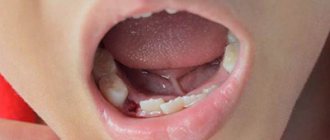
Symptoms of a tooth abscess
The inflammatory process in the tissues of the tooth and gums occurs in stages and is accompanied by different symptoms:
- At the beginning of development, discomfort appears, slight swelling, gum bleeding is possible when brushing teeth, and pain is sensitive when pressed.
- In later stages, swelling increases, and a reaction to hot and cold foods appears. There is prolonged pain and an unpleasant odor. In addition to local changes, the abscess is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, increased body temperature, and general malaise.
A bitter aftertaste is noticeable in the mouth, and a change in the shade of the tooth body is possible. It is important to remember: the symptoms of gum abscess can manifest themselves in different ways - everyone has their own pain sensitivity threshold and perceives signals subjectively. Therefore, you should not wait for acute conditions; a reasonable step is to visit a dental clinic at the first incomprehensible sensation.
Diagnosis of sepsis
Timely diagnosis of sepsis is crucial for the patient’s recovery. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of success. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical examination and laboratory and instrumental examination.
Clinical criteria:
- Body temperature is more than 38 degrees or less than 36 degrees.
- Heart rate is more than 90 or exceeds the age norm.
- Respiration rate more than 20 times per minute.
- Presence of edema.
- Confusion.
- An increase in blood glucose levels of more than 7.7 µmol/l in the absence of diabetes.
- Disturbance of hemodynamic processes - a decrease in systolic blood pressure of less than 90 mmHg, or its decrease by more than 40 mmHg. from the usual meaning. [5,6]
Laboratory criteria
A general blood test is performed with a leukocyte count and platelet count. In case of sepsis, leukocytosis is determined by more than 12*109/l or leukopenia when the number of leukocytes is below 4*109/l. There is also the release of immature forms of granulocytes into the bloodstream and a decrease in the number of platelets.
A biochemical blood test shows an increase in C-reactive protein, creatinine, and bilirubin. But these are nonspecific signs that can be observed in other diseases. Therefore, the search for more informative diagnostic methods continues.
Today, the main such markers are procalcitonin, presepsin, and CRP. Based on this laboratory indicator, a diagnosis is made and the dynamics of the disease are monitored.
Bacteriological culture
Detection of microorganisms in the blood is an important, but not mandatory, manifestation of sepsis. Even with the use of the most modern diagnostic systems and careful adherence to material sampling techniques, it is possible to isolate the pathogen from the blood in less than half of the cases. Therefore, a negative culture result in the presence of clinical symptoms should not be regarded as the absence of sepsis, and, conversely, the isolation of microorganisms from the blood in the absence of symptoms should be regarded as transient bacteremia or viremia, but not as sepsis.
However, biological studies should in any case be present as one of the stages in diagnosing sepsis for the following reasons:
- Possibility of determining the etiology of the pathogen.
- Selection or change of antibiotic treatment regimens.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
- In some cases, it allows you to determine the source of infection, for example, catheter-related infection, endocarditis, etc.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
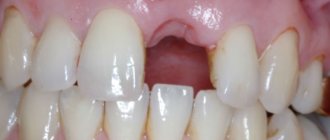
What complications can there be?
Even if the pain has dulled, the symptoms have become less pronounced, you should not postpone your visit to the dentist. This situation may be a signal indicating the death of the root and the further spread of infection to the organs of the head or neck.
The area cannot be heated. This approach will bring short-term relief, but will accelerate the formation of the fistula and stimulate the release of pus.
Possible serious complications: brain inflammation, pneumonia. There is a risk of sepsis, development of osteomyelitis, damage to the nasal sinuses or meninges.
Stages of sepsis development
The development and course of the septic process is individual and depends both on the properties of the pathogen and on the characteristics of the patient’s body. However, several phases of the course of this disease can be distinguished:
- Voltage phase. In response to the introduction of the pathogen, the body’s defense systems are activated and mobilized, in particular the pituitary-adrenal system is activated.
- Catabolic phase. The patient's condition deteriorates due to metabolic disturbances. The processes of metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates are enhanced, and they are extracted from the “depot”. Disorders of water-electrolyte metabolism and acid-base status also develop.
- Anabolic phase. At this time, recovery processes begin. This primarily concerns structural proteins.
- Rehabilitation phase. During this period, further restoration of metabolic processes occurs. In some cases, complete recovery is not possible.
As for the duration of the disease, everything is again individual. In some, stronger patients, sepsis is relieved within 3-4 weeks, in others it can last for years, periodically subsiding and flaring up.
In addition, when diagnosing sepsis, the following conditions are distinguished.
Toxic-resorptive fever
Toxic-resorptive fever is a condition that develops when bacterial toxins or tissue decay products are absorbed from the primary pathological focus. As a rule, this is typical for bacterial infections of wounds, catheters, etc. There are common typical syndromes that accompany infectious processes - fever, changes in general blood and urine tests (leukocytosis, proteinuria). Once the primary lesion is eliminated, the patient's condition stabilizes.
Septicemia
Septicemia is a form of sepsis in which there is a pronounced intoxication syndrome, hyperergy (increased reactivity of the body) and a rapid course. Septic foci are either minimally expressed or absent. This form of sepsis is more typical for children in the first years of life. The clinical picture is more characterized by general manifestations:
- Hemolytic jaundice, accompanied by yellowing of the skin and sclera.
- Rash. It first appears as small pink dots, which grow and merge with each other, forming pale pink or purple spots.
- In some patients, elements of the rash may become blistered or ulcerated. With deep lesions, subcutaneous fatty tissue may be affected with the development of phlegmonous inflammation.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome - hemorrhages in internal organs.
Septicopyemia
Septicopyemia is a form of sepsis in which in the body, in addition to general intoxication, metastatic abscesses begin to appear in organs and tissues, which are the result of bacterial embolism. Most often, the first abscesses are found in the lungs, and then the process spreads to other organs: liver, liver, heart, meningeal membranes, synovial membranes. Abscesses can break through and cause the development of pleural empyema, phlegmon, peritonitis, etc.
Causes of dental inflammation
The main causes of tooth gum abscess and pulp infection:
- Advanced caries affecting the root apex. Suppuration develops against the background of periodontitis.
- Untreated gingivitis and periodontitis (gum disease). They often develop as post-traumatic complications: pathogenic microflora accumulates in periodontal pockets.
- Weakening of the immune system after illness (flu, sore throat, etc.).
- Iatrogenic factors - bacteria entered after the use of unsterile instruments during treatment, injections, or incorrect tooth extraction.
The development of the inflammatory process may be preceded by damage to the oral mucosa and the formation of boils.
Clinical classification of sepsis by stages
Clinical staging of sepsis plays an important role, as it helps doctors choose the optimal tactics and achieve the best possible treatment results in each specific case. The following stages are distinguished:
- Sepsis is diagnosed when the core temperature (measured on the mucous membranes) of the body rises above 38 degrees or falls below 36 degrees, heart rate 90 bpm or more, respiratory rate 20 bpm or more, or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO2 ) falls below 32 mm. Hg Art. In this case, the level of leukocytes in the blood rises to more than 12,000/μl or falls below ≤4000/μl, or more than 10% of immature forms appear among them.
- Severe sepsis is sepsis that is combined with acute organ dysfunction.
- Septic shock is diagnosed when a patient has persistent hypoperfusion (low blood pressure) or tissue hypoperfusion (insufficient blood supply) despite adequate fluid resuscitation.
- Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome is a condition in which the patient has organ dysfunction (impaired functioning of internal organs), and its homeostasis cannot be maintained without drug intervention.
Protozoa
The decomposed cellular substrate in the organ is attacked by protozoa, which, processing this waste, act as garbage collectors in containers. Thus, dead cells, bacteria, and toxins are not just scattered throughout the organ, but cleaned, aligned cavities. This process is dynamic, each type of introduced microorganisms has time to become saturated and grow, multiply, that is, give birth to offspring.
The process continues until the immune system says: stop! It sends lymphocytes, leukocytes, macrophages, antibodies, sends energy and, depending on how well they cope, either recovery, improvement, remission (subsidence) occurs, or the disease turns into a sluggish chronic process. Protozoa are localized in the skin, eyes, tongue, intestines, liver, kidneys, bladder, genitals, etc.
Treatment of sepsis
Treatment of sepsis is based on three principles:
- Sanitation of the primary lesion. This can be achieved with surgery and/or adequate antibiotic therapy. If a primary lesion is discovered that can be treated surgically, it is necessary to do this as soon as possible. This may include opening and drainage of abscesses, removal of infected invasive devices (catheters, implants, etc.), drainage and lavage of the abdominal cavity, etc.
Antimicrobial therapy is another cornerstone of sepsis treatment, and its timeliness and adequacy are important. For example, if septic shock develops, drugs should be administered within an hour of the onset of symptoms. In this case, the drug must cover the entire spectrum of suspected pathogens and, importantly, penetrate the primary infectious focus. If it is necessary to prescribe combination therapy of several drugs, they are used for no more than 5 days, after which data from biological research methods must be obtained and the treatment regimen must be adjusted. [7]
- Ensuring oxygen transport - all clinical manifestations of sepsis are aggravated in conditions of lack of oxygen, so it is very important to control this process. To do this:
- Hemodynamic support - infusion of solutions that ensure replenishment of water and electrolyte balance, medications are prescribed to maintain blood pressure, etc.
Respiratory support - artificial ventilation, oxygen masks, etc.
- Correction of metabolic disorders
- Ensuring the supply of necessary nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates). If the patient is unable to take food or nutritional formulas on his own, replacement therapy is considered.
Monitoring glucose levels.
- Detoxification activities. [8-10]
One of the effective ways to treat sepsis is selective sorption on TORAYMYXIN columns. This technique is successfully used in many countries around the world. Currently, more than 200 thousand patients with septic shock and severe forms of sepsis have undergone such treatment. The effectiveness and safety of the technology has been confirmed in clinical studies. [11,12]
Flux (periostitis)
Another common complication of pulpitis is inflammation of the periosteum. This is the periosteum, a fibrous membrane covering bone tissue. Flux develops in the projection of the lesion on the gum side. Pus accumulates under the mucous membrane and an abscess forms. In this case, a fistula may appear on the gum.
A characteristic symptom of gumboil is swelling of the gums and soft tissues of the face on the side of the affected tooth. The patient complains of severe pain. As a rule, body temperature rises.
Treatment of pulpitis of a baby tooth
2280 rub.
Tooth restoration after pulpitis/periodontitis
from 3490 rub.
Treatment of tooth pulpitis
from 5060 rub. up to 9880 rub.