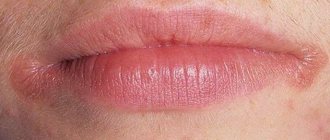
Causes of growths under the tongue
Formations on the tissues of the tongue and oral mucosa appear when the growth mechanism of epithelial cells fails. This process is provoked mainly by condylomatosis or the so-called papilloma virus. The disease is considered insidious due to hidden symptoms at an early stage of development, which complicates early diagnosis. In addition, it is contagious, the virus is transmitted even through kisses and shared household items, not to mention closer contacts of partners (sex of different types).
Children can become infected with condylomatosis at birth from an infected mother, therefore, when the disease is detected in a pregnant woman, it is recommended to allow labor by cesarean section.
Features of glossitis during pregnancy
The causes of glossitis of the tongue in pregnant women are due to the fact that the immune defense weakens to allow the fetus to develop, which means that the body during this period becomes practically defenseless in the face of various bacteria and viruses. The second risk factor is a lack of vitamins and minerals obtained from food.
According to statistics, most often pregnant women experience a picture of desquamative and Gunter's glossitis. Symptoms that should alert you during pregnancy include:
- Profuse drooling. During the period of bearing a child, a woman already secretes a larger amount of saliva than usual, but a sharp increase may indicate the onset of glossitis.
- "Lacquered Tongue" A specific symptom that indicates the development of B12 deficiency anemia.
- Color change. White spots on the surface of the tongue alternate with spots of rich red color.
- Refusal of food. Acute glossitis in pregnant women is characterized by severe pain in the tongue during chewing and speaking, which, among other things, affects appetite.
As for the treatment of glossitis in pregnant women, the safety of the fetus comes first. Therefore, all therapy is exclusively local in nature (sprays, rinses), eliminating the penetration of the drug through the placenta. It is recommended to adjust your diet in such a way as to remove any foods that irritate your tongue.
Attention!
In order to avoid complications that can negatively affect the health of the fetus, treatment of glossitis during pregnancy must be carried out under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist monitoring the woman.
Symptoms
You can recognize a problem in the oral cavity by the following signs:
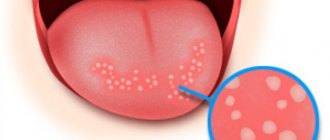
- seals, tubercles, small antennae or outgrowths form under the tongue, which are clearly visible upon visual inspection;
- the shape of the formation is filamentous or elliptical;
- the texture is soft and smooth, no peeling is observed;
- the color of the growth may be the same as the mucous membrane, or have a reddish, whitish tint;
- the formation is 2-20 mm in diameter.
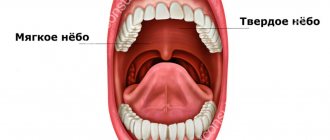
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.
External manifestations (+photo)
Growths under the tongue in humans form in the form of warts, papillomas, and condylomas. All varieties are signs of the presence of VPI in the body. Their differences lie in the type of epithelium and external manifestation. Papillomas can be either protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane or flat with rough tissue. And condylomas always rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with the help of a fairly high stalk.
Types of growths under the tongue:
Depending on the type and causes of formation, condylomas come in different colors:
- red;
- white;
- light with a yellow tint;
- pink;
- gray;
- from light to dark brown.
Growths in the oral cavity are most often localized in the following areas:
- on the mucous membrane under the tongue;
- on the bridle;
- on the gum under the tongue;
- on the inside of the tongue;
- along the rim of the tongue and other areas of the mucous membrane.
How and why we become infected with HPV:
- In most cases, HPV is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Infection is possible through household means, through touch, while staying in public places, such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, toilets or gyms.
- Self-infection, such as when you accidentally cut yourself while shaving.
- There are known cases of infection of a newborn during passage through the birth canal.
The danger of HPV lies in the fact that, once it enters the human body, it can remain in an inactive state for a long time, but then suddenly (during stress, a cold or other immune system failure) make itself felt in the form of the appearance of tumors on the body and growths on the tongue.
Diagnostics
Examination by an otolaryngologist
If characteristic growths are detected in the oral cavity, you should contact one of the recommended specialists (depending on the location of the focal zone):
- dentist;
- otolaryngologist;
- dermatovenerologist.
It would also be a good idea to visit an oncologist to rule out the possibility of developing a tumor of malignant origin.
Diagnosis of condylomatosis and other diseases associated with the formation of growths under the tongue consists of the following steps:
- visual examination by a doctor;
- taking anamnesis;
- laboratory research;
- histology.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Types of processes
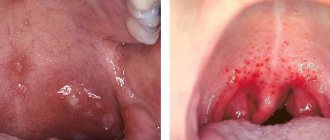
Most often, flat or pointed warts form in the oral cavity:
- Flat formations have a small protrusion above the mucous membrane and tissues, their shape is predominantly round. Condyloma differs in color from the general background in a brighter shade, so identifying it is quite simple. It is quite dense to the touch and is localized on the lower part of the tongue and oral mucosa.
Flat build-up
- Pointed papillomas form individually in the form of nodules or as a whole family, which makes them similar to cauliflower. They are moderately soft and elastic to the touch.
Pointed growth
Another type of growth is condylomas lata, which are localized not only on the tongue, but also on other parts of the oral mucosa. The reason for their appearance is syphilis.
Which people are susceptible to papillomas?
Based on the information we provided above, we can distinguish several “risk groups”, people in which are susceptible to the development of growths and neoplasms on the tongue and body.
The appearance of a process on the tongue is possible:
- In a situation where a person has reduced immunity as a result of stress, the presence of parasites in the body or ongoing inflammatory processes.
- If a patient with a growth in the mouth suffers from autoimmune diseases.
- In a person with HIV infection.
- In people who are promiscuous.
- In the event that a person has bad habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol especially contribute to the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths on the tongue.
- If there was any trauma to the tongue or damage to the mucous membrane occurs systematically.
Drug treatment
A mandatory part of treatment is sanitation of the oral cavity.
To eliminate growths under the tongue with condylomatosis, complex treatment is used, which includes:
- taking antiviral drugs;
- the use of antiseptic solutions and ointments for local treatment of the affected area;
- carrying out complete sanitation of the oral cavity at the dentist (treatment of caries, inflammation of dentin, and other problems);
- consumption of a vitamin complex to strengthen the body’s protective functions;
- taking immunomodulatory drugs;
- removal of growths using surgery, a laser beam or radio waves.
During the period of therapy, it is important to reconsider your usual lifestyle and make adjustments to it, getting rid of bad habits and casual relationships. To speed up the healing process, you need to avoid irritating the mucous membranes with hot or too cold drinks and dishes. Hygiene procedures should be carried out regularly, at least 2 times a day, using high-quality cleaning products.
Popular antiviral drugs include:
- Acyclovir (tablets);
- Panavir (solution for intravenous injection);
- Isoprinosine (tablets);
- Allokin-Alpha;
- Alpizarin (tablets).
The following are considered effective immunomodulators: Derinat, Likopid, Immunomax, Polyoxidonium.
For local impact on the lesion, the following means are used:
- Podophyllin;
- Cryopharma;
- Lapis pencil;
- Solcoderm;
- Verrukacid et al.
When using local preparations, you need to carefully read the instructions so that during the treatment of papillomas you do not burn healthy mucosal tissue.
How to avoid relapse of the disease?
After the growth has been removed from the patient's tongue, the person should not relax. Typically, single papillomas do not recur, but with multiple formations, the reappearance of growths on the body occurs quite often.
Therefore, after surgical removal of papillomas from the surface of the tongue, you should:
- Take precautions and limit risk factors (see above).
- Take a course of antiviral treatment as recommended by your doctor.
- Seasonally take immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes, which your doctor will also help you choose.
- Maintain oral hygiene and avoid tongue injuries.
One of the main conditions for achieving a favorable outcome in the fight against papillomas is choosing the right medical center, since much in the procedure for removing a tumor depends on the actions of the doctor. We hope that the recommendations of specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics helped you clarify the picture of the growth that has developed on your tongue, and now you can solve this problem without unnecessary emotional distress.
Removal methods
There are several ways to remove growths under the tongue. In each individual case, the specialist selects the best option, taking into account the localization of the formation and the extent of the affected area. Whatever method is used, it is complemented by antiviral therapy to prevent relapses. Only an integrated approach, including taking medications, will help get rid of the problem in the oral cavity.
| Treatment of growths under the tongue | |
| Method name | Process description |
| Surgical removal | An effective way to remove growth by cutting it off from soft tissue using surgical instruments: scalpel, scissors, electric knife, conchot. Sutures are subsequently placed on the wound. |
| Cryodestruction | The growths are removed using liquid nitrogen. The method copes with the task, but this type of influence can provoke malignancy of the formation, that is, have the opposite effect. |
| Laser removal | The essence of the method is to cut off the growth with a laser beam. The advantages of the method: quick and effective elimination of formations, absence of pain for the patient and bleeding, which prevents infection. The likelihood of relapse is very low; after the procedure, the process of cell regeneration is stimulated. |
| Radio wave therapy | The method is low-traumatic and painless; the procedure does not even require the use of a local anesthetic. Removal of growths occurs under the influence of high frequency radio waves. The specialist directs them to the base of the growth and cuts off the affected tissue. The rehabilitation period lasts 7-10 days. |
| Electrocoagulation | This method efficiently and quickly removes pedunculated growths on the tongue. The essence of the method is to throw a loop of special fiber over the formation and apply high-frequency current to the material. The hot fiber cuts off the growth, simultaneously soldering the microvessels, which prevents bleeding and infection of the wound. Electrocoagulation prevents further development of the virus. At the site of the removed growth, a crust forms, which after some time comes off on its own. |
| Galvanocaustics | The location of the small growth is cauterized with platinum wire heated under the influence of current. The method is fast, eliminating bleeding and infection of the wound. |
How to spot early symptoms of tongue cancer
20.06.18
The fear of getting cancer is quite common and is called cancerophobia, or less commonly, cancrophobia. I would say, given the inclusion of cancer in the top five most common causes of death, that this fear is quite constructive if it prompts you to avoid risk factors and be regularly examined by an oncologist. This is good form - modern and responsible.
Tongue cancer is less common than many other types of cancer, but the fear of it is great due to the expected disability and significant impairment of quality of life.
What needs to be done to catch it at an early stage, at which it is possible to do without crippling methods of treatment?
Tongue cancer is insidious - its early manifestations are masked by harmless symptoms and require an active search even with regular examination. The greatest likelihood of detecting the first symptoms occurs during a regular dentist appointment. Firstly, he knows well what a healthy tongue should look like, and secondly, he knows what to do if he suspects the onset of a disease. It is important to understand that the dentist will notice early symptoms if you ask about it at the appointment, present complaints or concerns. If dangerous symptoms are detected, the dentist is obliged to refer the patient to an oncologist.
Particular attention to the tongue and oral cavity should be given to smokers, people working with carcinogens - asbestos, perchlorethylene, petroleum products and heavy metal salts. The second place among the risk factors for developing tongue cancer is microtrauma from sharp edges of teeth, poorly fitting dentures and fillings. The so-called precancerous diseases and conditions are important - erosion of the tongue, leukoplakia, papillomas, hyperkeratic and ulcerative-erosive forms of systemic lupus erythematosus and lichen planus, Bowen's disease.
Men suffer from tongue cancer 6-7 times more often than women. The reasons for this are poorly understood, it is assumed that they are more likely to be exposed to harmful factors, but it is possible that cancer is inherited on the Y chromosome.
Most often the lateral surface of the tongue is affected, less often the root or bottom of the tongue, and least often the surface. The tip of the tongue accounts for only 3% of identified cases. To identify tongue cancer at an early stage, let’s remember its three main manifestations:
- the presence of papillary growths or whitish spots, compactions or redness on the tongue, special attention to the lateral surfaces!
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes
- soreness in the tongue without clear localization. This symptom is rare, more often it is simply a feeling of discomfort, an unusual sensation in the tongue.
At this stage, the oncologist will do a smear test or biopsy to identify the type of cancer or rule it out. By the way, for the initiated, in 95% of histologically, tongue cancer is classified as squamous, i.e. develops rapidly and metastasizes quickly.
At the second stage, it is called “developed”, the symptoms are more distinct, but the treatment prognosis is worse.
- the pain becomes more localized, radiating to the ear, temple or oral organs
- salivation increases
- there will be a bad breath
- There is numbness in parts of the tongue, difficulty pronouncing sounds, pain when swallowing
- with the papillary form, a distinct growth will appear on the tongue (see illustration), with the ulcerative form, a growing ulcer with a distinct ridge along the edges (also shown in the illustration)
- in the infiltrative-ulcerative form, deep fissure ulcers appear on the tongue; in the infiltrative form, the body of the tongue thickens
The advanced stage is quite obvious and we will not consider it within the scope of this material.
Treatment for tongue cancer is always complex, including surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Prevention consists of quitting smoking, limiting alcoholic beverages, and regular dental and oral care.
Timely diagnosis allows for a favorable survival prognosis, which some authors note at 95%. But here, the sooner the patient applies, the better the prognosis. Attention to health, accuracy and systematic reasonable self-observation can give many years of active life.
What to do at home if a growth appears - folk methods
In addition to traditional treatment of growths under the tongue, many patients use traditional recipes. It is impossible to replace treatment with a completely unconventional method, but nothing prevents you from trying it.
Popular folk recipes for growths under the tongue:
- daily rubbing of the formations with garlic juice or applying cloves of spice;
- lubricating newly appeared growths with egg white;
- treating affected areas with castor oil (using cotton swabs);
- rinse the mouth twice a day with decoctions of medicinal herbs (medicinal chamomile, string, sage, echinacea, etc.);
- ingesting rosehip decoction, freshly squeezed potato or carrot juice.
Any infections and viruses developing in the body signal a decrease in immunity, so during the treatment period you should take care of taking fresh vegetables and fruits. A good vitamin complex is also suitable for these purposes.
Before using an unconventional approach, you should consult your doctor to rule out contraindications.
Preventive measures
Use mouthwash after meals.
Preventing the development of a disease is always easier than fighting harmful microorganisms and the results of their vital activity. To prevent the formation of growths in the oral cavity, the following measures are recommended:
- perform hygienic cleaning of the mouth at least 2 times a day;
- after eating, use a mouthwash;
- develop a diet so that it contains mainly fresh vegetables and fruits (to strengthen the immune system);
- regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations;
- do not borrow other people’s household items (dishes, towels, cosmetics);
- undergo an annual examination with an oncologist;
- lead an active lifestyle (if you work sedentarily, include morning exercises and twice-a-day workouts on simulators in your daily routine).
HPV vaccinations
HPV vaccine
You can protect yourself from the formation of growths in the oral cavity by getting vaccinated against the papilloma virus. There are many different rumors around this vaccine, but they have no basis in terms of effectiveness.
The product contains substances of organic origin that promote the production of cells in the body that resist the development of condylomatosis.
Effective means are used for vaccination:
- Cervarix;
- Gardasil.
These vaccines are not used in the treatment process; they are intended solely for preventive purposes. The procedure must be performed before sexual activity begins; the maximum age of the patient is 26 years. When using the product at an older age, the effectiveness decreases significantly.
One vaccine protects the body from the papilloma virus for 8 years.
Features of child treatment
The treatment strategy for growths under the tongue in children includes two main stages: improving the immune system and eliminating formations in the mouth.
There are difficulties in selecting agents for local action on papillomas due to the constant contact of the drug with saliva. Therefore, the first recommendation for children is to change their usual toothpaste to a professional product that has a bactericidal effect.
When choosing antiviral drugs, the priority is not effectiveness, but safety. The ideal option is a drug that contains a combination of ascorbic and rutic acids (for example, Ascorutin). Recommended immunomodulators include: Amiksin, Viferon.
When determining the most suitable method for removing papillomas, the accuracy and speed of the procedure, as well as the low level of risks, are taken into account.
Manifestations of tongue glossitis in children
In children, glossitis usually occurs at an early age - from 1 to 5 years. The causes of this pathological process have not yet been fully studied and can be very diverse: from infection to poor heredity. Externally, glossitis in children is manifested by the appearance of spots on the tongue, which slightly swells and itches. Itching and a burning sensation are the most unpleasant signs of glossitis, since a small child begins to scratch the tongue, thereby contributing to the appearance of microcracks with their subsequent infection. However, the disease does not pose a threat to the child’s life. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky does not recommend panicking about this and self-medicating by giving the baby serious medications. As a rule, multivitamins and a gentle regimen will have a positive effect within a week.