In cases where pulsating sensations are accompanied by aching pain in the gums, we can talk about one of the most unpleasant dental problems, since even painkillers are usually powerless.
There is no single answer to the question why the gums are pulsating: it could be the result of the dentist’s careless work (a mistake made when filling a tooth) or a consequence of pathology.
This article is about the possible causes of pulsation in the gums and recommendations regarding actions that are advisable before seeking dental care.
What does pulsation in the gums indicate?
Pulsating sensations in the gum against the background of its swelling and pain are a clear signal of the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane associated with injury to soft tissues and the penetration of infection into them (the strength and frequency of attacks are important in diagnosis).
In addition, the symptom may be a consequence of various pathological processes. The most frequently diagnosed are:
- progressive caries short-term attacks of pulsating pain are possible with carious destruction of the middle and deep stages, most often provoked by external irritants - such as a reaction to cold/hot, sweet/salty.
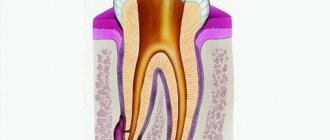
- acute pulpitis is a complication of caries associated with the penetration of harmful microorganisms deep into the dental tissues: upon reaching the pulp, they provoke a serious inflammatory process, accompanied by severe painful sensations, which usually intensify at night.
- periodontitis is a consequence of untreated pulpitis (or, alternatively, the result of poor-quality treatment of dental canals), accompanied by the formation of a purulent abscess at the root of the tooth.
Other factors can also provoke pulsating pain in the gum tissues; only a specialist can determine the real cause of the problem, therefore, if you feel pulsation in the gums, do not delay your visit to the dentist!
general characteristics
The pain is caused by changes in the gums and periodontium, which occur under the influence of local factors: poor oral hygiene, the presence of tartar, functional periodontal insufficiency due to a decrease in chewing load when eating too soft food.
Smoking plays a significant role. Common factors affecting the condition of oral tissues are gastrointestinal diseases, infectious and endocrine pathologies, natural changes in hormone levels, and harmful occupational exposures. The listed reasons entail the formation of an environment favorable for the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, the development of inflammation, disruption of the local blood supply and nutrition of the gums, and changes in its structure. The result is a pain syndrome. Often the periodontium is involved in the pathological process, the disease becomes chronic, leading to gross local changes and tooth loss.
Pulsation without pain
Pulsating sensations in the gums without significant pain are the most likely symptom of the development of apical periodontitis: the process of releasing space for purulent exudate that accompanies the problem causes the sensation of a distinct pulse within the jaw.
As a rule, there are no unpleasant sensations at rest, but they appear under any stress (during hygiene, when eating food, when applying pressure). The symptom is characteristic of any inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues, as well as in the initial stages of the formation of a hilar cyst.
Diagnostics
A dentist will determine the cause of pain in the gums. A dental examination involves assessing oral hygiene, studying the condition of soft tissues, identifying signs of inflammation and mucosal defects, determining the presence and severity of periodontal pockets and tooth mobility. As part of the additional examination, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Radiography.
In inflammatory periodontal diseases, osteoporosis is visible in the photographs. Horizontal destruction indicates a chronic course of the pathology, vertical destruction indicates the formation of abscesses. With periodontal disease, osteoporosis is combined with sclerotic changes. Based on the results of radiovisiography or orthopantomography, the type and severity of malocclusion is assessed. - Bacteriological or bacterioscopic examination
. Performed for Vincent's stomatitis and inflammatory periodontal diseases. This type of stomatitis is characterized by a large number of Borrelia Vincent. In other cases, various types of pathogenic bacteria are found, less often fungi. - Other laboratory tests
. The inflammatory process is accompanied by leukocytosis and an increase in ESR in the general blood test. If an allergy is suspected, intradermal, scarification, cutaneous drip, exposure and elimination allergy tests are performed.
Dental examination
Discomfort under the filling
Unlike the previous case, pulsation in the gum under a recently filled tooth does not always indicate a mistake by the dentist. It is important to distinguish the stage of treatment here:
- When installing a temporary filling, pain and pulsating sensations are acceptable during the first few days, since temporary filling is most often carried out with the addition of a devitalizing agent to destroy the neurovascular bundle. The killing of the pulp occurs gradually, but a visit to the doctor is justified if the discomfort persists for more than 2-3 days.
- If discomfort is felt under a permanent filling, it is advisable to get dental care as quickly as possible. The causes of pain can be different; a competent diagnosis based on an X-ray examination of the problem tooth is necessary.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Mandatory measures for pathologies accompanied by pain in the gums are professional oral hygiene and treatment of carious teeth. In case of allergies or mechanical injuries due to errors in the installation of prostheses, repeated prosthetics or correction of structures is necessary. Patients with malocclusion undergo orthodontic treatment. Depending on the nature of the disease, therapeutic regimens may include:
- Gingivitis
. Means for improving local immunity are indicated. After eating, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions. For intense pain, analgesics are prescribed. - Periodontal diseases
. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used for periodontitis. In case of periodontal disease, electrophoresis, hydro- and vacuum therapy are used to improve local blood supply. Movable teeth are fixed with temporary splints. - Vincent's stomatitis
. As part of local treatment, local anesthetics, sorbents, and drugs with proteolytic, antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effects are applied. At the resolution stage, keratoplasties are effective, accelerating tissue restoration. Common medications include antibiotics, NSAIDs, antihistamines, antipyretics, and painkillers.
Discomfort in the area of the extracted tooth
Unpleasant sensations, including throbbing pain, after tooth extraction are a natural and inevitable phenomenon, since it takes time to restore damaged tissue.
But after such an operation (especially after the removal of a wisdom tooth), patients should listen very carefully to their feelings so as not to miss the moment of possible complications, such as alveolitis (suppuration of the tooth socket as a result of the loss of a blood clot protecting the wound from infection).
Why are my gums swollen and sore?
In this article, we will help you figure out why your gums around the tooth are swollen, and how exactly it will be necessary to treat this tooth. Below we will list the symptoms that will allow you to make the correct diagnosis, but first take a close look at the teeth adjacent to the swelling in the mirror. In most cases, the gums swell precisely in the projection of the causative tooth. You need to define the following −
- whether toothache in one of the teeth preceded the appearance of gum swelling,
- does pain appear in one of the teeth when biting on it,
- whether the tooth has decay, a filling or a crown,
- Is this tooth movable?
- does pus discharge from under the gums - when you lightly press on the swelling.
Next, by comparing your symptoms with the symptoms characteristic of periodontitis or periodontitis (which we described below) - you can understand the cause of the inflammation and what treatment you will need in this case.
Waiting for a visit to the dentist: how to relieve pain
It's no secret that toothache appears unexpectedly, and dental care is not always available at the right time. Therefore, we have selected recommendations that will help you cope with pain while waiting for a visit to the dentist.
ethnoscience
The main recommendation is decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage and oak bark): a teaspoon of crushed dry plant in 200 ml of boiling water, infuse, strain and use for rinsing the mouth.
You can also:
- apply cold to the cheek;
- rinse with a soda-saline solution (2 grams of salt and soda per glass of warm water), for acute pain - every quarter of an hour;
- chew propolis (provides slight numbness of soft tissues);
- Apply a cotton wool soaked in eucalyptus or clove oil to the tooth.
Although these recommendations are time-tested, prior consultation with a doctor is advisable.
Pharmacy products
The choice of a pharmaceutical painkiller should be made taking into account the characteristics of the pain syndrome - its intensity and frequency:
- for moderate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Aspirin, Paracetamol) are suitable, which can reliably alleviate the condition for a couple of hours; if pain increases in the evening, you can add an antispasmodic (Spazmaton, No-shpa)
- with severe pain and pronounced pulsation in the gums, more powerful drugs will be required - such as Nise, Ketorolac, Nimesulide.
It is important to understand that painkillers do not solve the problem; pain relief is only a respite that does not relieve the need for dental treatment.
After eliminating the acute manifestations of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
By postponing a visit to the dentist, saving yourself from pain using folk or pharmacy remedies, you risk bringing the situation to a critical point, when saving the tooth becomes impossible!
Associated symptoms
Not only pain syndrome can indicate the development of diseases of teeth and gums. Warning signs are also:
- bad breath,
- bleeding gums,
- swelling of the cheek or lip,
- redness and swelling of the gums,
- mobility of teeth,
- local temperature increase.
Have you noticed several of the listed signs at once? Make an appointment with a dentist. An experienced doctor will help eliminate the problem and maintain dental health.
Periodontitis
Bone tissue is involved in inflammation. In the affected area, the teeth begin to seem to be squeezed out of the gums and become mobile.
The onset of the disease is indicated by more pronounced bleeding of the gums, a change in its color, and sensitivity may appear when brushing your teeth and from temperature irritants. The success of this treatment is determined not only by the doctor’s competence, but also by the patient’s active participation in the process and strict adherence to the dentist’s recommendations.
Treatment methods used by the doctor
The dentist chooses treatment methods depending on the type and severity of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
| Problem | Therapy methods |
| Periodontitis |
|
| Periodontitis |
|
| Abscess |
|
| Gingivitis |
|
| Frequent gum injury | Replacing a low-quality filling, adjusting a prosthesis or crown. Then the doctor prescribes pain-relieving baths and applications, antiseptic rinses, and healing ointments. For chronic injuries, the ulcers are excised together with dead edges and sutures are applied. |
| Problematic growth of wisdom teeth | Removal is simple or using incisions and drilling out of bone tissue. |
| Tartar | Removal of stones using ultrasound and laser. After cleaning, the teeth are ground and polished. Recommendations for choosing toothpaste and toothbrush, proper oral care. |
| Gum overflow on tooth | Removal of overgrown tissue. |
| Flux | Surgery is performed, the lump is opened, and the pus is removed. |
If pain occurs after dental procedures, it may be necessary to re-install a filling or crown. To eliminate infectious processes, antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed.
Tooth hurts after nerve removal and filling
Only a dentist after an examination will help you figure out why a tooth hurts after removing a nerve and filling its canals. Treating teeth on your own without a diagnosis is highly discouraged.
In dental practice, the procedure for treating tooth canals by removing a nerve is a rather complex manipulation. Cases of medical error are common. They are fraught with various complications, in which the filled tooth continues to hurt.
The main reason why a “dead tooth” (without a nerve) is bothersome is:
- removal of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth - this occurs due to incorrect definition
- working tooth length;
- the doctor filled the canal incorrectly;
- a tool broke off in the canal;
- root perforation of the tooth;
- If your tooth aches, you may be allergic to the filling material.
It is worth considering that a tooth under a filling can hurt even without a nerve. After all, during the extraction procedure, only a small part of it is removed from the root canal, which branches off from the main nerve trunk. In addition, when removing and filling canals, dental tissues are damaged. When an anesthetic is applied to a tooth, pain is not felt; it begins to be felt after the anesthesia wears off. Such painful sensations are called post-filling.
After removal of a nerve, neighboring teeth can often be bothered, but it seems as if it is the treated tooth that is hurting. An experienced doctor will examine the dentition to identify and eliminate this problem. However, it is worth sounding the alarm when the nerve has been removed for a long time, and the tooth continues to hurt - this symptom may signal the development of chronic pulpitis or periodontitis.
Possible complications
Complications with sore gums arise due to the spread of the infectious process throughout the body.
The most common complications :
- formation of a fistula, sometimes it affects facial tissues;
- loss of teeth due to increased mobility;
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis.
Severe dental diseases require surgical intervention. After them, you have to recover for a long time and follow all the rules of the rehabilitation period.
Content:
- Why it hurts to press on a tooth - the main reasons 1.1. Increased sensitivity 1.2. Traumatic injuries (history or recent) 1.3. Periodontitis 1.4. Inflammation of the gums 1.5. Poor quality dental prosthesis 1.6. Cyst 1.7. Caries 1.8. Pulpitis
- If pain occurs when pressing on a filled tooth
- What you can do yourself
When pain occurs in a tooth affected by caries, or at the base of which there is swollen and inflamed gum, everything is clear - you urgently need to go to the dentist and undergo treatment. But what to do if a person’s tooth hurts when biting and no visual defects are noticeable.
Is it possible to ignore this situation? Dentists are convinced that no. If acute or aching pain occurs when pressing on a tooth, you must definitely find out its cause. Otherwise, the risk of crown failure or root damage will increase in the future.
Consumer Reviews
Mrs. Doubtfire about Asepta Active mouth rinse (irecommend.ru):
“When I was faced with a serious gum problem, this rinse was recommended to me by a dental surgeon.
Asepta Active mouthwash is a medical product and is sold only through the pharmacy chain. The instructions recommend taking breaks in use. Personally, I use it in courses and during exacerbations of gum inflammation. I've been using it for about 2 years.
The mouthwash is minty, pleasant, slightly astringent. Improvement is felt from the first use. Bottle volume 150 ml. Manufacturer: Russia, St. Petersburg. A convenient measuring cup is included.
You can (better) buy it as a set, which also includes balm and toothpaste, which comes as a gift.
I’m very happy that such products from a domestic manufacturer have appeared!”
julia-06 about Asepta Active mouth rinse (irecommend.ru):
“A very good rinse for problem gums.
She had never encountered the problem of bleeding gums, but at her next visit to the dentist she noticed that when she only lightly touched her gums, they began to bleed. So the dentist gave me a mini version of Paradontax toothpaste and advised me to use a mouthwash after brushing my teeth. Mom bought Asepta active mouth rinse.
For some reason I used to be very skeptical about such remedies, but as it turned out, in practice it helps very well. My problem went away completely, my gums stopped bleeding. I don’t even want to read the ingredients and go into its details, it’s unlikely that everything is super natural, but since it helps, I give the mouthwash a solid 5 points. Of course, each case is individual, but I will recommend it based on my experience. And the price of the rinse aid is quite reasonable.”
What you can do yourself
If the tooth hurts severely, and for some reason it is impossible to get an appointment with a doctor today, you should rinse with a saline or soda solution. Warming compresses should never be used - they often aggravate the inflammatory process and provoke blood poisoning.
For unbearable pain, you can take an over-the-counter analgesic available in your home medicine cabinet. But this should be a “one-time event”. As soon as possible, the patient should see an experienced dentist.
Swelling of the gums due to periodontitis -
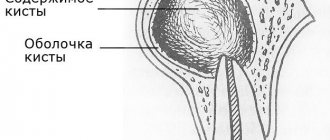
In case of poor-quality root canal treatment, due to tooth trauma, or in the absence of timely treatment of caries and pulpitis, inflammation occurs at the apex of the tooth root, which dentists call “periodontitis.” Sometimes the terms “granuloma” or “cyst” are used to refer to periodontitis, which you may well have heard. Such names are due to the fact that the focus of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root in these cases has the appearance of a purulent sac.
Symptoms - usually periodontitis has a chronic asymptomatic course, or there is only slight pain when biting on this tooth. But sometimes periods of exacerbation of inflammation occur, and in this case, acute pain may first occur in the causative tooth (especially when biting on it), and a little later, swelling of the gums usually appears in the projection of the causative tooth. But sometimes pain may be completely absent, and patients complain solely that the gums near the tooth are swollen (Fig. 1-3, 7-9).
Please note that with periodontitis, the source of inflammation is located at the apex of the tooth root, i.e. quite deep in the bone tissue. Therefore, swelling of the gums during periodontitis usually develops not just in the projection of the causative tooth, but most often in the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth. And in multi-rooted chewing teeth - no less often in the projection of the bone interradicular septum. But periodontitis is not characterized by swelling of the interdental papilla or the gingival margin adjacent to the neck of the tooth.
In general, if you have swelling on the gum in one of your teeth, pain occurs when you bite on it, and there is a crown, filling or carious destruction on the tooth, and also if, in addition to swelling on your gums, you also have swelling of soft tissues face (again in the projection of the causative tooth) - you can definitely make a diagnosis of “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.” An X-ray of this tooth will allow you to accurately determine the cause of periodontitis and the required amount of treatment.
What treatment may be required -
As we said above, if the gums are swollen and painful, then in most cases the reasons are poor-quality filling of the canals, or the lack of timely treatment of dental caries and pulpitis. Only according to official statistics, root canal fillings are performed poorly by dentists in at least 60-70% of cases. The main errors during treatment are underfilling of root canals, poor obturation of root canals with filling substances, breakage of instruments, perforation of the tooth root...
As a result of this treatment, a focus of purulent inflammation appears at the apex of the tooth root. Moreover, in the absence of timely treatment of the tooth for caries and pulpitis, exactly the same focus of inflammation will appear at the apex of the tooth root, but only against the background of unsealed root canals. In Fig. 10-12 you can see how the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root looks like during periodontitis (on the diagram, x-ray and on the root of the extracted tooth) -
Below we describe several treatment options that may be possible for patients with gum swelling due to dental periodontitis. In any case, the doctor will first be forced to take an x-ray. The image will allow us to determine whether this tooth can be saved at all, the size of the inflammatory focus at the apex of the root, and whether root canals have been filled in this tooth previously. The treatment tactics will depend on the latter, and below we will tell you how to cure a tooth and remove swelling from the gums so that it does not appear again.
1) If the channels are not sealed -
If root canal treatment has not previously been carried out on this tooth, then standard treatment of periodontitis is carried out with mechanical treatment of the root canals and treatment of the source of inflammation behind the root apex. On your first visit, they will open your tooth, expand the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them, and leave the tooth open for several days, prescribing antibiotics and anti-inflammatory therapy.
If necessary, your dentist may then refer you to an oral surgeon to make a small incision in the gum to allow additional drainage of pus. After about 3-5 days, the doctor makes an appointment for a second appointment and, if the inflammation subsides, completes the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seals them - either first with a temporary medicinal paste, or immediately with gutta-percha (the latter depends on the size of the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root). You can read more about the treatment of periodontitis at the link above.
How the gum incision is made - significant swelling of the gums, or if your gums and cheek are swollen at the same time - indicates the formation of a large purulent abscess, which will require not only opening the root canals of the causative tooth, but also making an incision in the gums to release the pus. The incision is made under local anesthesia, the wound is then washed with antiseptics and a drain is inserted into it (see video below).
2) If the channels are sealed poorly -
If an x-ray shows that canal treatment has already been carried out previously and the cause of inflammation was incomplete filling of the root canals to the apex of the tooth root, then there are 2 treatment options: either standard conservative therapeutic treatment, or an option associated with resection of the root apex.
- Conservative therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the filling/artificial crown is removed from the tooth, poorly filled root canals are unsealed, washed with antiseptics, and antibiotics are prescribed.
If necessary, the patient is referred to a dental surgeon to make an incision along the gum. Thus, to the treatment we described in the previous section, only 1 point was added here (unsealing the root canals). Then everything is the same - after the inflammation subsides, temporary or permanent filling of the root canals is carried out. If the source of inflammation is small, the canals are usually filled immediately and permanently with gutta-percha, and a permanent filling is placed at the next visit. If the inflammation is large, the canals are sealed with temporary medicinal paste for 1-3 months, and a temporary filling is placed. And only after this time the canals are filled with gutta-percha + a permanent filling or crown is placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This surgical method is much simpler and much cheaper than conventional therapeutic treatment, and it allows you to avoid removing the crown from the causative tooth in order to unfill and reseal the root canals.
However, this method is only suitable for those teeth in which the root canal was poorly filled only at the very apex of the root (and throughout the rest of the length the canal should be filled normally). This simple surgical operation is carried out within 25-35 minutes and consists of cutting off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal using a drill. To do this, an incision is made along the gum and a flap of the mucous membrane is moved back to give access to the bone tissue in the projection of the apex of the tooth root. Next, a small hole is made in the bone with a drill, through which the apex of the root is cut off and removed from the wound along with the granuloma/cyst at the apex. The wound is sutured and antibiotics are prescribed. Pros: cheap, simple, no need to remove the crown and re-treat the tooth.→ How is root resection surgery performed?
Causes of tartar
Dentists claim that during examinations they detect tartar in 70% of patients. It is a solid mass of yellow or brown color. This is a mineralized plaque consisting of food particles, soft deposits, mucus, dead cells and bacteria. You cannot remove it yourself.
The main causes of plaque formation include:
- irregular teeth brushing,
- using the wrong toothbrush,
- violation of salt metabolism,
- predominance of soft foods in the diet,
- long-term use of antibiotics,
- crowded teeth and malocclusion,
- smoking.
Solid deposits can appear even if all hygiene rules are followed. Therefore, you should visit your dentist twice a year to maintain healthy teeth and a beautiful smile.
Emergency measures
Emergency measures are suitable for temporary relief of symptoms when it is not possible to see a specialist. They include:
What to do if the gums near the tooth hurt
- Thorough cleansing of the oral cavity from plaque and food particles.
- Rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions that have anti-inflammatory properties (chamomile, calendula, plantain, sage). Instead of herbs, you can use soda or saline solutions. The rinsing procedure is repeated every 1.5 -2 hours.
- Rinsing your mouth with alcoholic drinks. The solution is kept in the mouth for 1 minute, after which it is spat out. The product is used only if there are no wounds or erosions on the surface of the oral mucosa.
- Applications to the affected area with clove oil. To do this, apply a few drops of oil to a cotton swab and hold it near the tooth for 2 minutes.
- Taking painkillers - Aspirin or Paracetamol.
If there is a problem, it is forbidden to: apply local anesthetics to the gums due to the risk of infection; carry out warming procedures. Under the influence of heat, pathogenic flora multiplies faster. This leads to the formation of purulent lumps and the spread of inflammation to neighboring areas.
High fever and pain due to inflammation of the hood
The eruption of the figure eight may be accompanied by general symptoms such as high fever, weakness, nausea, and lack of appetite. Such signs are associated with infection, so you need to consult a doctor, since treating intoxication at home is unsafe. First aid will be to drink plenty of fluids and take diuretics. A high temperature during the eruption of the figure eight can last for several days, so the doctor will individually prescribe antipyretics and tell you how to relieve pain and treat inflammation in the gum area in order to avoid unpleasant symptoms in the future. It is easy to remove inflammation and relieve pain at home, but this will only mask a serious disruption in the process of teething, so it is important to know the dangerous symptoms that require immediate consultation with a dentist.
When should you see a dentist if your figure eight is teething and your hood is inflamed?
- It is not possible to treat inflammation at home, and the symptoms only get worse;
- The gums near the figure eight are swollen, there is throbbing pain;
- It hurts to chew and swallow, the symptoms make it difficult to sleep at night;
- It is not possible to relieve pain in the gum area with analgesics;
- The gums around the figure eight swell, purulent exudate accumulates;
- The figure eight erupts incorrectly and puts pressure on the adjacent tooth.
What such phenomena can lead to without treatment, you will be told at the Leaderstom clinic, where consultation is not only free, but also saves the health of the eight and the entire dentition.