- Introduction
- Causes of tooth loss
- Causes of tooth enamel loss
- Partial and complete tooth decay
- Consequences of tooth loss
- The impact of tooth loss on the body as a whole
- Tooth-preserving operations
- Diagnostics before dental restoration
- Main stages of diagnosis
- Dental restoration methods: advantages and disadvantages
- Methods for restoring tooth roots with dentures
- Features of dental restoration in children
- How to choose a teeth restoration method
- Dental prosthetics
- Is it worth saving damaged teeth?
- Restoration cost
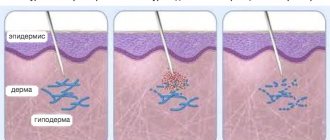
Causes of tooth enamel loss
Tooth enamel protects the tooth from external factors and is the hardest, but at the same time, fragile tooth tissue. Reasons why enamel loss or destruction occurs:
- Injuries, blows.
- Bad habits: smoking or drinking alcohol.
- Excessive consumption of sweets.
- Drinking very hot or very cold drinks.
- Malocclusion.
- Fruit acids in natural juices can be acidic and erode enamel.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- Gastritis, hypertension and diseases of the endocrine system entail a decrease in the enamel layer.
- Chemical exposure to harmful substances, for example, taking medications, carbonated drinks.
- Lack of fluoride and calcium in food.
- Bruxism.
- Incorrectly chosen dental hygiene products.
Causes of edentia
The problem of missing teeth sooner or later arises in almost every person. However, the causes of edentia can be very different. It all depends on whether it is primary (lack of tooth germs as such) or secondary (loss of already formed teeth).
| Primary causes of edentulism | Causes of secondary adentia |
|
|
Partial and complete tooth decay
As a result of loss of enamel, teeth are partially or completely destroyed. The depth of the lesion shows how far the inflammatory process has gone. Depending on this, treatment is selected. Diseases leading to partial and complete tooth destruction:
- Caries.
- Pulpitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Periostitis.
- Pericoronitis.
- Osteomyelitis
- Acute limited osteomyelitis.
- Acute diffuse osteomyelitis.
- Chronic odontogenic osteomyelitis.
- Periodontal disease.
The above problems are subject to therapeutic treatment. Some illnesses take time to heal. The doctor will do everything possible to save the tooth. But in an advanced stage, these diseases are the main causes of tooth loss leading to the need for prosthetics.
Classification of edentulism by the number of missing teeth
| Number of missing teeth | Classes | general description |
| Partial edentia (ICD K00.00) | – Partial primary adentia. – Partial secondary adentia. | With partial edentia, from one to 5 teeth or their rudiments are missing on one jaw. Most often, three teeth are missing. |
| Multiple edentia | – Multiple primary adentia. – Multiple secondary adentia. | Many experts combine the concepts of partial and multiple edentulism. Criteria:
And so on up to 15 units on one jaw. |
| Complete edentia (ICD K00.01) | – Complete primary adentia. – Complete secondary edentia. | Complete absence of teeth or their rudiments on one of the jaws. |
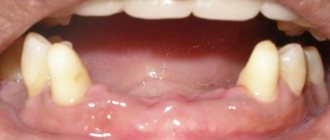
Consequences of tooth loss
Tooth loss does not go unnoticed for the human body as a whole and for various organs in particular. Even such a small organ as a tooth is of great importance in the human body, so it is important to take care of your health before the onset of illness.
For bone structures
the consequences of tooth loss are a shift in load - neighboring teeth can change their position in the mouth, the antagonist tooth does not receive the load and its root is exposed. Over time, the alveolar bone decreases in height and width. Over the course of a year, height loss is up to 4 mm. With complete edentia, the bone decreases even faster.
For soft tissues, tooth loss leads to a decrease in volume, the formation of bedsores, and discomfort. If prosthetics are not performed, the tongue will increase in size. At the same time, the tongue performs a useful function: it helps the denture to chew and limits its actions.
Aesthetic consequences of tooth loss
become more obvious with age. If the patient does not wear prosthetics, the face will look older than its age ahead of time. The height of the face decreases, the bite is disrupted, the chin begins to protrude, the corners of the lips droop, which is why the face looks sad. The nasolabial fold increases, the lip line becomes thinner. The tone of the facial muscles decreases and a double chin appears.
Psychological consequences
different depending on the patient's condition. There are patients who ignore tooth loss and continue to live as they lived before. For patients with a labile nervous system, the situation is more complicated and may lead to the development of a neurotic state. Losing a tooth and changing the appearance of the oral cavity negatively affects the patient’s mood and thinking.
The loss of a tooth and prosthetics, especially if they are removable dentures (“teeth in a glass”), are perceived as the onset of old age. Many skills that used to come naturally now become stepping stones to overcome. Patients need to relearn how to chew and speak.
Many people are very upset by diction defects when, due to dentures, it is not possible to pronounce certain sounds as clearly as before wearing dentures. The patient cannot eat all the foods he used to love. The fear of losing a prosthesis in public while socializing or eating together may prompt the patient not to leave the house and limit his social circle.
We recommend meeting with a psychologist who will help you cope with new circumstances, discover the potential of your body and organism, and not lose enthusiasm in training aimed at comfortable use of dentures.
Prevention of tooth loss
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it - this truism is remembered more often when the disease has progressed far and complex treatment is required. Tooth loss can be prevented by following these recommendations:
- Maintain personal oral hygiene: brushing your teeth should be done at least twice a day, morning and evening;
- use dental floss to clean the spaces between your teeth from food debris;
- Visit your dentist regularly, even if your teeth are not causing concern;
- strictly follow your dentist’s recommendations for dental care and disease prevention;
- take care of chronic diseases (if any);
- protect your teeth from injury.
The impact of tooth loss on the body as a whole
Loss of teeth
- a serious loss for the entire human body as a whole. Don't underestimate the loss of even one tooth. Changes in bones lead to changes in facial features, making a person look older. Difficulty in communication and speech defects in the pronunciation of certain sounds impose certain restrictions. Losing teeth and wearing removable dentures worsen the quality of life, nutrition, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract arise due to changes in the usual diet. We recommend that you do not delay your consultation with a prosthetist dentist, who will tell you what type of prosthetics is right for you.
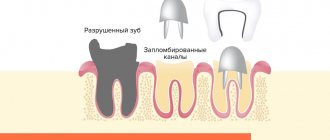
Methods for restoring tooth roots with dentures
The tooth root can be restored if the source of infection is stopped and the root walls are 1-2 mm, there is reason to preserve the tooth root. The root is assessed with prospects for prosthetics. The root will serve as the basis for placing the pin. If necessary, the root canals are expanded, and therapeutic treatment is carried out aimed at preparing a place for the anchor pin. The pin is suitable for use if there is no complete destruction of the tooth crown.
Another method for restoring tooth roots
serves as a stump tab. It is installed in the tooth canal, strengthening it. The inlay is called a stump inlay, since one part of it has the shape of a tooth stump, on which the tooth crown is then installed. The inlay is more reliable than a pin, it is easily replaced, can correct the bite, strengthens the tooth, and, thanks to the even distribution of the load, prevents tooth decay.
Features of dental restoration in children
Children's milk teeth need restoration.
Previously, milk teeth with a large area of carious lesions were preferred to be removed. Today, dentists have come to the conclusion that preserving baby teeth in a child’s mouth until they are physiologically replaced is very important for the development and proper functioning of the jaws.
It is important that the child’s chewing function is not impaired due to the premature loss of baby teeth. If a tooth is missing or incorrectly positioned, the development of a correct bite is disrupted. Missing teeth negatively affects diction, which can also cause psychological problems. The purpose of preserving baby teeth is to ensure proper eruption of permanent teeth.
Why do teeth fall out
Each tooth is located in its own socket and is securely held in it thanks to the periodontium. This is a whole complex of tissues, which includes root cement, dentogingival ligament and alveolar bone. They perfectly perform supporting and holding functions until inflammatory processes begin in the tissues. As a rule, the latter occur due to poor oral hygiene.
Within two hours after brushing your teeth, plaque begins to accumulate on them. It consists of food particles, saliva, the minerals it contains, and bacteria. There are especially many of them near the gums and between the teeth. Over time, plaque mineralizes and turns into tartar. It is the main cause of most dental diseases, including those associated with periodontal disease.
Inflammation of the tissues holding the tooth in the socket can be quite severe against the background of metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, hypovitaminosis and osteoporosis.
How to choose a teeth restoration method
Modern methods of dental restoration
are diverse and it is quite difficult for the patient to navigate medical terms on his own in order to assess for himself the advantage of a particular method. On our portal we provide comprehensive information on methods of dental restoration. You will find the addresses of trusted clinics and the names of doctors with a reliable reputation and extensive experience.
By studying possible ways to restore teeth before visiting a doctor, you will be prepared for a substantive conversation with the dentist. To choose the method that is most suitable for your particular case, it is most necessary to consult with your doctor. He will assess the condition of the tooth requiring intervention and select a treatment option. By agreement with the patient, the doctor begins work. In dental treatment, important aspects are the professionalism of the doctor, the quality of materials and the trust of the patient.
Is it worth saving damaged teeth?
Dentistry today has many tools in its arsenal to restore damaged teeth. To answer the question: does it make sense to save a decayed tooth, you need to consider several factors:
- Condition of the tooth and its root, bone tissue, canal.
- The cost of restoring a damaged tooth is lower than the cost of an implant or fixed denture.
- A natural tooth is better than any artificial tooth. If a tooth, root, canal can be cured, then the restored tooth will last for a very long time.
- The option of microprosthetics using Glasspan technology will allow for gentle intervention and achieve excellent results.
- The patient decides for himself whether to save the tooth or not, but the dentist will explain to him the prospects of this or that decision.
Missing part of teeth
If several teeth are lost, they can be replaced with dentures made of plastic or nylon, clasps and bridges. Dental prosthetics using implants installed in the jaw is considered extremely reliable. The latter method also provides the most aesthetic results. When implanting into the body of a bone, the validity period of the inserted implants is maximum; the adjacent teeth do not have to be ground down, which is necessary when using prosthetics with bridges. A dental prosthesis placed on an implant implanted into the bone is quite functional, and from an aesthetic point of view, it completely replaces the lost tooth.
Restoration cost
The cost of restoring a damaged tooth is important for the patient, since different tooth restoration techniques differ in price. The price will depend on the number of manipulations required to treat and restore the tooth, on the chosen technique and material. Only a doctor can tell the full cost after an examination and selection of materials together with the patient. For example, a doctor’s consultation starts from 500 rubles and above, a stump inlay from 6,500 rubles and above. The cost of services varies depending on the clinic. Convenient navigation on the portal will allow you to see different prices in different clinics.