers in the mouth are possible;
- diseases of the ENT organs - dry mucous membranes provoke the proliferation of pathogenic microbes, which causes sore throat, pharyngitis and other diseases;
- loss of sense of taste and inability to eat dry food.
Functions of saliva
Saliva is an integral element of a healthy oral cavity; its functions are quite numerous. Let's consider its main tasks:
- Participates in the digestion process. When food enters the mouth, it is crushed by the teeth and mixed with saliva, which contains special enzymes. One of them is amylase, which breaks down starch into maltose, which subsequently turns into glucose in the duodenum. Saliva moistens food, gluing its components into a smooth lump, allowing it to glide down the esophagus.
- The oral fluid contains lysozyme, a substance that can inhibit harmful bacteria, so it disinfects the oral cavity and cleanses it of food debris, preventing them from rotting.
- It has mineralizing properties - protects and partially restores tooth enamel. Saliva contains calcium and phosphate ions that fill empty cells in the crystal lattice of the substance that makes up the enamel.
- Another function is to wet the mouth, which facilitates articulation.
Water and chewing gum will help
First of all, you need to see a dentist who will check the functioning of your salivary glands. Also, with dry mouth, you can contact an ENT specialist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and neurologist, since xerostomia can be a consequence of diseases in their profile.
It is precisely because dry mouth is not a self-sufficient disease, but a symptom, that its treatment can be difficult. Doctors usually recommend the following methods:
- First of all, you need to treat the underlying disease. It is advisable to eliminate or reduce medications with the side effect of dryness.
- Special saliva substitutes will help moisturize the mucous membrane. They come in the form of gels, sprays, oils.
- A patient with dry mouth syndrome is recommended to drink more water, but not in one gulp, but in small sips.
- Chewing gum or lollipops will not help get rid of xerostomia, but they will temporarily alleviate the situation, as they promote salivation. However, it is better not to get carried away with sweet tastes, so as not to provoke the appearance of caries.
To quickly get rid of the disease, you need to give up not only sweets (especially at night), but also dry, spicy, too cold or, conversely, hot food. In addition, alcohol and smoking should be avoided, as these bad habits also “dry” the mucous membrane.
As a preventive measure and in the early stages, it is advisable to install an air humidifier in the room, as well as carefully monitor oral hygiene: add the use of dental floss and rinses to traditional brushing of teeth with paste. In addition, if you have problems with salivation, you should visit the dentist more often and have your teeth “cleaned” of plaque.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!
Therapeutic and prophylactic agents
When dryness rarely bothers you, for example, only in the mornings, in the heat or after intense workouts, to normalize salivation, your doctor may recommend:
- therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes;
- anti-inflammatory, antiseptic rinses;
- sprays and gels with moisturizing polymers;
- chewing gum and lozenges for dry mouth.
Most of the listed products are included in the product line of such well-known manufacturers as Miradent (Miradent Aquamed xylitol lollipops with passion fruit flavor), BioXtra, Dentaid (Dentaid Xeros tooth gel for dry mouth) and others. Branded products are developed and created specifically to improve the quality of life of patients suffering from xerostomia and its manifestations.