Some parents notice a small bubble of liquid on the lip of their breastfed babies. As a rule, this is a common callus, which appears as a result of prolonged and intense sucking of the breast or friction of delicate sponges against the nipple. However, sometimes such a watery blister may indicate the appearance of a disease, which may include herpes, stomatitis or thrush.
In this article, we will look at how to distinguish a normal callus on the lip of a newborn from signs of infection. And we’ll find out what to do to get rid of a baby’s callus.
Why does a callus appear on a newborn's lip?
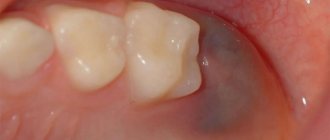
A callus on a baby's lip is a small watery formation with liquid inside, covered with skin on top. Sometimes the formation can become covered with a dense crust, then it becomes dry, hard and dense. Calluses on the lips of newborns can appear as early as 4-14 days of breastfeeding. After a certain time, they quickly disappear, but may subsequently appear again and even become a regular occurrence.
As practice shows, calluses can remain with a child until the end of breastfeeding and last up to 1.5-3 years. When is the best time to wean your baby and stop breastfeeding, read here.
In a newborn, a callus appears due to active sucking. Babies' skin, especially on the lips, is very delicate, soft and sensitive. Therefore, with regular, prolonged and strong friction, it rubs and is slightly injured. Pediatricians note that the presence of such a milk callus indicates the child’s good appetite, normal digestive function and a developed sucking reflex.
Infant tremor, causes
The characteristics of a newborn's body are always reflected in their behavior. Even full-term babies are born with undeveloped systems and organs. This is fine. Hearing, vision, digestive, immune and endocrine systems must adapt to new conditions, and this takes time. Nerve centers are responsible for coordinating movements. Their immaturity at birth is the main cause of chin tremors.
There are often cases when the chin of a month-old baby shakes due to the consequences of an unfavorable pregnancy and problematic childbirth.
Another reason is related to the imperfection of the endocrine system. Any emotional experiences in the life of children under 1 year of age lead to the release of an excess amount of norepinephrine into the blood. This hormone increases tension, which causes twitching of different parts of the body. In addition to the chin, the lower lip, limbs, and head may tremble.
A variety of factors can trigger the appearance of tremors. Among them there are also dangerous ones associated with serious neurological disorders. The following abnormalities are often detected in children:
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Hyperglycemia.
- Sepsis.
- Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
- Intracranial hemorrhage.
Without the participation of specialists, it is very difficult to understand the causes of involuntary twitching of the chin. Not every young mother is able to correctly assess the condition of the baby, understand what is happening and how to behave correctly in such situations. If in doubt, go to the doctor, and the slightest suspicion of pathology should be the reason.
What to do if a newborn has a callus on the lip
- First of all, determine whether it is really a milk callus and not a symptom of any disease;
- As a rule, a milk callus is located on the upper lip of a newborn. It can be observed much less frequently on the lower one;
- A real milk callus does not cause discomfort to the baby, he continues to eat and suck the breast or pacifier, behaves calmly, does not cry or be capricious;
- A true milk callus is white or light in color and has a clear liquid inside;
- Milk callus does not require treatment. It disappears on its own, may appear again and be regular;
- Do not open the bladder or release the liquid, otherwise you will injure the tissues and increase the risk of infection!;
- If the callus bursts on its own, treat the area with hydrogen peroxide;
- If the callus causes discomfort during feeding and provokes anxiety, then an infection has occurred and the disease begins;
- A watery blister with yellowish liquid and bright redness around indicates the presence of stomatitis or thrush;
- An elevated temperature and the appearance of several watery formations are signs of herpes;
- Herpes, stomatitis and thrush must be treated.
How to feed a baby with a cleft lip
The optimal source of nutrition for a child in the first months of life is breast milk. Try to save it for your baby.
You can try breastfeeding a baby with a cleft lip. In some cases, the child will be able to suck even if there is a wide defect in the upper lip. However, remember that during feeding, air access through the nasal passage must be required, otherwise there is a danger of aspiration of the contents of the oral cavity into the trachea with respiratory and cardiac arrest.
In the vast majority of cases, babies with clefts of the upper lip and palate cannot suck. Therefore, it is necessary to use other feeding methods. The most appropriate and simplest way is to feed the baby from a spoon: the newborn is placed in the mother’s arms in a semi-vertical position (head and upper body raised), expressed milk or mixture collected in a spoon drops dropwise onto the baby’s cheek mucosa and is then easily swallowed.
In the first days of a newborn baby’s adaptation to spoon feeding, it is advisable to use a coffee spoon, which you can then exchange for a more capacious one (silicone, plastic or metal). Within 1-2 days you can easily learn how to feed your baby this way. However, during feeding, be sure to control the swallowing of formula or milk. Do not allow a large volume of food in the oral cavity!
During feeding, your baby swallows a large amount of air along with food. Do not forget to take short breaks in feeding, during which the baby is held in a “column” and burps air.
During the feeding process, some auxiliary items can provide you with significant help: special bottles with spoons attached to them or Soft Cup from Medela. In some cases, special devices in the form of a syringe with a nipple from Avent will help you. By pressing the plunger and pressing the nipple against a larger portion of the palate or buccal mucosa, you can easily feed your baby. Some babies prefer the Medela Hubberman sippy cup.
In some cases, in babies with Pierre Robin syndrome, the most appropriate option is to use bottles with replaceable long latex nipples. You can change the number and diameter of holes on the nipple, thereby selecting the most optimal flow of formula or milk.
Please pay special attention: if the child’s somatic status is satisfactory, there is no need for prolonged tube feeding! The exception is newborns who require intensive treatment and appropriate care and observation due to their general (severe) condition.
In any case, after the birth of your child, we strongly recommend that you seek help and advice from a specialized institution. Medical staff will expertly help you choose the best way to feed your baby.
Stomatitis in a baby
Stomatitis involves inflammation of the oral cavity, damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue and gums. In this case, the baby feels anxious, refuses to eat, eats poorly and sleeps poorly. Three days after the onset of infection, a white coating forms on the tongue, which subsequently spreads to the hard palate, mucous surface of the cheeks and the entire mouth. In this case, cracks, “jams”, and a watery blister with a pronounced red shell and a yellowish liquid inside appear in the corners of the mouth and lips.
If stomatitis is detected, improve the hygiene of the baby and nursing mother, be sure to sterilize dishes and toys. After this, the infection will clear up in five to seven days. To speed up recovery and alleviate the baby’s condition, if the baby is not allergic to parsley, give the child an infusion with this herb. To do this, chop the parsley root and pour a tablespoon of the plant with cold water, bring to a boil and leave covered for an hour. Then strain and use a teaspoon all day long.
The mucous membranes of the mouth can be wiped with a solution of baking soda after feedings or naps, and treated in the morning after a night's sleep with sea buckthorn oil and aloe juice. They disinfect areas of the skin, tighten and heal wounds in a short time.
For severe forms of infection, the doctor may prescribe special antifungal ointments. Do not use medications without consultation and prescription of a specialist! How to cure stomatitis in infants and nursing mothers, see the link.
How to treat tremors in babies
Only a doctor can decide how to treat chin tremor. When diagnosing neurological abnormalities, medications are used, but most often children are prescribed massage, swimming and gymnastics. All therapeutic actions are aimed at relaxing the nervous system. A specialist may recommend herbal infusions based on mint, lemon balm, chamomile and valerian. Using sedatives, you can do baths and wipes.
If the baby is not yet 2 years old, the reaction to medicinal herbs can be unpredictable. Do not rule out allergic and toxic reactions. The younger the child, the more serious the complications can be. Natural helpers are safe only when used correctly. The duration of treatment, administration and dosage should be controlled by a doctor.
Caution must also be observed when performing relaxing massages. If there is no experience and sufficient knowledge in this matter, it is better to entrust the procedure to a specialist.
With adequate therapy, the state of the nervous system can be easily restored and normalized. If no pathology is identified, parents can help the baby. Learn to understand what causes your baby’s dissatisfaction and, if possible, eliminate all irritants. Follow your daily routine and diet, walk and swim more, create a favorable, calm atmosphere at home. For a child, a permanent contract with his mother is very important. When a loved one is nearby, children feel protected. This has a positive effect on health and behavior.
Thrush in a newborn
With thrush, a white coating with a red rim forms on the baby’s gums, tongue and cheeks. In addition, a rash and redness may appear on the body, and yellowish blisters or blisters on the lips. At the same time, the baby is capricious, refuses to eat, sleeps poorly, and feels discomfort.
In this case, it is also important to improve hygiene, disinfect things and objects that can get into the baby’s mouth. Products are boiled or sterilized for at least twenty minutes. To cure thrush, you can also treat your mouth with a soda solution up to eight times a day. To prepare this remedy, dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of boiled warm water.
Stomatitis and thrush can be caused by poor hygiene, too early or incorrect complementary feeding, fungus and thrush on the breasts of a nursing woman. To prevent the development of infection, maintain your hygiene and the hygiene of the mine. Be sure to clean your mouth after each feeding and burping, and remove any remaining milk or food from your baby’s lips. Thoroughly clean and sterilize bottles, nipples, baby dishes, toys and other objects with which the baby has constant contact.
Brush your mouth, tongue and teeth regularly. Up to six months, use special finger wipes or a sterile gauze bandage, after six months they switch to silicone finger brushes, and after a year you can already use a children’s toothbrush with soft bristles. Read more about oral and dental hygiene for a newborn in the article “How to properly brush your child’s teeth.”
Prevention of intestinal colic:
- Follow feeding technique: monitor the baby’s position when feeding so that the baby does not swallow air along with food. If the baby is bottle-fed, you can change the formula only after consulting with your pediatrician. After feeding, it is recommended to raise the baby to an upright position and wait for burping.
- Do not overfeed your child. Mom must adhere to a feeding schedule. If your baby is bottle-fed, it is important to follow the rules of preparation and dosage of food recommended by your doctor.
- Place on the tummy before feeding - this will strengthen the abdominal muscles and improve digestion. You can start with a couple of minutes and gradually increase the time.
- A nursing mother must follow a diet. It is important to exclude potential allergens (chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, seafood, milk, etc.), spicy and fatty foods, as well as laxatives and gas-inducing foods.
- Create a calm atmosphere. For the best results, it is important that the baby is calm. The mother can talk to the child, sing a lullaby, play a recording with monotonous quiet sounds (the sound of the surf, the rustling of a fan, the beating of the heart) or calm classical music.
To relieve gas, 30-60 minutes after eating, you can lightly stroke your tummy clockwise. After the massage, bend and straighten the baby’s legs several times. In some cases, warmth helps relieve an attack of colic: consult your pediatrician; perhaps a bath with soothing herbs or a warm diaper placed on the tummy will help your baby.
Milk callus or herpes
Herpes is another unpleasant disease that can be accompanied by the formation of a watery blister on the lip. Moreover, it can only develop in a baby inside the womb or during childbirth. If the mother has acute herpes, the risk of the child getting sick is 75%.
Herpes can appear as early as the second week after the baby is born.
In this case, bubbles and blisters form not only on the lip, but also on other parts of the body. In addition, the infection is accompanied by fever, drowsiness, and lethargy. The baby may experience convulsions and decreased muscle tone. Herpes is very dangerous for newborns, so urgent and competent treatment is required. Be sure to consult a doctor! Subscribe to our VKontakte group
When does tremors become dangerous?
Infant tremor is observed for the first time at 2 months of a child’s life. Sometimes the phenomena disappear at 4 months. In premature babies, chin trembling can be observed up to 1 year. If the symptoms do not go away for up to 6 months, are accompanied by the appearance of perspiration on the skin, increasing intensity and too violent a reaction to external stimuli, this is already a deviation. Spontaneous movements and convulsions can be dangerous.
Parents should be wary if the chin shakes for more than 30 seconds while crying. Simultaneous trembling of the legs, arms and head is also considered abnormal. The manifestation of these symptoms may indicate the presence of a pathology, but there is no need to panic. In infancy, such conditions can be treated easily and without consequences.
A child under 1 year of age needs regular examinations by a neurologist. Don't miss scheduled consultations. They are usually prescribed at the ages of 1 and 3 months, at six months and upon reaching 1 year. During these important periods, specialists evaluate the baby’s motor activity, his emotional state, muscle tone, reflexes, and the functioning of his senses. If deviations are detected, the necessary treatment is prescribed.
What it is
A callus is a keratinized top layer of skin that appears as a result of prolonged friction of an area of the dermis. A kind of protective mechanism that protects the skin from further damage.
There are three types of calluses:
- dry - a layer of dead epithelial cells forms a hard crust;
- wet - liquid (lymph) collects under the damaged layer of skin, forming a callus bubble as a barrier between the external irritant and the damaged dermis;
- blood - fluid mixed with blood accumulates in the callus.
What should be considered constipation in an infant?
It is understandable that the lack of stool in a baby causes concern for parents and often becomes the reason for unnecessary self-medication. On the other hand, lack of basic knowledge about the proper frequency of bowel movements in children sometimes leads to delays in necessary treatment and complications. Therefore, first, let’s figure out what constipation is.
According to generally accepted opinion, constipation in babies under three months of age is considered to be a delay in bowel movements for 2-3 days. If difficulties with bowel movements persist for two or more weeks, they speak of chronic constipation.2,3. At the same time, the frequency of stool decreases (in comparison with individual characteristics3), the feces become dense, fragmented, and acquire an unpleasant putrefactive odor.
To empty the intestines, the child strains hard and for a long time, his face turns red, his legs are drawn up to his stomach. Sometimes the contents of the rectum are so hard that they injure the delicate mucous membrane and cause painful cracks to form. In this case, the baby cries, and a strip of scarlet blood appears on the surface of the stool.
Constipation affects the general condition of the baby. He experiences pain and bloating in the abdomen, popularly called “colic,” he eats poorly, becomes lethargic and moody.
It is the appearance of common symptoms of constipation in a breastfed newborn that serves as a guideline for diagnosis4. If they are absent, the child eats well, does not spit up, gains weight normally, the condition is considered to be “pseudoconstipation”, which does not require any intervention4.
Up to contents
Types of pemphigus
People distinguish between true pemphigus (pemphigus) and other blisters on the skin. The true one is of the following types:
- ordinary, or vulgar - occurs most often. Externally intact and undamaged skin becomes covered with blisters with serous fluid inside, which burst easily and quickly and heal. Localization - the mouth area and the mucous membrane of the lips, as well as the nasolabial triangle. At first glance, harmless bubbles appear more and more often, each time occupying a larger area throughout the body. When they burst, they leave pink eczema in this place. The child should begin receiving adequate therapy between 6 months and 2 years. Otherwise, there is a danger of death;
- vegetative - the course of the disease differs from the usual type only in the consequences on the skin. In this case, instead of eczema, vegetation papillomas of a grayish tint remain. These papillomas are growing;
- leaf-shaped - got its name due to the visual appearance of the crusts formed after the bursting of bubbles. A distinctive feature of this species is the rapid development of pathology. In this case, the count is not in months, but in days. In this case, the skin peels off in whole pieces shaped like leaves;
- erythematous - is a complication after leaf-shaped and has no striking differences from the previous form of pathology;
- seborrheic - originates in the hair on the head and face. Small bubbles quickly become a yellowish crust. The progression of the pathology is slow, affecting the back, abdomen and limbs. After peeling off the crust, weeping eczema remains.
There are other types of pemphigus that are not related to pemphigus:
- infectious viral pemphigus in children - develops under the influence of viruses: Coxsackie, enterovirus 71. In this case, the latter option may have the nature of an epidemic. It has specific localization sites - feet and palms, butt and genitals;
- congenital syphilis - occurs when there is intrauterine infection with syphilis. It appears within a couple of days after birth. The blisters burst quickly and leave behind weeping pink eczema.
Untrue types of pathology in medicine refer to the symptoms of pemphigus in children. This course of the disease allows for faster and more correct treatment of pemphigus in children, aimed at eliminating the root cause. The most difficult thing in this pathology is establishing the true cause of the disease.
A rare but severe type of true pemphigus is the paratumor type. It has the most striking symptoms. It occurs against the background of leukemia and lymphoma, and also appears as a harbinger of the development of a malignant tumor.
Diagnostics
This pathology is rare, and pediatricians, as a rule, cannot determine it accurately. Therefore, the primary stage of diagnosis is the distinction between pemphigus and other dermatological diseases that are accompanied by rashes of blisters and blisters.
Differential diagnosis is carried out using a special method - Nikolsky's test. The essence of the test is to rub the skin near the bubble and on a distant area of the skin, as well as pressing the fingertip on the bubble. A positive result is considered to be the presence of signs of skin separation:
- spreading of serous fluid into adjacent layers of skin when pressed;
- slight peeling of the skin in the form of a ribbon when you gently pull the skin over the bubble - similar to a sunburn;
- friction on a healthy area shows the mixing of the upper layers of the epidermis.
One of the most informative diagnostic methods is a blood test for the presence of aggressive antibodies to the desmoglein protein. If these antibodies are present, a diagnosis of pemphigus is made.
Additionally, the following may be assigned:
- cytological studies of serous fluid samples from the bottom of the erosion or from the bladder;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- chest x-ray;
- consultations with related doctors - nephrologist, cardiologist, infectious disease specialist.