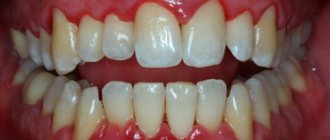
Periostitis is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum, the tissue covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Over time, the inflammation spreads to other tissues of the oral cavity , and a painful and unpleasant abscess can grow on the gum.
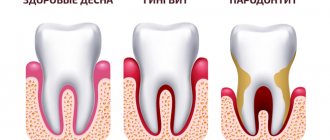
Periostitis is of two types: acute and chronic . the acute one , it goes on very quickly. Inflammation is manifested by asymmetric swelling of the cheek on the side of the diseased tooth and enlargement of the lymph nodes, and an increase in temperature is observed. Chronic periostitis can pass without obvious symptoms, while negatively affecting the condition of the child’s teeth, destroying them from the inside. The chronic form often occurs due to untreated acute periodontitis, pulpitis or due to injury.
Quincke's edema in children
- Symptoms of the disease
- How does Quincke's edema begin in a child?
- Causes
- First aid
- Treatment of Quincke's edema in children
Attacks most often occur in children with urticaria. Pediatricians associate swelling with hay fever, bronchial asthma, and atopic dermatitis.
Important! This is a dangerous condition, which in a quarter of cases provokes swelling of the larynx.
Quincke's edema occurs in newborns and older children. Its nature is most often allergic, but this phenomenon can be hereditary and also have no clear origin. Source: I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria and angioedema in children // Pediatrics, 2009, v. 87, no. 2
The prognosis is usually favorable; it becomes poor with frequent relapses and associated swelling of the internal organs and larynx. The consequences may be anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm.
For prevention, in some cases vaccination is carried out. Its necessity is determined individually. Clinical recommendations for parents: provide the child with a low-allergen diet, take antihistamines at intervals recommended by the doctor, minimal or no contact with the allergen.
Treatment
Treatment for childhood gingivitis is practically no different from how adults are treated. Only medications used for them are softer and more gentle. Treatment begins with professional cleaning of hard deposits and plaque of tooth enamel - mechanical or ultrasonic.
If caries is detected during the examination, then therapeutic treatment is carried out. Gingivitis is then treated with medications with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. Measures are taken to eliminate detected pathologies (bite, frenulum, etc. are corrected).
Ointments and gels are considered effective for children under 4 years of age. For example, Cholisal ointment has analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it possible to prescribe it to alleviate the patient’s condition, especially when baby or permanent teeth are cutting. Ointments and gels are applied directly to the inflamed area.
Antibiotics in tablets or in the form of injections are prescribed to children in difficult cases (the presence of infections of bacterial origin in the body). At elevated temperatures, rinses, drinking plenty of fluids, antioxidants, antipyretic drugs for children, and taking vitamins are prescribed.
Prevention measures should include regular visits to the pediatric dentist, training in oral care rules, and parental monitoring of the development of hygiene skills.
Symptoms of the disease
The reaction develops rapidly; signs of angioedema in children are swollen lips, neck, and face. The upper torso, hands, feet, and genital area are often affected. Quincke's edema is visible in the eyes of a child - the eyelids swell on one or both sides.
- When the tonsils are affected, the picture is similar to a sore throat.
- Edema of the larynx is indicated by a hoarse voice, difficulty breathing, a gusty cough, blue discoloration and then gradual paleness of the skin.
- Swelling that appears in one area may occur in another. This mainly applies to large-scale swelling.
- When the mouth and tongue swell, speech becomes difficult.
- If the process is localized in the gastrointestinal tract, the child may complain of tingling of the tongue, followed by diarrhea and vomiting, and sharp pain in the intestinal area.
- Rarely, swelling of the meninges occurs. With it, the child cannot fully tilt his head forward, complains of a headache, and behaves inhibited. Convulsions and vomiting may occur.
- If only the skin is affected, joint pain, fever may appear, and the child may lose consciousness.
The pathological condition can last from an hour to several days.
How does angioedema begin in a child?
Immediately after contact with the allergen, the listed symptoms increase sharply. This happens in a matter of minutes. Source: G. I. Smirnova. Urticaria and Quincke's edema // Allergic diseases in children. Ed. M.Ya. Studenikina, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: Medicine, 1998: 279-287 If you press on the swollen area, the child will not experience pain, but you will feel a dense swelling, on which, after pressing, there will be no characteristic depression.
What to do after removing a baby tooth: general recommendations
In dental clinics, milk teeth are removed under anesthesia. An exception is made only for moving, strongly swinging units. Anesthesia is selected differently:
- local - a small injection with preliminary anesthesia of the gums;
- nitrous oxide sedation - delivering laughing gas through a mask to reduce anxiety;
- under anesthesia - with multiple removals or individual indications for treatment during sleep.
When local anesthesia is used, the lip and cheek in the area of the tooth being removed lose sensitivity. Sensations are restored within 1.5-3 hours, and during this period of time parents should keep an eye on the baby and distract him.
Strange sensations of numb tissues lead to the fact that children begin to bite them with their teeth. And since there is no sensitivity, the bite can severely injure the lip or cheek from the inside. To prevent this from happening, you should keep your child busy with something interesting - watch cartoons or play your favorite games.
Nutrition after baby tooth extraction: how much you can’t eat, choice of foods
The second point that adults need to consider is nutrition. And this is not only the traditional question of how much you can’t eat after a baby tooth is removed. Dietary restrictions apply to:
- fasting interval time - 2 hours after removal;
- choice of products - for several days you need to remove solid foods from the menu, offer the child purees, jellies, omelettes, instant baby cereals.
The drinking regime also has its own peculiarities:
- Avoid drinking through a straw and carbonated drinks;
- give up fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, drinking yogurt;
- remove excessively cold or hot drinks;
- drink a lot during the first 24 hours.
Rodikova Tatyana
Children often ask what a baby tooth looks like after removal. I show. Many guys ask to take the tooth with them. Children place their extracted teeth under their pillow at night and receive gifts from the “tooth fairy.” A pleasant fairy-tale tradition that turns removal into a small adventure.
Do's and Don'ts after tooth extraction in a child
The child leaves the doctor's office with a sterile swab in place of the extracted tooth.
The cotton wool is removed after 20 minutes. The first three days after the surgical procedure you cannot:
- actively engage in sports - experience significant physical activity;
- warm up the area of the extracted tooth - apply compresses, visit a bathhouse, sauna;
- pick the hole with sharp objects (toothpicks, matches), touch with your tongue or hands;
Correct behavior after tooth extraction;
- chew food on the side opposite the removal site;
- Gently rinse your mouth after meals (take some water, hold it and spit it out);
- brush your teeth with a soft brush, avoiding the socket.
- take medications prescribed by the doctor in a dosage appropriate to your age;
- Apply ice to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth to reduce pain.
Adults are advised to distract the child from thoughts about the removed tooth. It is best to keep your baby busy with calm board games, watching a favorite fairy tale, or reading books.
This approach will reduce stress and relieve the child from worrying about the dental procedure. It will also help to avoid unnecessary investigative curiosity and studying the wound in the gum.
How to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction in a child
Rinsing in the first days after removal is strictly prohibited. Aggressive active movements can cause a clot to fall out of the socket and cause bleeding.
Instead of rinsing, the pediatric dentist-surgeon will definitely recommend oral baths. They are easy to make. The child puts an antiseptic solution into his mouth, holds it at the removal site for several minutes and gently allows the liquid to flow out by simply opening his mouth slightly.
The composition for the baths can be almost any. A weakly concentrated saline solution or soda solution is recommended for children. For older children, you can offer Miramistin, Chlorgesidine solution - sold in any pharmacies.
Soldatenkova Alina
Most recommendations after tooth extraction are aimed at preserving the blood clot in the socket. It is very important that it does not fall out. The clot serves as a natural protection for the wound from bacteria and accelerates healing. It is especially important to monitor the socket when removing the 4th milk tooth in children (chewing). Healing of wounds after extraction of incisors or fangs occurs faster and usually without consequences.
Causes
A complex of immunological reactions is most often caused by:
- Food;
- medicines;
- volatile allergens (pollen, chemicals, etc.);
- insect bites.
The disease may be non-allergic in nature. In this case, in addition to allergens, it is caused by: stress, infectious diseases, external factors (for example, hypothermia), intoxication of the body. Source: A. V. Lyapunov. Urticaria and Quincke's edema in children // Children's allergology. Ed. A.A. Baranova, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: GeotarMedia, 2006; 486-497.
Medicine also knows quite a lot of cases where the reason for such a reaction of the body has not been established.
Causes and risk factors
The mucous membrane of the child's oral cavity is often injured. The appearance of ulcers can be caused by temperature effects (hot food and drinks), biting the inner surface of the cheeks or lips; damage by sharp edges of the filling, braces or the tooth’s own tissues in case of chipped enamel. Normally, the immune response allows the pathological process to be quickly eliminated, the mucous membrane heals, and bacteria do not have time to cause severe inflammation and ulceration.
Weakened children's immunity cannot cope with this task, which leads to the development of aphthous stomatitis. A small number of opportunistic bacteria that populate the oral cavity begin to actively multiply. Often the disease occurs against the background or as a result of a severe infection: influenza, ARVI, acute tonsillitis, infectious mononucleosis, etc.
Main risk factors:
- food allergies, allergic reactions to hygiene products, such as toothpaste;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements due to a strict diet or impaired digestion of food;
- hereditary predisposition;
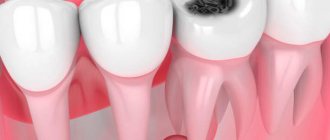
- foci of infection in the oral cavity: caries, chronic periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis;
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- severe systemic diseases: pathologies of the endocrine system, blood vessels, metabolic disorders, etc.
Ask a Question
First aid
call an ambulance immediately . Doctors may decide on emergency hospitalization if the patient has difficulty breathing, a swollen tongue, or symptoms indicating intestinal damage.
What to do before the doctors arrive?
First aid, which should be provided at the first symptoms of angioedema in children, involves clearing the airways, checking breathing intensity, heart rate, and blood pressure. Sometimes it is necessary to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation, so after the first case, parents are recommended to take first aid courses. At the final stage, medications should be administered to the child.
First aid equipment includes:
- glucocorticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”);
- antihistamines;
- adrenalin.
Sequence of administration: adrenaline, then glucocorticosteroid, then antihistamine. If the reaction is moderate, then adrenaline is excluded.
| Adrenalin | It is injected intramuscularly into the thigh (middle third outside) at the rate of 0.01 mg for each kg of the child’s weight. If there is no effect, then the injections are repeated every 15 minutes. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Injected intramuscularly into the buttock or intravenously. You can pour the medicine from the ampoule under the tongue - this way the effect will come faster. The dosage of Prednisolone is from 60 to 150 mg, Dexamethasone is from 8 to 32 mg. |
| Antihistamine | Intramuscular injection is preferable. It is possible to take a pill, but the effect will come later. The dosage depends on the medicine. For example, “Loratadine” – 10 mg, “Cetrizine” – 20 mg. |
Important! In case of swelling of the larynx, a tracheostomy is performed urgently.
Treatment of angioedema in children
- stopping contact with the allergen;
- removal of the allergen from the body (sorbents, drinking plenty of fluids);
- the use of antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids, diuretics and other drugs, depending on individual indications.
The treatment plan may vary and include other interventions and complex drug therapy. It depends on the type of disease, the number of relapses and other factors. It is necessary to obtain specialist advice.
Sources:
- I.I. Balabolkin. Urticaria and angioedema in children // Pediatrics, 2009, v. 87, no. 2.
- G. I. Smirnova. Urticaria and Quincke's edema // Allergic diseases in children. Ed. M.Ya. Studenikina, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: Medicine, 1998: 279-287.
- A. V. Lyapunov. Urticaria and Quincke's edema in children // Children's allergology. Ed. A.A. Baranova, I.I. Balabolkina. M.: GeotarMedia, 2006; 486-497.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: allergist
Experience: 23 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Republican Children's Clinical Hospital
What is lymphadenopathy in a child? This is an enlargement of lymph nodes in one or more areas of the body due to a disease. What are they needed for? Lymph nodes are “customs” for a large area of the human body. Although these are small round formations the size of beans or peas, they are nevertheless intended to be the first barrier to pathogens of infectious diseases: bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, preventing the spread of infection deep into the body. Therefore, lymph nodes are located singly or in groups, but always in strategically important places.
Lymphadenopathy is a symptom of the disease. Which one exactly? The doctor will answer this question. Unfortunately, this important symptom is not always assessed adequately and in a timely manner. Parents should know that if one or more enlarged lymph nodes are detected in one group, the child should be consulted with a pediatrician. In most cases, the cause of enlarged lymph nodes is infectious processes (viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoal), less often - autoimmune diseases, storage diseases. However, such causes can also be malignant neoplasms.
Among infectious causes, enlargement of lymph nodes is most often caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal infections - tonsillitis, pharyngitis, scarlet fever, complicated caries, boils, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, and less often - diphtheria, tuberculosis, plague. In this case, complaints, a thorough examination, medical history, analysis of Mantoux reactions and the vaccination calendar will help determine and prescribe treatment. Often the cause is “cat scratch” disease, when a child, a few days or even 2-3 weeks after a child has been scratched on the arms or legs by a tormented cat, the lymph nodes of the axillary or groin areas, respectively, enlarge and become painful. In this case, the doctor will prescribe adequate antibacterial therapy.
Among viral infections, one should think about rubella, chickenpox, mumps, cytomegalovirus, infectious mononucleosis, and HIV infection. To diagnose these conditions, an increase in body temperature, a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, pain when opening the mouth, puffiness of the face, snoring at night, purulent sore throat, and the presence of contacts with patients the day before will be important.
However, with this variety of causes, a doctor who is alert to cancer will identify a group of patients with suspected malignant tumor or blood disease and refer the child to an oncohematologist for consultation.
When treating cancer, early diagnosis is the most important step on the path to recovery. Treatment of a patient at the first stage is the most promising and cheapest. Unfortunately, many people are convinced that malignant tumors practically never occur in children. However, it is not. Being, fortunately, a fairly rare disease, malignant tumors rank second after injuries among the causes of death in children under 15 years of age. As data from statistical studies show, every year out of 100 thousand children of this age, 14-15 are diagnosed with malignant neoplasms.
Symptoms that should alert a child with lymphadenopathy include significant weight loss in a short time, persistent loss of appetite, bone pain, increased fatigue (the child gets tired faster than usual, forgetting even about his most favorite games), lethargy, pale skin, bruises on the body without obvious injuries, hemorrhages in the mucous membranes, unexplained rises in body temperature.
But despite the presence or absence of these symptoms in the child, parents should understand that until the reasons are determined, they should not warm the lymph nodes, carry out any physical procedures (electrophoresis, applications, etc.), or lubricate them with anything. Any physical procedures on the area of the lymph nodes are contraindicated, as they can aggravate the process, causing rapid progression and thus reducing the chances of recovery with even more expensive treatment. There are cases when such errors became fatal.
Thus, the attentiveness and prudence of parents plays a huge role in timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment. Who, if not parents, will be able to notice changes in their child’s condition in time - and contact specialists in time, without making mistakes along the way? As American oncologist Charles Cameron wrote: “Be neither too careless about the possibility of cancer in children nor too worried. But be on your guard!”
| Pediatric hematologist, KRU "DKB" | Tarasenkova A.A. |
Answer
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
Diagnosis of adenoviral infection
Diagnosing adenovirus infection in most cases is not difficult. The doctor collects anamnesis, conducts an examination, identifies characteristic symptoms and makes a diagnosis based on them. This method is called clinical. It is especially accurate when the disease is widespread, in winter or spring.
In rare cases, a more accurate diagnosis of adenoviruses is required due to the similarity of symptoms to influenza or other, more rare respiratory infections. In this case, laboratory research methods are used, blood is taken for analysis4.
There is an accurate method for detecting adenovirus infection through blood testing.
As additional diagnostic measures, microscopic examinations of the contents of the nose and oropharynx can be carried out to exclude a bacterial infection.