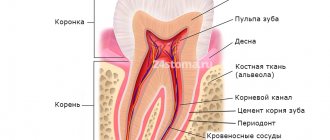
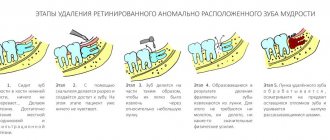
- Treatment of caries and pulpitis of milk teeth
- Treatment of caries and pulpitis for children and adolescents under 16 years of age
- Children's prevention and hygiene
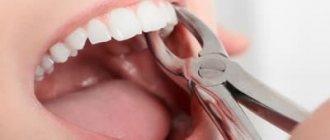
- Tooth extraction for children
- Anesthesia for children
If we talk about tooth extraction in children, then first of all we will talk about the removal of milk teeth for dental reasons and during the period of physiological change of teeth to permanent ones.
Permanent teeth have to be removed in children for the same reasons as in adults, and you can read about this in our article on tooth extraction.
How does baby teeth fall out?
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones is a physiological process. By the age of 3, a child grows 20 milk teeth in his mouth, which differ in structure from permanent teeth. They have thinner enamel and walls, and more branched roots. Then, gradually, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve. At the age of 5-6 years, baby teeth begin to loosen and fall out in the order in which they appeared, and in their place permanent teeth grow from the rudiments. The period of formation of a permanent dentition lasts up to 13-14 years and the appearance of 7 teeth - the second molars - ends. Healthy baby teeth and natural, timely replacement of teeth guarantee the child healthy teeth in his permanent dentition. Therefore, it is best if baby teeth fall out on their own and do not require additional doctor intervention, but this does not always happen.
Why treat baby teeth?
Rotten baby teeth do not always attract the attention of parents. Especially if the pathological processes are painless and do not bother the child. Adults think that when the bite changes, the bad teeth will disappear by themselves, and instead of rotten teeth, normal molars will grow. Dentists warn about the fallacy of such a misconception.
Rotten milk teeth are:
- damage or destruction of tooth germs - a high risk that the root units will grow sick or not appear at all;
- early loss of primary occlusion units - leads to displacement of existing teeth, the appearance of crowding, and the formation of a pathologically abnormal bite;
- an ugly smile, an unaesthetic appearance - the appearance of complexes due to appearance in young children, decreased contact with peers, uncertainty, isolation;
- deterioration of diction - rotten, breaking teeth interfere with the correct movements of the tongue during speech, leading to a lisp, burr;
- gradual spread of infection - damage not only to the surface of the teeth, but also to the pulp, development of pulpitis, the appearance of an abscess, as well as a tendency to ENT diseases and gastrointestinal diseases.
Is it possible to remove a baby tooth at home?
The human body is programmed to independently change teeth without complications. If the child does not have dental or general diseases, then the natural loss of a baby tooth is the most desirable scenario. You don't need to do anything to do this. Just when a child’s tooth is loose, pay extra attention to hygiene, because brushing a child’s loose teeth on their own is painful. Make sure that the child does not touch the tooth with his hands - it can cause an infection.
How to help a baby tooth fall out on its own?
The simplest and most effective way is to give your child something hard to chew on, such as an apple. It is better to refuse threads and other fancy devices.
If you decide to help the process a little and remove the interfering tooth yourself, clamp it with a sterile napkin, try to turn it a little around its axis and remove it. Do not “twist” the tooth with force or put pressure on it, so as not to damage the bone and soft tissue. After removal, have your child bite on a sterile cotton swab for 10-15 minutes. There is no need to rinse your mouth after removal; do not feed your child solid food or hot foods for several days.
If you suspect that the tooth has not been completely removed, or the child complains that there is a sharp edge in the hole that “scratches” - contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Possible treatment options
The method of preserving a damaged baby tooth depends on the degree of damage. Sometimes the dentist suggests taking an x-ray to diagnose damage to adjacent crowns, tooth dislocation and assess the condition of surrounding tissues. Before restoring a tooth, the dentist performs hygienic treatment of the oral cavity.
Treatment methods for a chipped baby tooth
- Enamel chipped - polishing the sharp edges of the crown.
- A baby tooth has broken off within the dentin - building it up with photocomposite material or covering the chip with a crown fragment.
- Fracture exposing the dental nerve - reconstruction using a tooth fragment.
- Mobility, displacement of teeth - applying a splint to the damaged tooth and two adjacent crowns (one on the right and on the left) under local anesthesia.
- A child has a cracked baby tooth in the root zone - sealing the damage and strengthening the crown with an onlay.
Thanks to the precise selection of the color of the composite material, the restored baby tooth does not differ from healthy crowns. The child will not experience psychological discomfort, but the teeth must be treated with care to avoid repeated chipping.
When should a pediatric dentist remove a baby tooth?
There are cases when a baby tooth needs to be removed without waiting for natural loss.
If the tooth is not loose, it CANNOT be removed at home; this can ONLY be done by a pediatric dentist. Temporary teeth have long roots, underneath them there are the rudiments of permanent teeth that can be damaged, and baby teeth themselves are fragile and easy to break. Tooth extraction is a mini-operation, for which you need to contact a specialist.
In what cases does a baby tooth need to be removed?
- The tooth is damaged by 50% or more by caries and cannot be restored.
- Serious complications of caries have led to the fact that the tooth is a source of infection that cannot be cured - periodontitis, periostitis, phlegmon.
- A fistula has formed on the gum next to the tooth.
- A cyst was found on the root of a baby tooth.
- The tooth is injured (severely chipped, twisted by a blow, broken and scratches the mucous membrane)
- The tooth wobbles for a long time, but holds tightly and cannot fall out on its own, which prevents the child from eating.
- The loose tooth became infected and inflammation began.
- A permanent tooth has already erupted next to the milk one, but the milk tooth is not going to fall out.
- If, according to the timing, the baby tooth should have fallen out a long time ago and a permanent one should have grown in its place, but nothing happens. This indicates a delay in root resorption. In order to understand how to proceed, an X-ray diagnosis of the presence of a permanent tooth germ is needed. If there is a germ, then it is better to remove the baby tooth to cause the growth of a permanent one.
- Sometimes a tooth needs to be removed for orthodontic reasons.
Diagnosis of root resorption
The problem with diagnosing internal root resorption is that nothing bothers the patient, and this can last for years. Therefore, X-ray diagnostics should be given its due.
| Internal resorption | External resorption |
| Smooth, clear focus of destruction | Asymmetrical, corroded lesion |
| The defect is always located within the root canal | The defect is located on the root surface and can change its position |
| Fuzzy, barely noticeable contours of the root canal | The contours of the root canal are clear, superimposed on the outlines of the defect |
X-ray examination also helps in diagnosing external resorption. Defects usually have uneven edges, can go deep into the dentin and are detected on any root surface. However, there are cases when the focus of clearing has clear contours, as with internal resorption; in this case, you should take an x-ray in several projections and make sure that the contour of the root canal overlaps the contours of the defect, or even better, do a CBCT scan.
But it is more difficult to distinguish replacement resorption from inflammatory resorption. Radiologically, with replacement resorption, there are no foci of clearing and periodontal cleft due to bone formation. Ankylosis occurs more easily due to the chronicity of the process.
The diagnosis of cervical invasive resorption is established on the basis of clinical and X-ray diagnostics. The condition is asymptomatic, as with VRC we see a “pink spot” on the enamel, periodontal inflammation, but the pulp is not damaged.
What anesthesia is used to remove baby teeth in children?
If we are talking about removing a baby tooth that is already loose, without complications and signs of inflammation, then such removal does not require pain relief.
If a problematic baby tooth is removed or it sits firmly in the jaw, then local anesthesia is used for children, sometimes with sedation.
Tooth extraction under anesthesia (general anesthesia) is possible in special clinics where a team of anesthesiologists works. From a medical point of view, in most cases there is no need to remove baby teeth under anesthesia. This is usually due to the fear of the child and his parents. The use of anesthesia is justified only in cases of serious mental disorders or complex illnesses, because it has more dangers than benefits .
Contraindications
- Acute inflammation in the mouth, such as candidiasis, gingivitis or stomatitis;
- Pneumonia, tonsillitis, whooping cough;
- Various tumors near the temporary tooth, when it needs to be removed along with it in the hospital.
It is recommended to remove temporary teeth only when the acute stage of dental disease has passed. During removal, it is necessary to take into account possible pathologies of the patient, such as cardiac pathologies, problems with blood vessels and the nervous system, kidney diseases and various blood diseases.
What are the dangers of early removal of baby teeth?
If a temporary tooth is forced to be removed before its natural loss by more than a year, then we are talking about early removal. This situation provokes malocclusion and improper development of the entire dental system, including delayed jaw growth.
Neighboring teeth strive to take the place of their distant counterpart, and all of them are displaced.
adjacent teeth and their roots, antagonist teeth also move into the resulting free space. As a result, permanent teeth can erupt chaotically and even outside the dentition. In the future, such a problem will require long-term orthodontic treatment.
In addition, earlier removal of chewing teeth leads to a redistribution of the load on the front teeth, which, in turn, begin to collapse.
Therefore, it is so important to strive to keep all baby teeth in their places for as long as possible, preferably until the time of their natural replacement.
Types of resorption
There are also two types of resorption, each of which, without treatment, can provoke complete tooth loss or partial tooth loss.
Internal resorption
Dentin (or cement shell) is absorbed into the root canal, dissolves, and disappears. Inflammation begins inside the tooth and then spreads to the outer surfaces. Usually the cause of the pathology is injury, burn (thermal, chemical), infection. Inflamed cells increase in size. The structure of soft and hard tissues changes. Symptoms of resorption:
- Changing the shade of the dental unit to pink. The tissue of the neurovascular bundle turns into granulomatous. After dying it turns gray.
- Painful sensations appear.
- The mobility of the units is noticeable.
Without diagnosis, the tooth becomes an empty shell. It is susceptible to caries, fragile - it splits at the slightest load. In the early stages, it is detected during preventive examinations or as a concomitant option in the treatment of other teeth.
External resorption
The reason is a consequence of injury, infection or a rapid change in the position of the roots (possible when installing braces). The enamel also changes color to medium red or pink. Develops at the junction with the tissues of the jaw. Causes:
- The action of pathogenic microflora inside the root canal.
- Dislocation of teeth.
- Necrosis of the nerve bundle.
There are no obvious symptoms. Blood capillaries of the gums and surrounding tissues penetrate into the tooth root, changing the shade of the crown. Changes can be detected by taking an x-ray. Rarely diagnosed in the early stages, loss of chewing teeth or loss of central teeth is possible. Doctors note an aggressive course, rapid development with extensive destructive processes, resorption of the dental bone tissue begins.
What to do if a child has a baby tooth removed early?
If trouble happens and the child has one or more milk teeth removed ahead of schedule, it is necessary to take measures to restore the dentition and preserve the space after the extracted teeth.
For this purpose, special dentures are used - removable plates with artificial teeth or special orthodontic structures are installed. In any case, after early removal, you must take the child for a consultation with an orthodontist - he will suggest the right solution. For more information about the treatment of malocclusion problems in children, read: “Children’s orthodontics - correcting the bite in children.”
Complications
If a baby tooth is removed prematurely, a year before the primary tooth erupts, complications can occur. Those teeth that the child has left may move apart and begin to take up empty spaces, which will lead to problems with the growth of molars, since they will not be able to appear in their proper place.
When removing multiple baby teeth at the same time, be careful to ensure that the child does not develop an overbite. To do this, you can use dentures made of removable plates with artificial teeth inserted into them. This will help prevent the process of teeth moving apart and the molars will be able to erupt in their designated place.
List of possible complications when removing temporary teeth:
- Tooth fracture;
- During removal, soft tissue may be affected;
- Damage to the mucous membrane or gums;
- Dislocation of the jaw;
- Fracture of the alveolar process;
- Nerve damage;
- Aspiration of a root or blood clot;
- Injuries to nearby teeth.
When should a baby tooth not be removed?
There are situations when it is IMPOSSIBLE to remove a baby tooth, so as not to aggravate the child’s condition or provoke serious complications.
- If a child suffers from an acute infectious disease, then removal should be postponed until complete recovery.
- If there is an acute inflammatory process in the oral cavity - stomatitis, gingivitis, candidiasis (thrush), then removal is carried out after the acute stage of the disease subsides.
- If the tooth is located in the area of any tumor, removal is carried out together with the tumor and in the hospital.
- Teeth removal is carried out with caution in small patients suffering from diseases of the central nervous system, heart, kidneys, and blood.
How to go to the dentist, remove a baby tooth and not scare your baby?
It is recommended that a child’s baby teeth be removed by pediatric dentists: it will be painless, safe and timely. For everything to go smoothly, a visit to the dentist should be associated with something pleasant and calm. Modern dentistry has a friendly atmosphere, new painkillers have appeared, and instruments (especially in children's offices) do not inspire fear.
Finally, our advice: don’t worry and don’t let your child worry. The calmer you are about going to the dentist, the calmer your baby will behave. Stay nearby in the dentist's office, because parental support is extremely important to him.
What to do after a child’s tooth extraction?
- Make sure that the child spits out the tampon that was placed after removal after 15-20 minutes.
- After removal, a blood clot should remain in the hole, which protects it from inflammation. There is no need to clean the hole from blood, rinse the mouth, the child should not touch the removal site with hands or objects.
- If the child has been given anesthesia, explain to the child that he should not bite on the numb side until the feeling of cold and pins and needles goes away.
- Feed your baby only warm, soft food for several days.
- Maintain good hygiene; brushing your teeth is not only possible, but also necessary, with a soft toothbrush, carefully avoiding the extraction site.
- If the tooth extraction was difficult, then try to limit the child’s physical activity so as not to provoke bleeding.
How to properly prepare a child for tooth extraction in pediatric dentistry?
- A brave child is one who is familiar with the place and situation, so parents need to try to ensure that the first visit to the dental clinic is not associated with treatment, much less tooth extraction and pain. Go with your child to the dental clinic for preventive examinations, children's parties, which we regularly hold, take your child with you when you go to have your teeth treated.
- A good, cozy clinic is not a dream today, but an accessible reality. Go to the clinic yourself without your child, meet the doctor. The atmosphere should be calm, the space should be thought out for small patients. And, of course, no screaming or crying behind office doors.
- Never frighten your child with the dentist or doctors in general, and do not be afraid of them yourself - children subtly sense the mood of their parents.
- Ask your doctor whether it is better to leave your child alone or be present during the procedure. NEVER leave your child alone at the dentist's office if this is their first appointment with the dentist.
- Do not shame your child in the dentist's chair, do not blackmail him with a gift or threaten him with punishment. Introduce him to the doctor and help establish contact between them, using the child’s natural curiosity - he should be interested, not scared.
Other causes of enamel darkening in children
Rotten baby teeth in a child look different in the photo. Usually these are black spots, lumpy enamel, deformed crowns - unpleasant, ugly, even creepy. But an unaesthetic appearance does not always indicate rotting. Sometimes the reasons lie in other diagnoses or pathologies:
- black plaque;
- enamel hypoplasia;
- abnormalities in tooth shape.
Black plaque - stains on baby teeth
Dark spots on teeth are not always tooth decay. It could also be:
- Priestley's plaque - appears due to the increased activity of certain bacteria that secrete a black pigment. The defect is aesthetic, but dentists advise cleaning the enamel from plaque, since it can prevent caries or other dental diseases.
- Dark deposits due to taking iron supplements are an aesthetic problem, which professional cleaning helps to cope with.
Dark pigmentation is also caused by dysbiosis, lack of calcium, and taking antibiotics. Plaque is removed using gentle dental cleaning methods, returning the enamel to its natural whiteness.
Enamel hypoplasia and tooth shape abnormalities
Hypoplasia manifests itself as a change in the structure and color of the enamel and is not a carious lesion. Is it congenital or acquired? In the case of systemic hypoplasia, the shape of the dentition units may also be affected. Externally, the pathology manifests itself as:
- an altered line of the tooth edge is a natural deformation, and not due to rotten teeth;
- barrel-shaped crowns, cone-shaped - due to changes in the tooth at the dentin level;
- spots on the tooth surface of different sizes and shades - altered enamel thickness, insufficiently developed tissues.
For isolated manifestations, hypoplasia is not treated. In case of severe defects in baby teeth, the doctor will suggest remineralization and filling of the affected areas.