Natural color of the tongue in a healthy child
There are many cases when light-colored accumulations on the uvula do not require treatment. For example, during the examination in the morning, the mother may notice light deposits in a small amount. They are easy to clean off and are considered normal. At 1 year of age, such plaque is also diagnosed. These are often milk traces from mother's milk or its substitutes. Therefore, a thin light film is quite acceptable. But the natural shade of the surface of the tongue should be visible through it.
In healthy children, the color of the muscle organ is pale pink. At the same time, it must be mobile, all movements must be made unhindered and without difficulty. The condition of a child's tongue is significantly affected by humidity levels, as well as the temperature in the room where the baby is. For self-diagnosis, the mother needs to conduct visual examinations of her child’s oral cavity. Cleaning the baby's mouth is also necessary. First, this is done using special pharmaceutical wipes, and when the child grows up, a children's brush with a surface for treating the tongue is used.
Let's sum it up
Modern doctors, just like their ancient predecessors, rightly consider the condition of the tongue to be one of the criteria for human health. When examining the tongue, its mobility, density, color, moisture, presence or absence of plaque and other factors are assessed. A white coating found on a child’s tongue can be a “signal” of the onset of a disease, even in cases where other symptoms have not yet manifested themselves. In this case, the coating can cover both the entire surface of the tongue and its individual sections, be dense or loose, and be easily or difficultly removed from the surface of the tongue.
Causes of plaque
Factors that provoke the appearance of light masses can also be diseases. The reasons for the appearance of a white coating on a child’s tongue often arise due to disturbances in the functioning of the body. It is very difficult, almost impossible, to remove such dense layers.
- The surface of the muscular organ suffers when hygienic manipulations of the oral cavity are violated;
- A light film covers the mucous membranes when taking certain types of medications;
- Excessive development and active reproduction of pathogenic microflora has a detrimental effect on the health of the oral cavity, so there may be a white coating on the tongue of a newborn;
And this is only a small part of those aspects that have a bad effect on the health of the mucous membranes. If symptoms of plaque appear, a small child should be shown to a local pediatrician. This is the only way to accurately determine the factors that provoked the appearance of deposits. By the way, a child may not only have a dry and burning mouth, but also a high body temperature. Often a plaque with red spots is diagnosed, which in medicine is called geographic tongue. In any case, self-medication is prohibited. Contact your pediatrician, he will competently develop a therapeutic program.
Inflammatory processes
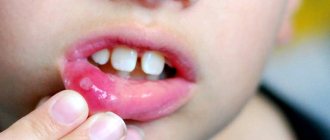
Often a baby will develop a white coating on the tongue due to stomatitis. The symptoms of the disease are very unpleasant. The disease is characterized by deposits that have a heterogeneous structure. Whitish grains are clearly visible on the muscle organ. If you try to eliminate them, blood is released. The baby is irritable and suffers from burning and pain in the mouth, as there are ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
At 3 years of age and earlier, as a rule, stomatitis of candidal origin. Light layers are present on the cheeks, gums, and even on the lips. The pain intensifies when eating sour-tasting foods. A visit to a medical facility is mandatory. Therapy consists of anti-inflammatory and painkillers that are used to treat the affected areas.
Fungal diseases
If the treatment of baby teeth is not carried out in a timely manner, this leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, including fungi. A white film on the lips and tongue often indicates that the baby has thrush (another name for candidiasis). In babies:
- the oral mucosa turns red;
- dryness appears;
- discomfort;
The younger the children, the worse they tolerate the disease. A one-year-old child becomes very capricious, he refuses to eat. Removing the film causes bleeding. The mucous membranes become covered with plaques and papules. To alleviate the condition, remove severe burning and itching, make an appointment with a pediatrician.
Caries
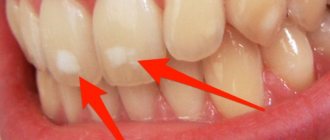
With caries, a dense white mass can form on the muscular organ and in the oral cavity. It doesn’t matter whether the child is 10 years old or a baby with baby teeth. This is due to the fact that the disease in its advanced form is a source of infection. Pathogenic bacteria thrive in the whitish mass on the tongue. They actively reproduce and aggravate the situation.
At 2 years old, when the baby has unstable teeth, parents should also monitor the oral cavity and prevent carious lesions on the units. Preventing the disease is possible. It is necessary to observe the rules of oral hygiene, and regularly. This is the only way that unwanted microorganisms will not settle on the mucous tissues of the tongue and a film will not form from the products of their vital activity.
Pathologies of the respiratory systems
If the tongue is covered with a white coating, this may indicate problems in the airways. Can be diagnosed:
- Viral form of the disease;
- Diseases of a bacterial nature;
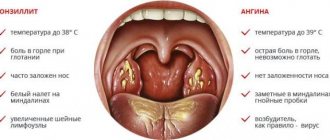
With the flu or acute respiratory infections, the temperature rises, the throat turns red, a cough appears, and the tongue becomes covered with a whitish film. A sign of pharyngitis and tonsillitis is the covering of not only the tongue, but also the tonsils with white masses. Clumps on the tip of the tongue indicate bronchitis. Deposits with a foamy consistency indicate chronic bronchitis.
Infectious diseases
When an infection enters the body, the body defends itself by raising body temperature. In this case, whitish masses of dense and thick consistency often form on the muscular organ. With scarlet fever, reddish islands are visible on the white tongue. The tonsils and the root of the tongue are covered with a particularly thick coating. Severe intoxication is detected in the child’s body.
Diphtheria affects different areas of the oral cavity. It is not uncommon for a child to develop gum inflammation. There are dots with a white tint on the tonsils, and light grayish deposits on the tongue. Remember that the formation of pus requires an immediate trip to the doctor.
Gastrointestinal diseases
When bottle-fed, formula often leaves a slight residue, which is not dangerous for the baby. But it happens that quite serious diseases develop from such food:
- The film in the central zone of the muscular organ and the formation of cracks and grooves indicate gastritis.
- A one-month-old baby is more susceptible to dysbiosis than others, since his digestive system has not yet been adjusted. In such a situation, the tongue is completely covered with whitish masses.
- At the age of 7, when hormonal changes begin and baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones, children are susceptible to enterocolitis. Inflammation in the intestines leads to deposits on the back of the tongue.
Why do adenovirus infections most often affect children?
During the first 6 months of life, children practically do not suffer from adenovirus infection. This is due to the fact that at this age children have passive immunity, inherited from their mother. Then innate immunity is lost, and children begin to get sick.
Until the age of 7 years, a child manages to get sick with adenovirus infection several times. Each time the body develops specific immunity to a specific type of adenovirus, but since there are several of them, the child has to get sick more than once. After 7 years, as a rule, they already have acquired immunity to all types of adenoviruses, and they are no longer afraid of adenovirus infection.
Over time, immunity is lost, so adenovirus infections can also affect adults.
Treatment of white plaque on a child’s tongue
Before starting treatment, you need to show the child to the pediatrician. Depending on the clinical picture, especially if there is bad breath, he may refer you to a gastroenterologist, dentist, internist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist or toxicologist. In order to treat correctly, a diagnosis is made, and then a therapeutic program is developed.
- Most often, at 2 months and up to a year, children suffer from thrush. To combat this disease, antifungal drugs are prescribed, which are used to treat pathological areas.
- In one-year-old children and 2-year-olds, infections and viruses are a common problem. In such a situation, antibiotics and immunoglobulins are usually prescribed. For herpes stomatitis, the dentist prescribes solutions with an analgesic and wound-healing effect.
- Preschoolers and school-age children are most often diagnosed with aphthous and allergic stomatitis. The range of medications for older children is wider than for infants. Antiseptic therapy is carried out.
Parents must remember that only timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions will eliminate the problem and prevent the development of serious complications.
Symptoms of adenovirus infection
The incubation period (the time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms) ranges from one day to a week (in some cases longer).
The disease, as a rule, begins with the appearance of signs of intoxication.
For an adenovirus infection, a complex of catarrhal phenomena is typical (manifestations of nasopharyngitis - rhinitis and pharyngitis at the same time): runny nose, nasal congestion, sore throat. Sometimes the palatine tonsils are affected (symptoms of tonsillitis are observed), in such cases a diagnosis of rhinopharyngotonsillitis is made.
The infection can travel down the respiratory tract, causing bronchitis and even pneumonia. Complications such as otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear) and sinusitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus) are also possible.
In almost all cases of adenovirus infection, inflammation of the eye mucosa is observed to one degree or another. The combination of symptoms of respiratory disease and conjunctivitis form a typical picture of an adenovirus infection. In bright light, symptoms worsen.
There is an intestinal variant of the disease. In this case, the adenovirus attacks the intestinal mucosa.
Headache
Headache is a typical sign of intoxication. Headache can occur with various infectious diseases.
More about the symptom
Muscle pain
Muscle or joint pain is another sign of intoxication. This condition can be described as aches throughout the body. Usually this symptom precedes a rise in temperature.
Chills
The patient is shivering - this is the beginning of a rise in temperature
Loss of appetite
The body spends a lot of energy fighting the infection. Digestive processes slow down and appetite disappears.
Weakness
Intoxication of the body often manifests itself in the form of weakness. If the child is older - and in the case of adenovirus infection this is usually the case, he becomes whiny and lethargic.
More about the symptom
Temperature increase
The rise in temperature begins somewhat later than the appearance of signs of intoxication. In most cases, the temperature remains low-grade (up to 38°C), but sometimes it can reach 39°C.
Stinging in the eyes
Inflammation of the eye mucosa is a typical symptom of adenovirus infection. It usually manifests itself as a burning (itching) sensation in the eyes.
More about the symptom
My eyes are watering
The eyes become watery and may fester.
More about the symptom
Abdominal pain
The intestinal variant of adenoviral infection usually manifests itself as abdominal pain.
Stool disorder
Stool upset is another symptom of the intestinal variant of adenoviral infection.
Carrying out diagnostics
Keep in mind! The first specialist you need to contact after identifying a tongue coated with a white coating is a pediatrician.
After carefully examining the child’s oral cavity, the doctor will assess the condition of the teeth and gums and check the lymph nodes.
After this,
he will make a diagnosis and prescribe effective medications to eliminate the underlying disease.
If it was not possible to determine the cause of the formation of layers during the examination, the pediatrician will give a referral to an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists.
In some cases, doctors prescribe a bacterial culture from the surface of the tongue and a general blood and urine test.
Based on the results of laboratory tests and examination, the small patient will be prescribed suitable treatment.
When should you consult a doctor?
Remember! Experts strongly recommend visiting your doctor and undergoing a medical examination in cases where:
- plaque persists throughout the day , and not just in the morning;
- deposits cannot be removed with a toothbrush or a damp bandage;
- In addition to the tongue, plaque forms on the inside of the cheeks ;
- the layers have a thick cheesy consistency.
The appearance of one or more additional symptoms in a child also becomes a signal informing about the need to undergo an examination.