Polyp
is a pathological proliferation of the mucous membrane. By its nature, this is a benign formation, however, there is a risk of the polyp degenerating into a malignant tumor.
The mucous membrane lines the inside of the hollow organs of those systems of our body that communicate with the external environment, in particular the respiratory, urinary, reproductive and digestive systems. The functions of the mucous membrane are varied - this includes a protective function, absorption (typical of the gastrointestinal tract), hydration, and some others.
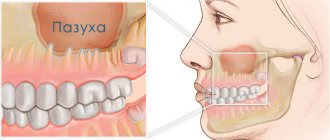
As a result of various reasons, the mucous membrane may become weakened, and then it begins to grow. So the body tries to compensate for the loss of properties of the mucous membrane by increasing its area. The result is a polyp that looks like a mushroom-shaped body on a stalk or on a thick base. Polyps can be either single or multiple (in this case the disease is called polyposis
).
Causes of nasal polyposis
Modern medical science has not yet achieved a final understanding of why polyps form in some cases and not in others. However, there are known factors that contribute to the occurrence of polyps. These factors can be divided into two groups: local and general.
Local causes of the formation of nasal polyps are factors affecting exclusively the mucous membrane of the paranasal (paranasal) sinuses and nasal cavity. First of all, this:
- allergic rhinitis (chronic runny nose of allergic origin). This kind of runny nose is an allergic reaction to dust, pollen, and animal hair. Allergic rhinitis accounts for 80% of polyp formation;
- private colds;
- chronic sinusitis (inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses) - sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- abuse of vasoconstrictors (drops for the common cold);
- curvature of the nasal septum, blocking the anastomosis of the nasal sinuses;
- fungal infection.
The formation of a polyp may be due to the influence of several factors.
Common factors that contribute to the formation of polyps are:
- individual reactivity (that is, the body’s ability to respond to certain challenges). There is a congenital predisposition to the formation of polyps. Also, the likelihood of polyps increases with age, since life circumstances can contribute to the development of a predisposition to this disease;
- state of the immune system;
- some systemic diseases.
If polyps are detected in the nose, it is recommended to undergo an examination of the intestines; it is possible that polyps have formed there too, but have not yet manifested themselves.
Potential Risks
“Polypous tissue is initially non-cancerous. This is not an oncological pathology, but a benign formation. But at the same time, everything that will be removed in the operating department will be sent for histological examination, so that the doctor studying the biomaterial can give a clear answer to the question of what it is,” noted Vladimir Zaitsev. In addition, it will tell you how fast the growth rate is. This is the main thing. This indicator also determines what the effect of the operation will be, for example, whether the polyps will grow again. “It happens to one person that they removed them and the polyps grew back literally six months later. He may attribute this to a poorly performed operation, but in fact the problem is precisely the growth rate. And for some, after one operation they may not grow back. Everything is very individual,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Symptoms of nasal polyposis
In the early stages, the disease may occur without any noticeable symptoms.
Having arisen, the polyp gradually increases in size, filling the cavities available to it. If a polyp has formed in the paranasal sinus, you may not suspect it until it, having filled the sinus itself, penetrates through its outlet into the nasal cavity.
In advanced cases, polyps can descend from the nasal cavity and nasopharynx below, making it difficult to eat. The pressure of polyps on the walls of the sinuses can be very painful, and on the nasal septum - lead to its deformation.
Typical symptoms of nasal polyposis are:
Nasal congestion
Further growth of the polyp usually leads to difficulty breathing through the nose. Usually they complain of persistent nasal congestion; sometimes the polyp feels like a foreign body in the nose. Often the formation of polyps is accompanied by a decrease or complete loss of smell.
Runny nose
As always, when the nose does not breathe well, a runny nose develops, there is a decrease in hearing and, as a result, a lack of attention. Headaches, increased fatigue, and chronic fatigue are also possible.
More about the symptom
Nosebleeds
Mechanical impact on the polyp (for example, by sneezing or blowing your nose) can lead to damage (especially in the peduncle area), and then the polyp may begin to bleed. If there is periodic bleeding from the nose against the background of constantly difficult nasal breathing, then the cause is most likely a polyp.
Stages of development of neoplasms
The severity of signs and symptoms directly depends on the stage of the disease. When the tumor is small, a sign of its appearance is a feeling of congestion. This symptom looks like the beginning of a cold, so often at this stage a person does not diagnose and treat growths. Treatment boils down to the use of vasoconstrictor drops, which ultimately do not help. During this period, the body is more vulnerable to all kinds of infections, and otitis media, tonsillitis and other inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs can occur.
At the next stage, symptoms such as loss of smell and the appearance of a nasal voice appear. If the tumor blocks the opening of the auditory tube, signs of hearing loss appear.
In the third stage, the symptoms of the disease appear most intensely. Nasal discharge, headaches, constant congestion, breathing through the mouth - all these are signs that the polyp has reached an impressive size.
The symptoms of the disease are actually not as harmless as they look. To get rid of them, you must definitely contact an ENT doctor to prescribe competent treatment.
Unfortunately, few patients come to an otolaryngologist at the first signs of illness, when conservative treatment is still possible. Most of them turn to an ENT doctor when only surgical treatment can really help.
Treatment methods for nasal polyposis
Polyps that impede normal nasal breathing, as well as bleeding polyps, must be removed. There is no way that would make it possible to reduce the body of a polyp without resorting to surgery. Sometimes small polyps are not removed. But in this case, periodic monitoring of the condition of the polyp is necessary, since its growth can begin at any moment. It should also be remembered that polyps can degenerate into malignant tumors.
An important task is to prevent the re-formation of the polyp. In most cases, simply removing the body of the polyp is not enough. Since its formation is caused by a disruption of the normal functioning of the mucous membrane, it is necessary to establish the cause of this disturbance and eliminate it. Since polyps most often form against the background of allergic diseases, treatment of polyps should be combined with treatment of allergies. It is also important to help strengthen the overall immune system. Therefore, along with contacting an ENT specialist, you may need to consult an allergist-immunologist.
Drug treatment
Conservative (medicinal) treatment methods can be used to slow down the growth of the polyp, but such drugs cannot be used constantly.
Removal of polyps
Removal of nasal polyps in Moscow is possible in the Family Doctor network of clinics. For the treatment of polyps of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity, doctors at Family Doctor recommend using the Surgitron radiosurgical device. Removal of nasal polyps using Surgitron does not require hospitalization and can be performed in any of the Family Doctor clinics. If necessary, surgery to remove a polyp can be performed using a laser at a surgical hospital.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Nasal polyps: diagnosis
When examined by an ENT doctor, nasal polyps can be identified visually.
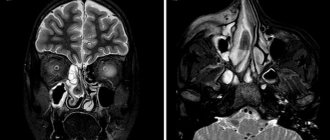
Additional methods, such as computed tomography, provide additional information about the extent of the pathological process. Examination by an ENT doctor.
First, the specialist asks about the patient’s complaints and previous diseases (allergies, sinusitis, etc.). Symptoms such as problems with nasal breathing, impaired sense of smell or frequent sinusitis already raise suspicions about polyposis rhinosinusitis.
Then the doctor carefully examines the ENT organs. Large nasal polyps that protrude into the nasal cavity may already be visible to the naked eye. With the help of speculums and a nasal endoscope, the doctor often finds smaller polyps located more deeply.
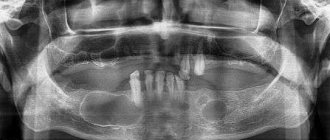
Radiation diagnostics.
To obtain accuracy in diagnosis, it is necessary to understand the extent of the spread of polyps in the paranasal region; imaging methods, in particular computed tomography (CT), are suitable for this purpose. Conventional x-rays of the sinuses are considered obsolete. Ultrasound and MRI can be used in the diagnosis of nasal polyps only in rare cases.
Complications
Polyps can cause a number of unpleasant consequences for the body.
The first problem is that a person switches to mouth breathing. The natural way of breathing is through the nose, because... The air passing through the nasal cavity is warmed, moistened and purified. When nasal breathing is impaired, a person begins to breathe through the mouth, and the air enters the lower respiratory tract unwarmed and polluted. This means there is a risk of getting pharyngitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, etc. increases significantly.
The second problem is impaired ventilation of the paranasal sinuses. This leads to frequent sinusitis (sinusitis, sinusitis, sphenoiditis, ethmoiditis). These diagnoses are dangerous and, if not treated correctly, can lead to dangerous complications, such as sepsis or meningitis.
Problematic breathing through the nose can cause breathing pauses during sleep - obstructive apnea. These are the first signs of the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Polyps aggravate the course of bronchial asthma and intensify its symptoms.
Overgrowths of mucous membrane in the nose that appear in infants interfere with proper sleep and sucking milk: this leads to malnutrition, weight loss, problems with the respiratory and digestive systems, a deviated nasal septum, problems with teeth, bite and other facial deformities.
How to fight
There are two treatment options, notes the otorhinolaryngologist. The first option is surgical, when all polypous tissue is removed. The second option is conservative. “Special nasal sprays are used. But here it is important to remember that all therapy is exclusively under the supervision and as prescribed by a doctor,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
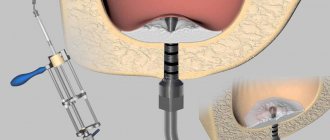
Polyps are removed in different ways. If they are small and located in the vestibule of the nose, the operation can be performed in an ENT office. But when they are large and located deep, in the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth, a person can be put under anesthesia and removed in an operating room using an endoscope, says the ENT doctor.
Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. “Unfortunately, if you compare a polyp and a cyst, the probability of malignancy of a cyst is very small, and the probability of malignancy of polypous tissue is very high, especially if there is a predisposition. Therefore, the polypous tissue is sent for examination,” says the otolaryngologist. And if a person does not act, there is a risk that the polyp will begin to grow deep into the brain tissue, which can lead to the death of the person in a fairly short time. Polyps cannot be treated with coolness; one must always be wary of them, the otolaryngologist sums up.
Rehabilitation after polypotomy
The postoperative period depends on the extent of surgical intervention performed on the patient. If a polysinusotomy was performed, the patient's nasal cavity is tamponed to avoid postoperative nosebleeds. In the case of endoscopic shaver or laser polypotomy without opening the sinuses, tampons are not needed.
Rehabilitation takes up to one week for any type of intervention.
With minimally invasive interventions, this period is reduced to 2-3 days, until the reactive postoperative swelling of the mucous membrane subsides. After surgery, it is recommended to limit physical activity for 2-3 weeks.
After surgery, topical steroids are prescribed to prevent the regrowth of polypous tissue. Patients with polypous rhinosinusitis should undergo a course of topical steroids several times a year.
Local anesthesia
In children over 7 years of age and adults, polypotomy can be performed under local anesthesia. Before the operation, the child is given a sedative intramuscularly. An anesthetic solution (10% lidocaine solution) and vasoconstrictor drugs are sprayed or applied into the nasal cavity to relieve swelling from the mucous membrane and improve vision. Afterwards, a less concentrated anesthetic solution (2% lidocaine or ultracaine) is injected into the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity to enhance the analgesic effect. During the operation, the patient is conscious and perceives everything around him. Local anesthesia is indicated only in the case of surgical interventions limited to the nasal cavity - polypotomy.
Consequences
When removing polyps, a person needs to listen to the opinion of a doctor. “Sometimes polyps are so small that the operation will not be noticeable, there is no point in fighting them like that. But when the polyps are very large and do not allow the nose to breathe, this provokes a rise in blood pressure, hypertension, cerebrovascular accidents, neurological conditions and diseases. Of course, in this case it makes sense to have surgery, because it is fraught with heart attacks, strokes, arterial hypertension and hypertensive crises,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Research to prepare for surgery
Before the actual surgical intervention, it is necessary to carry out a set of procedures to prepare the patient for the operation. This complex includes:
- Complete blood count (CBC/DIFF) with leukocyte formula/ESCBC/DIFF) with leukocyte formula/ESR;
- Blood type, Rh factor;
- Blood chemistry
Find out more
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
General anesthesia (anesthesia)
In children under 7 years of age, polypotomy is performed under general anesthesia, so the intervention takes place without pain and, which is especially important for the child, without psychological stress. The clinic uses drugs of a high safety class, they are non-toxic and do not cause complications, so anesthesia is easily tolerated even in childhood and feels similar to normal sleep. Endoscopic polysinusotomy (FESS) and polypotomy, in case of a large volume of intervention, are also performed under anesthesia in children and adults. The type of anesthesia is selected by the operating physician together with the anesthesiologist according to indications.