11.12.2011
Author: Dentist-periodontist Tamara Valerievna Kudzieva
- Periodontium
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Periodontal disease
- Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the lips and tongue
- Plastic surgery of the oral vestibule (vestibuloplasty)
Most patients believe that tooth loss is associated with the occurrence of caries and its complications. But this is by no means true! In recent years, the most common disease in dentistry is periodontal disease.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, caused by the adverse effects of local and general factors and occurring without disruption of the periodontal junction.
Forms of gingivitis:
- a) catarrhal gingivitis - inflammation of the gingival margin. There are chronic and acute forms of catarrhal gingivitis. The acute form of catarrhal gingivitis often develops against the background of some general infection or intoxication. Often catarrhal gingivitis occurs during the period of spring hypovitaminosis, after suffering from influenza and acute respiratory infections.
- b) ulcerative gingivitis is an inflammatory process characterized by the appearance of ulcers and necrotic plaque on the surface of the gingival margin. The development of ulcerative gingivitis is facilitated by the presence of multiple untreated caries and damaged tooth roots. More common during puberty.
- c) hypertrophic gingivitis - leads directly to gum hypertrophy. There is swelling and inflammation. Patients complain of an increase in the volume of the gums, the color of the gums is slightly changed, there is no pain or bleeding of the gums when irritated. The gum has the appearance of a thickened cushion at the base, the gingival papillae are compacted, and the surface is lumpy.
- d) gingivitis of pregnant women and teenage gingivitis, these are those types of gum inflammation that do not occur against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
Severity of gingivitis:
- light,
- average
- and heavy.
Course of gingivitis:
- spicy,
- aggravated,
- chronic.
Indications for surgery
Vestibuloplasty is indicated in the following cases:
- absolute absence of gum attachment;
- a symptom of tension, the signs of which are pallor and displacement of the gingival margin when the lip is pulled back;
- lack of attached gum zone – distance less than 1 mm;
- signs of inflammation of the gum tissue;
- preparation for orthodontic therapy - installation of a structure to correct the bite will not bring the required effect with a small vestibule due to the fact that the alveolar processes of the incisors will return to their original position due to gingival tension;
- the need for further prosthetics;
- elimination of recession or atrophy of gum tissue.
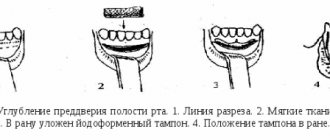
The small vestibule of the oral cavity is often diagnosed not only in adults, but also in childhood. In this case, during the mixed dentition, observation of the child by the dentist is indicated. The operation is permissible after complete eruption of all teeth.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of periodontal tissues, characterized by progressive destruction of the periodontium and bone of the alveolar process of the jaws.
There are 3 degrees of severity.
- 1st degree – bone destruction up to 1/3
- 2nd degree – bone destruction up to 1/2
- 3rd degree – bone destruction more than 1/2
If the inflammatory process has reached degree 3, then the teeth cannot be saved!!!
Course of periodontitis:
- spicy,
- chronic,
- exacerbation of chronic
- abscess
- and remission.
The prevalence of periodontitis can be:
- localized (the cause may be incorrect position of the teeth, poorly made orthopedic construction or filling)
- and generalized (untimely removal of supra- and subgingival dental plaque, hereditary predisposition, general diseases).
Signs of periodontal disease:
- Bleeding gums.
- Pain when brushing teeth and eating.
- Bad breath.
- Exposing the necks of the teeth.
- The appearance of tooth mobility.
If you have at least one of these points, contact your dentist URGENTLY!
Consequences
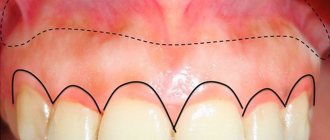
The depth of the vestibule and the attachment of the gums play an important role in the process of protecting the marginal periodontium from external influences.
In case of insufficient attachment or complete absence of attached gum tissue, the following problems may arise:
- trauma to the marginal periodontium while eating food;
- increased muscle tone of the chin;
- impaired blood supply to gum tissue;
- formation of pathological bite;
- partial decrease in lip mobility;
- slower growth of the upper jaw row;
- loosening of teeth;
- inflammatory diseases of the gums, their atrophy;
- development of periodontitis.
Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is a degenerative process that affects all periodontal structures. Its distinctive feature is the absence of inflammation on the gingival margin and periodontal pockets. The course of periodontal disease is always chronic.
According to severity they are distinguished:
- a) mild – exposure of tooth roots up to 4 mm;
- b) average – 4-6 mm;
- c) heavy – more than 6 mm.
The prevalence of periodontal disease is generalized.
Flap surgery is a periodontal operation that involves cutting out and folding a mucoperiosteal flap, followed by careful treatment of the surfaces of the roots of the teeth, bone pockets and the inside of the flap.
The advantages of this operation are the complete removal of pathologically altered tissues under full visual control.
Operation stages:
- the mucoperiosteal flap is cut out and folded back,
- subgingival dental plaque and granulation tissue are removed using an ultrasonic tip and curette,
- antiseptic and antibacterial treatment of periodontal tissues,
- if necessary, implantation of bone tissue,
- the flap is then placed in place and secured with sutures.
- Next comes the application of a healing bandage.
- After a week, the sutures are removed.
Curettage is the removal of pathological tissues around the tooth (supragingival and subgingival calculus and granulations). There are closed and open curettage. The essence of these manipulations is to clean periodontal pockets using special instruments - curettes.
In this case, pathological tissues are removed mechanically (with constant irrigation of the surgical field with antiseptic liquids), which are irritants that support inflammation.
It is important to realize that if pathological tissue is not removed, the process will worsen due to the presence of that same irritant. Ultimately, this will lead to the loss of a tooth, which, by the way, may be completely healthy.
Splinting of teeth is a manipulation aimed at combining mobile teeth into a single block, the so-called “splint”. Splinting is most often carried out in the area of the lower incisors, because It is they who suffer more during the generalized process of periodontitis or periodontal disease. To do this, a special wire or an orthodontic retainer is glued to the composite material on the inner surface of the teeth undergoing splinting.
Before installing a splint, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene - remove stones, plaque and thoroughly polish the surfaces of the teeth.
Gumplasty is an operation to correct changes in the appearance of the gingival margin, in the form of excessive growth, or vice versa - recession (reduction in the volume of the gum, accompanied by exposure of the tooth root). Gum plastic surgery is often performed to achieve maximum aesthetic effect. For example, in orthopedic dentistry to increase the clinical height of the crown, when forming an ideal smile. Also after patch surgery, implantation, surgical treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis, etc.
Recession is a decrease in gum volume, accompanied by exposure of part of the root. Recessions can be localized or generalized.
Recessions arising from:
- structural features of the jawbone - when the teeth have a massive root, and the bone in this area is thinned.
- negative microbial flora – the presence of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out professional oral hygiene at least 2 times a year.
- chronic trauma to the gingival margin. This occurs more often due to improper brushing of teeth (incorrect brush movements, use of brushes with hard bristles, often the use of electric brushes).
- bad habits - using toothpicks, matches to clean the contact surfaces of teeth, biting pencils and other objects.
- external trauma of teeth in the form of dislocations accompanied by chipping of the edge of the socket.
- orthodontic pathology.
During recessions, patients mainly complain about an aesthetic defect and also about increased sensitivity of the teeth. The problem of recession can be solved either orthodontically (if the cause of recession is orthodontic pathology) or surgically.
Surgical methods for treating recession include various types of plastic surgery:
- Moving the pedicle flap
- Relocation of the free flap, with the autograft most often taken from the palate.
- Moving the gingival trapezoidal flap coronally to the defect area.
After surgery, a healing period begins and in less than a month, the patient sees the result.
Causes
A small vestibule of the oral cavity can be the result of both surgical intervention and congenital pathology.
Acquired pathology is a consequence of the following points:
- surgery to correct nonunion of the upper lip;
- surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of burns, mechanical trauma to soft tissues, and removal of tumors.
The cause of a congenital reduction in the size of the vestibule is most often heredity and the presence of certain pathologies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus.
What is a crooked jaw and methods for straightening it.
We will tell you here about how long the swelling lasts after compactosteotomy.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/polozheniya/etiologiya-razvitiya-i-metodyi-korrektsii-protruzii.html we will discuss why tooth protrusion occurs after braces.
Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the lips and tongue
The frenulum is a connective tissue cord present on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. There are frenulums of the upper and lower lip and tongue.
If the frenulum develops incorrectly, various functional disorders develop.
- with a short frenulum of the tongue in children, there is a violation of the pronunciation of individual sounds; by the age of 15-18, this can lead to exposure of the necks of the teeth on the oral side.
“How to determine that a child has a short frenulum?” There are the following signs of a short frenulum of the tongue:
- child's speech delay
- The frenulum does not start from the middle of the tongue, as is normal, but is woven into its tip
- if you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, the tip of the tongue bends downwards
- If you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, it splits
- if you ask a child to reach his nose with his tongue, then ischemia (blanching) of the frenulum is visible
- with a short frenulum of the lip (most often observed on the upper lip), there is a gap between the central teeth (diastema)
Signs of a short frenulum of the lip:
- blanching of the frenulum when the lip is pulled back
- presence of diastema
- low weaving of the frenulum (directly into the gingival margin).
With age, a short frenulum of the lip can lead to exposure of the necks of the teeth.
The short frenulum of the tongue can be stretched with the help of speech therapy exercises, but with severe pathology, surgery is necessary - frenulotomy (dissection of the frenulum).
Diastema can be corrected with the help of orthodontic structures, however, if the cause, in the form of a short frenulum, is not eliminated, over time the teeth will return to their original position.
The most effective treatment for short frenulum of the lips and tongue is surgical excision. Excision of a short frenulum is a fairly simple operation, it takes little time and healing also takes place in a short time.
Contraindications for vestibuloplasty:
- Multiple caries with complications.
- Recurrent chronic diseases affecting the oral mucosa.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Cerebral lesions.
- Genetic predisposition to the formation of keloid scars and collagenosis.
- Blood diseases - leukemia, hemophilia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Received radiation therapy in the head and neck area.
This operation is performed under local anesthesia and the soft tissue usually heals within 10-14 days. Otherwise, the recovery period depends on the method of performing the operation.
Rehabilitation
The duration and severity of the rehabilitation process depends not only on the dentist’s manipulations, but also on the patient’s compliance with the following recommendations:
- at the end of the procedure, use a cold compress to relieve swelling from the operated area;
- Avoid eating too hard, spicy or hot foods for two weeks after surgery;
- reduce the amount of dairy products consumed, as they contribute to the formation of persistent plaque;
- use soft-bristled toothbrushes for daily hygiene;
- rinse the mouth with special anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs;
- after five days after the operation, begin performing myogymnastic exercises recommended by a specialist;
- visit the dentist on the appointed days to monitor the recovery process.