Most often, a child's gums itch when baby or molar teeth begin to emerge. Some parents may assume that this process occurs at a fairly early age, 2 - 3 months, but sometimes it happens later. Read more in our article:
Sometimes the child experiences very strong painful sensations. If parents do not know how to help him, the situation becomes more complicated. There is no need to panic, the main thing is to understand the reasons for the baby’s condition. The child needs to be somehow distracted from the obsessive state, play with him, and provide first aid in the meantime.
Symptoms of sore gums
Each child experiences teething differently. The most characteristic symptoms are:
- inflammation of the gum tissue, itchy condition;
- excessive secretion of saliva (the mucous membrane secretes biological fluid to protect the inflamed area from greater damage);
- capricious behavior (the baby cries due to obvious discomfort in the oral cavity);
- disruption of the normal nature of sleep.
Other symptoms that are less common, but also characteristic of teething, are:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- intestinal problems (diarrhea, constipation);
- nausea, vomiting;
- difficulty breathing;
- cough.
Such conditions of the baby can seriously frighten parents. The best way out of the situation is to visit a pediatrician. In this case, a comprehensive examination of the child will be carried out, an accurate diagnosis will be made, and the medications required to be taken will be prescribed.
How to avoid making a mistake with a diagnosis?
As you can see from the information above, teething in children and serious gum disease have similar symptoms. Children's immunity is not able to protect the body from all kinds of infections and bacteria that surround the baby. Parents may be mistaken about the causes of the symptoms that appear and thereby allow a dangerous disease to progress.
The appearance of baby teeth is almost always accompanied by copious amounts of saliva and coughing. The cough caused by the disease is characterized by the presence of wheezing and sputum production.
Important! If the cough worsens over time, the doctor should examine the child for the presence of inflammatory processes in the respiratory system.
The teething process is often accompanied by diarrhea. If the diarrhea does not last long, up to three days, this is normal; if more, it’s time to contact your pediatrician. Especially when mucus or blood is found in the stool. In this case, the cause of diarrhea may be an intestinal infection.
Why do my child's teeth itch?
Smooth, moist, light pink gums are healthy. If it looks different, and there is bleeding in the mouth and an unpleasant odor is felt, the baby begins to be capricious, stops eating, and constantly scratches his teeth. In such a situation, parents should know the main sources of itching. Children's gums begin to itch for various reasons.
Allergy
A child may experience itching in the gum area when brushing their teeth with unsuitable toothpaste or eating exotic foods. Teenagers may experience an allergic reaction to installed braces.
Dental diseases of the oral cavity
Children often do not understand that it is important to practice oral hygiene, they are in a hurry when brushing their teeth or even skip this procedure in the evening.
As a result of this attitude, various gum diseases can develop. Most often, children experience the same dental diseases as adults: gingivitis, stomatitis, etc.
When itching of a child's teeth is accompanied by throbbing pain, there is a possibility of pulpitis.
Gingivitis occurs during eruption. Plaque forms and increases on the teeth, the gums turn red, and bleeding occurs. With stomatitis, blood or bluish smears, pain in the soft tissues of the mouth, and blisters appear.
Lack of vitamins
When a child does not eat enough vegetables and fruits, his body does not get important nutrients. Itchy teeth may be due to a lack of vitamin C and calcium. And the consequences of such a shortage are bleeding gums, destruction and loss of teeth (scurvy).
Other reasons
- The child is cutting a tooth. Before the age of one year, babies begin to put various objects in their mouths to scratch their teeth. At the same time, their gums may swell and bleed. Such signs appear when the baby cuts a tooth. Additional features may include high temperature, strong salivation, and clear snot. In this situation, a teether comes to the rescue. It is first frozen and then given to the baby. Ice has an analgesic effect on the gums, which begin to itch less. If the itching does not stop, then parents should consult a pediatrician to choose a medicinal ointment.
- Fungal disease. The gums may itch when a white coating develops in the mouth, which appears due to thrush (candidiasis). This fungal disease often occurs in children who taste the surrounding objects. Thrush is the result of weak immunity. To treat this disease, white plaque on tissues is often treated with a soda solution and antifungal drugs are taken while following a diet.
- Other diseases. Teeth begin to itch during colds, if swelling occurs in the mouth. In some children, weather sensitivity manifests itself through itching. If the teeth do not stop itching after long-term treatment, dentists conduct additional research and carefully study the baby’s tests. As a result, a change in composition or acidity is detected in the saliva, to which the increased immunity reacts with itching.
Causes of itching
1. If you are allergic to hygiene products. Itching can be caused by dentures, or rather by the material from which they are made.
2. Diseases of the oral cavity that can cause discomfort accompanied by itching:
- periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- hyginitis;
- stomatitis;
- candidiasis;
- leukoplakia.
3. People who do not adhere to a healthy diet may develop a vitamin deficiency in their body, which will lead to itchy gums.
4. Nervous disorders. A person may experience a condition where he feels like his teeth are itching. This usually occurs with a mental disorder or severe depression.
5. Dental problems, which include:
- plaque and tartar, which occur due to poor oral hygiene. Or due to disruption of the endocrine system;
- night grinding of teeth (bruxism), which wears away the enamel of the teeth and injures the gums;
- after tooth extraction, when during the healing process of the hole of the extracted tooth, new tissue grows.
What to do
Parents should always ensure that their child brushes their teeth thoroughly in the morning and evening after meals.
If your gums still start to itch, you should immediately purchase a brush with soft bristles and medicated paste.
This way you can determine whether the itching is an allergic reaction of the body.
You also need to pay attention to the foods your baby eats. Introduce more fruits and vegetables into your diet, this is especially important in the spring. Serve only warm food, because... hot increases gum irritation.
After brushing your teeth, rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions and medical solutions.
Rinses to help relieve itching
Teeth stop itching if you treat the oral cavity with solutions containing soda or salt.
In folk medicine, decoctions are used:
- sage;
- oak bark;
- chamomile flowers.
A tablespoon of herbs is poured into a glass of boiling water and cooled to room temperature. The resulting decoction is filtered and used for rinsing the mouth. The procedure should be performed up to 6 times a day.
It is usually difficult for children to explain what is bothering them, so parents should themselves examine the baby’s teeth, gums and tongue from time to time. If, during such an examination, an adult discovers signs of illness in the child’s mouth, then you should immediately contact a dentist.
How often do you look into your baby's mouth? Many parents are sure that it is enough just to control that the child is not lazy to brush his teeth before bed and in the morning. And some don’t even have time to do this. Otherwise, adults follow the logic: since the child does not cry and eats ice cream with a wide smile, then everything is fine.
But, for example, gingivitis in children can be almost painless. At first. But if the sore is neglected without paying attention to it, there is a risk of facing very, very unpleasant consequences - even losing teeth!
Let's figure out what kind of illness this is, how to detect it and cure it.
Treatment with folk remedies
You need to know what to do if your child’s gums itch, and what folk remedies to use. They help temporarily soothe the itching.
- Special teethers for scratching, which are cooled in the refrigerator and allow the baby to scratch his gums.
- You can put a cold spoon in your mouth.
- Apply a piece of ice to areas that itch. But no more than 2 times a day.
- Concentrated chamomile decoction is applied to areas of redness. The solution relieves swelling and soothes itching.
- Peppermint tea can help improve sleep and relieve scratching symptoms.
Teething is an essential part of every baby's development. You just need to survive this period and help cope with it. At what time the gums begin to itch depends on the individual characteristics of the child.
Symptoms of gingivitis in children
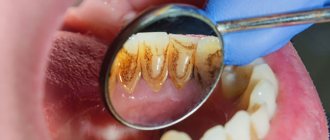
Gingivitis in children is an inflammatory disease that affects the gum tissue adjacent to the teeth and located in the spaces between them. Remember: have you ever noticed blood on your toothbrush? This is just one of the first symptoms of gingivitis. This also includes: redness and swelling of the gums, pain during brushing, gum hypertrophy (overgrowth), high fever.
“There are five types of gingivitis: catarrhal, ulcerative-necrotic, hypertrophic, atrophic, desquamative,” lists pediatric dentist Suleiman Ibragimov. – And each has its own symptoms. For example, catarrhal gingivitis may not manifest itself in any way, except that when brushing your teeth, weakened gums begin to bleed. With other variations of the disease, everything is more serious.
During ulcerative necrotic gingivitis, the gums itch and hurt. In addition, the temperature may rise and the lymph nodes may become inflamed. The process is accompanied by general malaise and increased salivation, and after a while ulcers appear and gum tissue begins to die.
Hypertrophic gingivitis in children, symptoms: gums increase in size, bleed heavily, pain develops into constant pain. The hypertrophied tissue gradually grows so much that it “crawls” onto the teeth. Well, underneath is the kingdom of pathogenic microflora, which is extremely difficult to combat.
Atrophic gingivitis in children manifests itself in the fact that the teeth become very sensitive, as the gums seem to be depleted, decrease in volume, and the necks of the teeth and even the roots are exposed. According to Suleiman Ibragimov, at this stage the disease enters its most severe stage: it is no longer gingivitis, but practically periodontitis, that is, the process moves to the jaws.
The appearance of desquamative gingivitis is indicated by purulent blisters on the surface of the gums, as the upper layer of the mucous membrane is destroyed.
Treatment of gingivitis in children
“In children suffering from gingivitis, as a rule, at the appointment we find a thick layer of plaque and hard deposits, as well as caries that affects many teeth at once,” notes Dr. Ibragimov.
A key role in the development of gingivitis is played by bacteria that multiply in dental plaque. In addition, the appearance of sores is facilitated by: infections (such as acute respiratory viral infections or chronic tonsillitis, for example), allergic diseases, hypovitaminosis, diabetes, problems of the digestive system, and so on. If your child has an incorrect bite, the child diligently avoids the toothbrush or brushes his teeth incorrectly - all this can also affect the occurrence of gingivitis.
Have you noticed your baby’s gums are red and slightly swollen? This may already be the first call. And coupled with a high temperature indicates a serious inflammatory process. See a doctor urgently! Until this moment: bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, if necessary, antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol).
– Gingivitis must be treated comprehensively, taking into account the individual characteristics of each little patient. To begin with, find and eliminate the cause: for example, cure caries, tonsillitis (other common diseases), or deal with malocclusion pathologies, says Suleiman Ibragimov.
Then comes the treatment of gum inflammation itself. It is carried out in stages:
- removal of soft plaque and hard dental deposits;
- a course of anti-inflammatory procedures: rinsing the mouth with antiseptics (for example, Miramistin) and herbal decoctions (eucalyptus, sage or regular chamomile are suitable). You need to rinse your mouth after each brushing of your teeth, twice a day. For the youngest (who do not yet know how to rinse their mouth, and there is nothing to clean there yet), the doctor will prescribe applications with a gel containing cetalkonium and choline salicylate, plus treatment of the oral mucosa with antiseptics.
- additionally: vitamins, limit carbohydrates, enough fruits and vegetables.
“The duration of treatment depends on the form and severity of the disease,” explains Suleiman Ibragimov. — In the initial stage, the development of gingivitis in children can be stopped in 5-7 days. A severe form of the disease will have to be treated for about a month.