- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
- Drugs
Stomatitis is more often referred to as a disease of kindergarten or primary school age: it is an infectious inflammation that is transmitted through shared toys, by contact or by airborne droplets.
But the disease can also occur in a very young child. Parents detect stomatitis at the moment when the child opens his mouth while crying or by characteristic rashes that often appear in the corners of the lips and even on the chin1. If your baby shows signs of stomatitis, do not rush to use homemade ointments and untested remedies - immediately take your baby to the pediatrician. Stomatitis is an infection, and due to the imperfection of the immune system, weakened immunity, it can spread to the ENT organs, liver, kidneys and other organs2.
Causes
Herpetic stomatitis, or as it is also called aphthous stomatitis, is dangerous, first of all, for young children. It is a serious viral disease, which, in addition to damaging the oral mucosa, causes general intoxication of the body and provokes malfunctions of the nervous, immune, and reticuloendothelial systems.
Herpes, which is the causative agent of the disease, may not make itself felt for a long time, although infection usually occurs in early childhood.
When the baby’s immunity is weakened, the herpes virus is activated and begins to multiply, causing an increase in temperature, enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, acute inflammation of the mucous membrane, and the formation of bleeding and painful ulcers on its surface.
Main reasons:
- decreased baby's immunity;
- previous infectious diseases;
- lack of vitamins;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- direct contact with patients with herpes stomatitis.
Infants are more likely to become infected with the herpes virus during childbirth, provided the mother has a herpes infection. In children under one year old and school-age children, the virus is activated against the background of an organism weakened by disease and vitamin deficiency.
Causes of stomatitis in infants
The main cause of stomatitis in infants is weakness of local and general immunity. A newborn baby can be called “sterile”: neither bacteria nor viruses are unfamiliar to its immune system. Therefore, even minor damage to the mucosa can become an entry point for infection. And the low activity of protective mechanisms leads to the active reproduction of viruses, microbes and the appearance of inflammation of oral tissues.
The following can also contribute to the development of stomatitis in a child:
- Intrauterine infections
- Birth injuries
- Infecting a child with infectious diseases during childbirth
- Lack of vitamins and microelements
- Taking antibiotics, hormones, sulfa drugs
- Congenital malformations5
Children in the first year of life often develop traumatic stomatitis. Its cause is damage to the gums and tongue from the sharp edges of toys or trauma to the mucous membrane that occurs due to a strong “hobby” with teethers. Infection immediately penetrates into the resulting wounds, causing inflammation. Therefore, it is very important to ensure that your baby’s toys are safe and clean: rattles and teethers should be washed from time to time in hot water and baby soap6.
Main symptoms and signs of the disease
Acute herpetic stomatitis in children develops gradually and is preceded by an incubation period lasting from two days to 3 weeks.
Early symptoms of the disease are:
- burning in the mouth;
- increased salivation;
- headache, nausea, general weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- the appearance of bad breath.
«
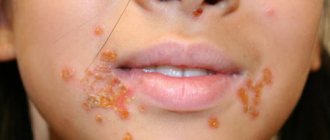
If the parents do not respond to the first signs, after a few days the mucous membrane becomes covered with multiple rashes. Small painful blisters itch, respond with acute pain to the touch, and when they rupture, a cloudy liquid flows out of them. The rash appears on the baby’s gums, cheeks, tongue, lips, and wings of the nose.
Herpes stomatitis can affect not only a school-age child, but also an infant.
The mild form of the disease can be easily treated at home; in moderate and severe forms, hospitalization of the small patient is indicated.
Classification and diagnosis
Herpetic stomatitis is classified both according to the severity of the disease and the characteristics of its course.
According to the characteristics of the course, acute and chronic (recurrent) forms are distinguished. Acute stomatitis is characterized by a sudden onset, pronounced symptoms, and rapid development. Without proper treatment, it quickly becomes chronic and can drag on for years, periodically exacerbating.
Based on the degree of severity, there are mild, moderate, and severe forms.
In mild forms, the following are noted:
- slight increase in body temperature;
- redness, swelling, inflammation of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- a small number of painful ulcers.
The average degree is characterized by:
- significant increase in body temperature;
- general weakness, nausea, headache;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of a blistering rash on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, tongue, and around the mouth.
The severe form causes:
- temperature rise to a critical level;
- lymphadenitis of the cervical, submandibular lymph nodes;
- a sharp disturbance in general well-being;
- the appearance of severe muscle pain, headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- multiple rashes that spread to the eyelids, conjunctiva, and perioral area.
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult for an experienced doctor. It is based on an analysis of the main symptoms, the order of clinical manifestations of the disease, the nature, and multiplicity of ulcers.
It is necessary to differentiate herpetic stomatitis from viral stomatitis; for this, in the first few days of the disease, a cytological examination of scrapings from erosions and aphthae should be done.
How long does the disease last and how many days is the child contagious?
Depending on the complexity of the form, herpes stomatitis in children lasts from several days to 2-3 weeks. With a mild form, the main symptoms disappear on the third or fourth day, treatment of a moderate form takes one to two weeks. The severe form is the most dangerous; healing lasts for weeks and requires mandatory hospitalization of the baby.
The disease is characterized by a high degree of contagiousness precisely during the period of exacerbation.
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets (including through kissing), when using shared dishes, cutlery, toys, and hygiene items.
Herpes is contagious and can easily be transferred to healthy parts of your own body.
It is necessary to wash your hands thoroughly after treating the surface affected by the sores with medications to prevent the spread of the virus.
Types of stomatitis and causes of occurrence in children
The causes of stomatitis in children can be different, and they are directly related to the type of disease. In this section, we will look at the main types of stomatitis and their causes in children.
Herpetic viral stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is the most common and common. Sometimes this type of disease is simply called herpetic stomatitis or viral . Typically occurs in children aged 1 to 4 years.
Often infection occurs through airborne droplets. Infection with herpetic viral stomatitis is also possible through children's toys, dishes and other objects. Against the background of weak immunity, the virus enters the body and settles in the most damaged areas of the mucous membrane. Such places can serve, for example, as small wounds that appear after a child bites his lips.
Aphthous (allergic) stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is often also called drug stomatitis , since the main reason for the appearance of this type of disease is allergic reactions to various medications. It is impossible to say exactly which drugs can cause stomatitis; this is an individual predisposition, and can only be accurately determined by visiting a pediatric dentist after all the necessary diagnostics have been carried out. This type of disease occurs infrequently and, most often, in preschool children.
Traumatic stomatitis
As the name implies, this type of disease occurs after mechanical trauma to the child’s oral cavity and the entry of dirt and bacteria into these places.
Injuries can be of a completely different nature. This could be purely a dental problem. For example, due to an incorrect bite, a child may constantly bite his tongue or lips. Other types of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane include burns, for example, from food that is too hot, a pacifier that is too hard, various bad habits (pulling toys into the mouth, chewing a pencil, etc.).
Candidal (fungal) stomatitis
The main cause of candidal stomatitis is Candida fungi. Basically, this type of disease is typical for children under 1 year of age who are breastfed. Particles of mother's milk remaining in the baby's mouth after feeding provide an excellent environment for the development of this type of fungus. For this reason, sometimes this type of stomatitis is called thrush .
Infectious (microbial) stomatitis
The main reason for the appearance of infectious stomatitis in children is a decrease in immunity against the background of diseases such as tonsillitis, sinusitis, pneumonia and other diseases of the nasopharynx. This type of disease occurs in children of both school and preschool age. Infectious stomatitis develops especially often in the autumn-winter period, when the child’s immunity is weakened.
How and with what to treat herpetic stomatitis in children
As Dr. Komarovsky notes, treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children, regardless of age, depends on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the patient’s immune system, and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases.
The main question that interests young parents is which doctor should they contact if they suspect herpetic stomatitis. Both a qualified pediatrician and a dentist can advise the child.
Therapeutic methods include both general and local treatment. Common activities include:
- prescription of antiviral drugs (acyclovir, Zovirax, Herpevir, Virolex);
- taking antipyretic and painkillers (paracetamol, Panadol, Eferalgan, Tylenol);
- prescription of antihistamines (diazolin, claritin, erius, fenistil);
- correction of the immune system (immudon, sodium nucleinate);
- vitamin therapy (vitamin C, ascorutin, multivitamins, B vitamins).
Children of older preschool and school age are recommended to be treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics to avoid possible complications.
For newborns and infants, antibiotic therapy is prescribed only as a last resort, with preference given to local therapy:
- applications of painkillers (solution of lidocaine, trimecaine, pyromecaine);
- treating the baby’s oral cavity with antiseptics (solutions of furatsilin, potassium permanganate, brilliant green, blue);
- Treatment of aphthae with iodine should be avoided, as it causes a burn to the mucous membrane;
- the use of antiviral medications in the form of ointments, lotions, solutions (interferon, acyclovir);
- applying an oil solution of vitamin A, sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, solcoseryl to the mucous membrane of the baby’s mouth).
If the symptoms of the disease do not disappear on the 3-4th day of treatment, but only intensify, the child is indicated for treatment in a hospital setting, otherwise stomatitis will become chronic, from which it is impossible to get rid of it.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis
Causes
Aphthous stomatitis is caused by staphylococcus, a microorganism that is found in large quantities in dental plaque and lives in carious cavities. Every person has this microbe and usually does not manifest itself in any way, but against the background of immune disorders. Often aphthous stomatitis can develop against the background of allergies, gastrointestinal diseases or injuries to the oral mucosa. Another factor in the development of the disease is dirty hands. This disease is often associated with children putting unwashed toys into their mouths, thereby increasing the total number and variety of microbes in the mouth.
Symptoms
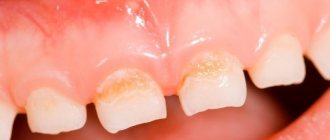
Most often, manifestations of chronic aphthous stomatitis occur on the lips, transitional fold, gums, under the tongue and on the tongue - in places where the mucous membrane can be injured by teeth or spicy food.
- Minor change in general health. Characterized by enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, fever and weakness.
- On an externally unchanged mucosa, aphtha appears - a spot 5-10 mm in size, slightly rising above the surface of the mucosa, covered with a whitish film tightly fused to the mucosa and surrounded by a bright red rim. Aphthae are very painful when touched. Most often there are one or two aphthae, less often – several.
Must remember! It is necessary to accurately determine the type of stomatitis: herpetic or aphthous. With herpetic stomatitis, there are many small blisters that turn into erosions and sometimes merge with each other, and rashes on the lips are possible. With aphthous rashes, larger, single rashes occur only in the mouth. If you have stomatitis, you should definitely consult a dentist to determine the type of stomatitis and choose the right treatment tactics.
Treatment
Elimination of the factor that caused the disease:
- exclude all allergens (citrus fruits, chocolate, brightly colored foods...);
- if you are taking medications that can cause allergies, then you also need to take this into account (tell your doctor what you are taking and for how long);
- exclude rough, spicy, salty, sour foods;
- if stomatitis is caused by allergies, antihistamines (suprastin, loratadine) are prescribed;
- If the aphthae is due to injuries from sharp edges of a tooth or filling, it is necessary to put the tooth in order.
- in the first 3-4 days, treatment of aphthae is carried out exclusively with antiseptics (rinses, gels). You can use chlorhexidine, rotokan, miramistin, givalex, stomatidine, listerine, chamomile and calendula decoctions - you can take any of these drugs (or any other analogue). Use according to the instructions (there are preparations in ready-made form, and there are those that need to be diluted). Rinse (or wipe the mucous membrane in small children) 3-4 times a day.
- after 3-4 days, epithelializing agents are added: solutions of vitamins A and E, rosehip or sea buckthorn oil, solcoseryl.
- If relapses occur frequently, you should pay attention to your general health. In some cases, only joint treatment with an immunologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist and other specialized specialists can help cope with the disease.
Must remember! Aphthous stomatitis is, first of all, a microbial lesion. Oral hygiene, adherence to personal hygiene rules, as well as timely treatment of caries, caries complications, and removal of tartar in many cases are sufficient to avoid aphthous stomatitis.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
When treating herpes stomatitis in children, it is extremely important to prevent the development of complications and transition to a chronic form. Therefore, all folk remedies are auxiliary in nature and should not replace full treatment.
To strengthen the child's immunity, a decoction of echinacea leaves, ginseng root, and rose hips is well suited.
Rinsing will help relieve itching, burning and pain. For these purposes, you can use decoctions of chamomile flowers, sage, calendula inflorescences, St. John's wort, alder cones, rose petals, and oak bark.
The healing of ulcers and aphthae is facilitated by treating their surface with brilliant green, blue and iodine; they have a drying effect. An alcohol solution of propolis helps well, it relieves the inflammatory process and has an analgesic effect on the oral mucosa. Use with caution to treat small children.
Newborns and infants are recommended to lubricate the inflamed oral mucosa with natural honey. This should be done with extreme caution, since honey is a fairly strong allergen.
Stomatitis - what kind of disease
Childhood stomatitis is an inflammatory dental disease of the oral cavity that affects the mucous membrane. Pathology can appear in any area: the inside of the cheeks, tongue, palate, lips, gums, etc. As a rule, there is no localization of the affected area. The more advanced the disease, the larger the area of inflammation.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children:
- temperature increase;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- redness of the inner lining of the mouth;
- pain;
- the formation of papules and then painful ulcers.
The child has a hard time with the pathology: he is capricious, often cries, refuses to eat, and sleeps poorly.
Treatment of stomatitis in young children involves local and systemic therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation or infection, strengthening the immune system and accelerating tissue regeneration.
Possible complications
Primary infection with herpetic stomatitis is highly treatable. Within 7-10 days, with proper treatment, the child can fully recover. Without appropriate drug therapy, the following complications may develop:
- herpetic keratoconjunctivitis (a dangerous herpetic eye infection that leads to blindness);
- dehydration (due to refusal to eat and drink).
To avoid undesirable consequences, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease, strictly adhere to all instructions, give the baby plenty of fluids, monitor oral hygiene, and wash your hands after each treatment of a surface affected by herpes.
Prevention in children
Preventing infection with the herpes virus is extremely difficult, since 90% of the population are carriers of it. It is important to delay infection as much as possible; the younger the child, the more difficult the disease is to tolerate. It is necessary to avoid contact with people who have an acute herpes virus. From infancy, the baby should be taught to use personal hygiene products, not allowed to drink from someone else’s mug after someone else, or to use used spoons, forks, and plates. You should not kiss someone who has a herpetic sore on their lips.
To prevent herpetic stomatitis, you need to do general strengthening of the child’s immune system, systematically give him B vitamins, multivitamin complexes, and carry out hardening procedures.