Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, the tissue covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Over time, the inflammation spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity , and a painful and unpleasant abscess can grow on the gum.
Periostitis is of two types: acute and chronic . the acute one , it goes on very quickly. Inflammation is manifested by asymmetric swelling of the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth and enlargement of the lymph nodes, and an increase in temperature is observed. Chronic periostitis can pass without obvious symptoms, while negatively affecting the condition of the child’s teeth, destroying them from the inside. The chronic form often occurs due to untreated acute periodontitis, pulpitis or due to injury.
Why is periostitis dangerous?
It is impossible to delay the treatment of periostitis , as this can lead to very dangerous consequences:
• acute purulent periostitis – it is manifested by swelling and hardening of the gums, tooth mobility, and increased body temperature. The child's appetite and sleep deteriorate. In this situation, the baby urgently needs medical attention and hospitalization;
• and dentia - the inflammatory process can quickly spread into the bone tissue, damage the rudiments of permanent teeth and destroy them. In the future, because of this, a tooth will not be able to grow .
• f legmon – inflammation of the tissues located under the skin, accompanied by severe swelling, thickening and suppuration. If not treated in time, it can cause blood poisoning.
Why do my gums hurt when teething?
To appear on the surface, the tooth needs to pass through the jaw bone and gum tissue. Although this is a natural process, it can be painful, because the tooth “grows” through the gum and violates its integrity. The gums become sensitive during tooth eruption, and pain may occur when pressing on them. These unpleasant sensations go away as soon as the tooth moves apart the gum and looks out.
Signs of periostitis in a child:
• aching or nagging pain in a tooth or gum. Moreover, painful sensations intensify with any touch (including during meals);
• redness and swelling of the gums;
• when a lump appears above or below a tooth;
• o tech cheeks;
• enlargement of the lymph nodes (usually on the side where the source of inflammation is located);
• bad breath ;
• elevated temperature . It may not be present, but even if the temperature is normal and other symptoms are present, the child must be taken to the doctor;
• capriciousness and lethargy of the child.
What you need to know about gum disease in children
Healthy gums of a child are very vulnerable and delicate pale pink tissues that are easily subject to all kinds of injuries, which is not so typical for the tissues of the oral cavity of an adult. Fortunately, they are capable of rapid regeneration. It is also interesting that children’s gums can reflect the general condition of the body, acting as a litmus test for systemic diseases.
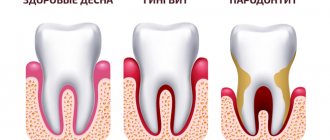
Among the most common diseases around dental tissues and gums
- Gingivitis
This inflammation occurs in 80% of children. The development of the disease in infants is facilitated by the adverse effects of general and local factors. - Gum atrophy
Up to 50% of the child population faces this serious problem. - Stomatitis
Various types of this disease are diagnosed most often in infants and preschool children. - Periodontitis
In this disease, inflammation develops in the periodontal tissues. About 5% of young dental patients are diagnosed with this condition. - Periodontal disease
Similar degenerative changes that affect periodontal tissues practically do not occur in childhood.
Gum diseases that most often occur in children
Inflammatory diseases
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs due to general or local exposure. Over time, untreated gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, that is, a condition where inflammation affects the periodontal tissues (bone tissue and muscle ligaments that hold the tooth in the jaw). In children, this disease is extremely rare, but still, preventive measures should not be neglected. If the development of a serious disease is not noticed in time, this can lead to loosening and further loss of the tooth. If gingivitis in a child responds well to treatment, and you can get rid of it without health consequences, then periodontitis, as a rule, becomes chronic, which is practically incurable.
The inflammatory process that accompanies the granulating form of periodontitis can provoke the formation of a cyst, and even the occurrence of a fistula on the gum. However, these complications are more typical for carious disease of dental tissues. Be that as it may, if you notice that the baby’s gums have acquired a bright red color, and deep grooves have appeared between the teeth and gums, and there is an unpleasant odor coming from the child’s mouth, then most likely the inflammation has affected not only the gums, but also deeper located periodontal tissues. You need to immediately contact pediatric dentistry, where the doctor will promptly prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Dystrophic diseases
Very often, infants and preschool children experience a pathology such as gum atrophy. The development of this negative phenomenon is facilitated by:
- incorrect orthodontic treatment;
- oral injuries;
- crowded teeth;
- all kinds of malocclusions.
Atrophy of gingival tissue is usually local in nature. It usually develops in the area of the canines and front incisors. The development of the disease is accompanied by mild inflammation. The child feels virtually no pain and has no complaints. After some time, degenerative changes cause exposure of the neck of the tooth and its root, the appearance of pathological sensitivity and severe pain.
Periodontal disease is a dystrophic disease that affects all periodontal tissues. This pathology practically does not occur in children. Its development is possible only in seriously ill babies whose immune systems are suppressed. Their body is in a state of deep vitamin deficiency. This disease is characterized by atrophy of the gums and other periodontal tissues. This incurable process can lead to complete resorption of bone tissue. In most cases, teeth that have already acquired unhealthy mobility cannot be saved. Only surgical intervention aimed at removing the affected tooth can bring a certain effect.
Risk factors
Local risk factors
Gum disease in children can be caused by a number of local factors:
- Microbes
Tartar, the formation of which is promoted by poor-quality oral cleaning, can provoke various gum diseases. First, yellow plaque accumulates on the teeth, in which pathogenic bacteria feel at ease. Then, at first glance, harmless plaque turns into hard dental deposits, which subsequently cause serious pathological changes in dental tissue and gums. - Teething
The development of gingivitis can be triggered by teething, as well as their replacement with permanent ones. - Uneven load on the dental system
This entails the development of malocclusion in the child, lethargy of chewing, the habit of chewing food on one side, a short frenulum of the tongue and lips contribute to the occurrence of gingivitis. - disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system (adolescence and associated hormonal changes);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory system diseases;
- pathologies of the immune system, autoimmune diseases;
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency.
- swelling of the gums and bleeding;
- bad breath;
- burning and itching in the gums.
General risk factors
The following systemic diseases and changes in the functioning of body systems can provoke gum disease:
Attention: first signals!
The following factors can signal the development of gum disease in children:
The occurrence of these symptoms necessitates a visit to the dentist. The sooner the child receives help from a qualified specialist, the higher the likelihood of easy relief of the disease at the initial stage and the opportunity to reverse the nascent process.
Causes of periostitis:
• of thorough oral care Small children do not yet know how to properly take care of their teeth, so plaque and food debris accumulate in the gum pockets, which can cause inflammation;
• injury to the gums . Children, especially toddlers, love to put almost everything in their mouths. Foreign objects can not only injure the gums, but also introduce harmful microbes into the wounds;
• to caries and its complications . Baby teeth are more vulnerable, so any defect can cause infection;
• angina , tonsillitis . _
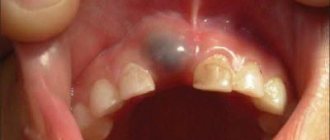
There is a lump with pus on the gum - what to do?
If a lump does appear on the gum, you should consult a doctor. In an advanced stage, when discomfort becomes obvious, you should not hesitate with treatment. You will not be able to remove the lump on your own using herbal rinses.
Most often, a neoplasm noticed at the wrong time above a baby tooth causes fear in parents. It seems like something very serious is going on. And sometimes this is true, so do not hesitate to contact the clinic.
The problem can occur anywhere on the gum, mainly above the chewing teeth. The abscess may be red-blue or white-yellow, depending on the cause of its appearance. In any case, you cannot open the abscess yourself, apply ointment, apply compresses, and try in every possible way to cure the gum on your own. This is very dangerous: the infection can spread even further and deeper. It is important to continue your normal oral hygiene routine even if brushing your teeth is uncomfortable.
Treatment of periostitis
The main thing to remember is that you cannot try to treat periostitis on your own . There are several actions that absolutely cannot be performed while waiting for a doctor’s appointment, so as not to aggravate the disease:
• apply hot compresses , rinse with soda or drink hot drinks and decoctions. Heat will only increase swelling;
• give painkillers , and even more so antibiotics;
• try to cut the abscess yourself .
Gel for teething. How to choose?
If a child becomes restless and capricious during the teething period, first of all you need to create a calm environment for him, pay him more attention, pick him up more often, hug him, and talk to him.
Pain can be relieved mechanically or with medications. You can massage the gums with a clean finger or a rubber brush, let your baby suck on a dryer or chew on a teether, especially a cooled one. There are special dental gels to relieve gum pain in babies during teething. The advantages of children's gum gels are that they quickly relieve pain.
There are many more disadvantages to using them. The main two:
- If the gel contains the anesthetics benzocaine and lidocaine, they can be dangerous to the child’s health. Such drugs provide pain relief for a short time - the medicine is washed off with saliva and swallowed. It is difficult to accurately calculate the dosage when squeezing the gel out of the tube. If you also exceed the number of applications of the medicine recommended by the instructions, you may exceed the permissible limit. An overdose of lidocaine threatens with such dire consequences as convulsions, breathing problems, heart rhythm disorders - even death.
- Herbal gels provide mild pain relief, but help relieve inflammation. Their action does not give quick results. An allergic reaction to herbal components is possible, so after the first use you need to monitor the child’s reaction.
If you still decide to use a teething gel for your baby, choose either a herbal gel or a combination drug with an anesthetic and herbs. It will help relieve acute pain and reduce inflammation. But use combination gels very carefully, only as a last resort when other methods do not work and the child is in severe pain.
It is important!
Teething is a difficult period for the baby and his parents, but it is a natural stage of growing up, which allows the transition to solid food after breast milk.
Treating gum disease at home
How to relieve gum inflammation in a child? The best decision is to contact a pediatric dentist. However, before visiting a doctor, you can use home treatment that will help relieve symptoms for a while.
At home you can use:
- a decoction of chamomile, St. John's wort or calendula (room temperature) - used as a mouth rinse;
- baking soda solution;
- brewing black tea (has tannins);
- honey and sea buckthorn oil - you can lubricate inflammation areas with them.
St. John's wort decoction against gum inflammation