Flux is the name given to a purulent abscess that occurs under the periosteum as a result of infection. The disease is also called periostitis, and must be treated by a dentist. Should I do anything to make the flux break through faster at home? Depends on the situation in which the patient finds himself.
Why does pathological formation occur?
The main reason for the development of the pathological process is injury to the soft tissue of the gums. The disease also often develops against the background of:
- Caries.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket.
- Violation of the rules of oral hygiene.
- Infectious diseases: tonsillitis, furunculosis, etc.
Pathology is characterized by gradual development:
- The initial stage is characterized by the appearance of mild pain when touching the gums.
- In the second stage, swelling and redness of the gums develop, and the pain becomes intense.
- If left untreated, pus appears in the gum pocket, body temperature rises, and swelling spreads to the cheek.
- Next, an extensive inflammatory process develops, characterized by the appearance of acute throbbing pain and an increase in the area of edema. The patient's general condition deteriorates significantly.
Read more about: what is flux
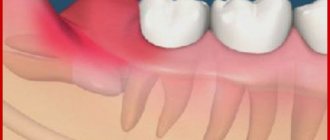
In detail, gumboil is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the dental periosteum. The development of flux begins from the internal dental tissues or gum pockets when food debris gets into them. As a result, serious suppuration begins, which grows to the periosteum, and the soft gingival tissue on the inside of the cheek begins to swell.
Flux is accompanied by severe pain with a certain frequency. If the symptoms of flux are not diagnosed in time and you do not visit the dentist, the infection can reach the brain. The most common symptoms of gum gum disease are presented below.
Types of disease
Flux is classified according to its development into the following types:
- Odontogenic. Pathology occurs against the background of advanced diseases of teeth and gums,
- Hematogenous. The disease develops when infection penetrates through the circulatory system.
- Lymphogenic. The cause of the disease is pathogenic microorganisms in the lymphatic system.
- Traumatic. Flux occurs at the site of injury to the periosteum, often after unsuccessful dental procedures during dental treatment.
According to the degree of spread, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- An ordinary flux that does not affect the periosteum.
- Fibrous flux, characterized by the onset of inflammation in the tissues of the periosteum.
- Orthodogenic flux, which develops as a complication - osteomyelitis, which requires tooth extraction.
- Albuminous flux, characterized by a chronic course, subfertile temperature and the occurrence of suppuration.
Development of the disease
Periostitis can be suspected by the unpleasant pain that constantly appears closer to the root of the tooth. The disease develops in several directions and often ends with a breakthrough of pus:
- primary flux - accompanied by swelling of the face on the side of appearance;
- inflammation spreads to nearby tissues, causing a purulent process;
- the gum pocket between the teeth and soft tissues becomes infected;
- There is extensive swelling of the face and severe swelling on the side of the diseased tooth.
While periostitis develops, it cannot be opened using additional methods. During the purulent process, the patient feels a tugging pain, his temperature rises, and painkillers do not work.
Inflammation should be treated with antibiotics prescribed by the dentist.
It is dangerous to treat flux at home due to the risk of complications. If the swelling becomes global, phlegmon may begin - the purulent contents of the tumor penetrate between the muscles of the face, into the neck, and can seep into the chest. As a result, sepsis begins, infected blood enters the brain and leads to coma or death.
If you open the abscess with a needle or other mechanical means, the patient will feel slight relief. But after some time the process will resume with renewed vigor .
Diagnostic methods and treatment methods
An accurate diagnosis is a guarantee of successful treatment. To do this, the doctor conducts the necessary examination. It includes a diagnostic examination and fluoroscopy. To assess the degree of the inflammatory process, laboratory blood tests are performed.
There are two methods of flux treatment used in dentistry:
- Making an incision on the gum to open the purulent sac. After removing the pus, drainage is installed, which prevents premature healing.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal. This procedure is carried out when the cause of the flux is caries or the infection has penetrated through an existing crack in the tooth.
Special rinses are effective in treating flux. Solutions have regenerating and anti-inflammatory properties, therefore they can speed up healing. The simplest composition that can be used for rinsing with flux is a soda solution. If you carry out the procedure every couple of hours, you can quickly reduce pain and inflammation. To prepare the composition, dissolve a couple of teaspoons of soda in a glass of warm water. This amount of solution is enough for a day.
You can reduce swelling with a weak solution of manganese. This composition has strong disinfectant properties, which makes it possible to fight pathogenic microorganisms. For a similar effect, you can use the antiseptic agents Chlorhexedine or Miramistin. These drugs need to be used to irrigate the oral cavity.
An effective medicinal preparation for rinsing is Rotokan. It has a natural composition and contains extracts of chamomile, yarrow and calendula. For the solution, one spoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is carried out 4-5 times a day.
Do I need to treat burst flux?
Dentists note that it is necessary to treat gumboil. After all, the disease is dangerous because it leads to many complications, including phlegmon (purulent inflammation of the jaw tissue) and even sepsis - with this pathology, the infection spreads throughout the body.
So, why treat periostitis if the abscess has broken through:
- the pus will not come out completely - its remains will still be under the gum and can give rise to an inflammatory process with even worse consequences,
- the root cause of the flux has not been eliminated: the infection accumulated in the root canals will continue to provoke further suppuration if appropriate measures are not taken.
Recommendations after opening the flux
When the first symptoms of flux development appear, you should not self-medicate. It is a mistake to believe that swelling and pain can be relieved with warm compresses, lotions based on herbal infusions or other folk remedies. Independent experiments aimed at combating flux can lead to complications.
It is important to remember that you should not take painkillers less than 3 hours before visiting the dentist. Otherwise, there will be problems with making a diagnosis. After the tooth flux has been exposed, you should not take aspirin, as it increases the risk of bleeding. If after 12 hours the condition has not improved, you should consult a doctor immediately.
What happens if periostitis is not treated?
It's simple. An increasing amount of pus will cause further development of swelling and puffiness of the face. Further, the lymph nodes located in the neck may become larger. Inflammation will also cause fever and pain.
A very dangerous complication of flux is phlegmon. This is a breakthrough of the “bag” in which the pus is located, and the free spreading of the contents over the muscles and tissues of the cheek, neck, etc.
Jaw osteomyelitis is another possible complication of untreated gumboil: it is an inflammation of the jaw bones (usually this occurs in the lower jaw).
In other words, it is better not to allow serious consequences, but to seek qualified medical help as soon as possible.
Prevention
Understanding what gumboil is, you need to monitor the condition of your teeth and gums. Prevention consists of following hygienic rules for caring for the oral cavity. It is important to buy a quality toothbrush and good toothpaste to minimize the risks of developing caries. You need to brush your teeth twice a day: morning and evening.
After eating, it is necessary to remove food debris from the interdental spaces and use a mouth rinse to treat the oral cavity. To do this, you can buy the product at the pharmacy or prepare it based on propolis tincture, sea or table salt.
It is important to visit the dentist twice a year for preventive examinations. All diseases at the initial stage are successfully treated. Tartar should be removed regularly. It is in these deposits that pathogenic bacteria multiply, which, if the soft gum tissue is accidentally injured, can cause the development of gumboil.
To strengthen your gums, you must include fresh fruits and vegetables in your daily diet: apples, carrots, etc. They clean plaque on tooth enamel, which reduces the likelihood of tartar formation.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on factors such as the localization of inflammation and the causes of its occurrence, the body’s resistance, and the duration of the disease. Patients experience:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- deterioration of health;
- loss of appetite;
- weakness;
- temperature rise is possible.
Patients complain that not only the tooth hurts with gumboil: the painful sensations radiate to the ear, temple, and neck. In addition, swelling appears, due to which facial features lose their configuration. Depending on the location of the pain, the cheeks, upper or lower lip, chin, zygomatic and infraorbital areas swell from the flux. At the same time, the mobility of the jaw and lips is limited, and the patient has difficulty opening his mouth. The pain can be periodic: relief occurs when purulent exudate periodically pours into the oral cavity through the formed fistula.
In chronic periostitis, the symptoms are less pronounced. The pain is periodic, not severe, the contours of the face change slightly.
Causes of periostitis
Flux can occur for a number of reasons, like any disease. An oral disease associated with infectious infection is called periostitis. It can cause plaque, tartar, periodontal disease with pulpitis. Causes of a flux blister:
- Past illnesses such as sore throat, influenza, and furunculosis.
- Injections of medications.
- Injury to the jaw, oral mucosa.
- A filling containing arsenic left in a tooth cavity.
Infection of delicate tissues can cause a blister to form in the mouth. It is important to begin therapy for periostitis immediately after consultation with your doctor, otherwise the diseased tooth will be destroyed under the influence of dangerous microorganisms.
If the flux was caused by pulpitis, the disorder will be accompanied by severe pain. Soon the painful sensations subside, and the patient begins to think that he is healthy. The disease begins to proceed unnoticed, as the pulp has died.
It is difficult to make a diagnosis, since the form of periostitis is hidden. Infection at the root of the tooth leads to the accumulation of pus. The mass of pus that has reached the limit can lead to damage to the jaw bones.
Treatment of flux (periostitis) in 2021
The doctor’s actions will depend on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the clinical situation.
The first step is dental diagnostics - computed tomography. This 3D visualization allows you to see all the structures of the tooth, assess the volume of inflammation and its distribution. Such a diagnosis will clearly show whether the canals have been previously treated.
The dentist also carefully collects anamnesis from the patient. Based on the medical history and diagnostic results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and chooses treatment tactics.
An advanced case: they resort to tooth extraction. In others, they try to preserve it. To do this, anesthesia is administered and mechanical and medicinal treatment of the root canals is carried out. If necessary, an incision is made at the gum to drain the exudate. Antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and vitamins are prescribed.
After this, the canals must be sealed at the next visit. If even after all the treatment measures the tooth hurts, the swelling returns, then it needs to be removed.
How to cure gumboil
With periostitis, there can be no talk of any home treatment. Prompt medical attention is required. At best, home treatments will briefly relieve symptoms; at worst, they will accelerate the course of inflammation. It is strictly forbidden to heat the affected area (as the pus spreads faster), take antibiotics and painkillers without a doctor’s prescription (there is a risk of bleeding). If you ignore the problem, you can achieve sepsis - blood poisoning - and even death.
At the clinic, the doctor conducts an examination, consultation, and, if necessary, prescribes x-rays and blood tests to determine the extent of the disease and the level of leukocytes. If the patient seeks help at an early stage of periostitis, the specialist prescribes therapeutic treatment. This is taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs that destroy pathogens. If the situation is advanced, the doctor removes the flux through surgery: administers anesthesia, makes an incision in the gum, cleans out the pus, disinfects the wound and installs drainage. Additionally, laser therapy or iontophoresis may be needed.
This is followed by a period of rehabilitation: taking antibiotics, immunomodulators, rinsing with antiseptics. Monitor the condition of the oral cavity for 3-4 days. If during this time the symptoms do not subside and the swelling does not go away, you should consult a doctor again. If the tooth crown is destroyed by more than 50%, as well as in case of relapse of periostitis, the tooth will have to be removed.
Forecast
If the patient strictly adheres to all recommendations and carefully monitors hygiene, then there is no need to fear relapses.
If treatment was started already in the acute stage of flux or interrupted in the middle, then the prognosis becomes less pleasant. Flux can become chronic, which increases the risk of re-development several times. If the patient does not seek qualified help on time, then the flux can even cause blood poisoning, which leads to death.
It is very important to use only proven treatment methods and consult with experienced specialists, since some consequences of self-medication can be even more unpleasant than the disease itself.
Is it necessary to remove a tooth during periostitis?
Previously, with an advanced form of the disease, a unit whose roots were damaged was torn out. Today doctors prefer conservative technologies. Removal is carried out only when the crown is completely destroyed and the quality of the roots is unsatisfactory.
If the image confirms that the root canals are not inflamed, prosthetics are performed. A tab is installed inside the root. It is held securely in place by dental cement. A crown made of metal, metal-ceramics, zirconium oxide or other material is fixed on top.