- Why is it important to care for baby teeth?
- Which toothpaste to choose for a child
- How to choose a toothbrush for a child
- How to choose an electric brush for a child
- How to reduce the risk of developing caries and not give up sweets
- How to teach a child to brush their teeth
- Tips from a pediatric dentist: video
The age group from 3 to 8 years is characterized by the primary dentition, as well as the beginning of the mixed dentition - the appearance of the first permanent teeth. A child at this age learns to brush his teeth and can use an electric brush independently.
Today we will look at what oral care products you need to have at home for children of this age group. You will learn how to help a child with the habit of brushing their teeth daily, what to use to form healthy permanent teeth, and how to reduce the risk of developing caries without giving up sweets.
What is caries?
Dental caries is the most common disease of modern humans, affecting more than 90% of the world's population. Caries is a chronic source of infection, which increases the risk of developing sinusitis, otitis, gastritis and bad breath. The prevalence of caries among little Ulan-Ude residents is 86%! 5% of children under 1 year of age have caries. This is a serious problem!
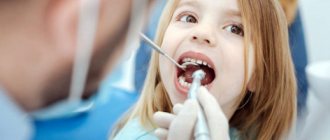
Article - Pediatric dentistry
Features of anesthesia in children in dentistry
In pediatric practice, pain relief plays a primary role.
If an adult patient is able to endure mild discomfort and spend several hours in a row in a chair, then the child’s psyche is not yet ready for this. A painful procedure can instill a lifelong fear of dentists and interfere with quality treatment. Moreover, anesthesia gives the desired psychological effect and helps the child trust the doctor. Features of pain relief in children
- Most drugs can only be used from the age of four, which imposes severe restrictions on the treatment of very young patients.
- The anesthesiologist must be highly qualified and be able to correctly calculate the dosage.
- The child may be afraid of treatment and dental instruments, especially needles.
- Children are often allergic to anesthetics.
The choice of one type or another depends on the procedure to be performed by the doctor, the age and psychological state of the child.
Application anesthesia
- Local anesthesia in children in dentistry is not complete without the use of special anesthetic solutions or gels (most often based on lidocaine), which are used to treat the gums before starting treatment. The active substance easily passes through a thin layer of the mucous membrane and dulls sensitivity. As a rule, topical anesthesia is used to numb the site of the future injection - this is a typical feature of anesthesia in children in dentistry. But even one “freezing” with a gel or spray is enough for some procedures - for example, to remove mobile baby teeth, the roots of which have almost completely dissolved.
- Topical anesthesia products in children's clinics have a pleasant taste and aroma to make it easier for the child to tolerate treatment.
Injection anesthesia
- In pediatric practice, articaine-based anesthetics are most often used, which are administered using a syringe. This drug is approximately five times more powerful than novocaine, but is less toxic and less likely to cause allergies. It can be prescribed from the age of four.
- Injection anesthesia has its own varieties. Pediatric dentists use infiltration or conduction anesthesia depending on the indications. In the first case, an injection is made into the mucous membrane at the border of the alveolar process and the transitional fold so that the anesthetic reaches the endings of the dental nerves. In the second case, the solution has an effect on the branches of the trigeminal nerve. Conductive anesthesia in children in dentistry is permissible from the age of six and is indicated for tooth extraction - mainly in the lower jaw.
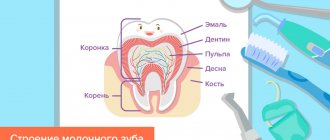
Child's oral hygiene
Dentists recommend taking care of the prevention of dental ailments in children even before the appearance of their first teeth. What does this mean, how to properly care for children’s teeth, and do the rules of oral hygiene differ between children and adults?
According to WHO (World Health Organization), 92% of people around the world brush their teeth incorrectly, therefore, adults also teach their children to brush their teeth incorrectly. Only a few people pay attention to the fact that the child’s oral cavity has significant differences from the adult’s oral cavity, which means that the hygiene of baby teeth is also different. Dentists advise paying attention to the structure of baby teeth, especially the first molars. The sixth teeth are more vulnerable than others. They erupt faster than others and often the distal tubercles are late freed from the “hood”, which serves as a place for plaque accumulation. In addition, it is in childhood that the probability of caries occurring is close to 100%. This is due to the inability of the child’s body to resist bacteria, the structure and vulnerable structure of the tooth itself, and other factors.
The best option for parents is to consult with a hygienist, who will show your child how to brush their teeth properly and tell you how often this should be done. There is one golden rule in oral hygiene that is relevant for both adults and children: after eating, brush your teeth. However, it is not always possible to follow it, especially when it comes to snacking on the go, at a party or in transport. At home, this rule must be followed strictly. The most important thing is not to forget about this important procedure and bring it to automaticity. What are the basic rules of children's hygiene?
The first months of life - taking care of your gums
In the first six months of life, the oral cavity is massively populated with microbes, which creates favorable conditions for the occurrence of caries, infantile thrush, stomatitis and other diseases. There are a lot of cases when microbes do not sleep, for example, when adults who are carriers of caries kiss a child, lick a pacifier, neglecting boiled water, and taste food with the spoon that will be fed to the baby. The risk of infection increases tenfold. To prevent something irreparable from happening, after each feeding the baby should wipe the gums with special fingertips or napkins with a weak soda solution.
Learning to brush baby teeth
Children who have already acquired teeth, with parental help, begin to brush their first baby teeth themselves using a special toothbrush for children. In this case, you need to start with 15-20 seconds for each cleaning, gradually increasing the duration. The main task of the mother at the stage of introducing the child to the brush is to awaken interest in a routine but necessary activity. There are at least two win-win ways:
- Teaching children oral hygiene goes a long way if parents offer the child a game. Having heard how the kind toothbrush aunt cleans her teeth one after another, making them beautiful and driving out harmful microbes, most kids will willingly open their mouths and patiently wait for the process to end.
- Another effective training method is to do as mom does. Often, children copy their parents' behavior, speech and facial expressions. In the same way, they learn how to brush their teeth properly. By doing daily brushing with your baby, and at the same time helping him, you will make sure that after some time the child will reach for the toothbrush on his own. The main thing is that the child likes the taste of the toothpaste!
Professional oral hygiene in children
Professional hygiene is usually understood as a set of procedures, the purpose of which is to improve the health of the tissues and organs of the oral cavity and prevent the occurrence of dental ailments. This includes removing soft and hard plaque from teeth, closing fissures, that is, dental dimples, making them less vulnerable, as well as covering the dental surface with a special varnish. The dentist's office is not as treacherous as it looks at first glance. In addition to the preventive procedure, the doctor can conduct an oral hygiene lesson, select a toothpaste and brush for the child based on the individual characteristics of the oral cavity structure, and also give useful and competent care tips.
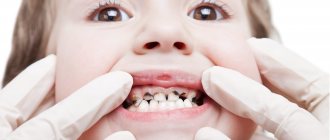
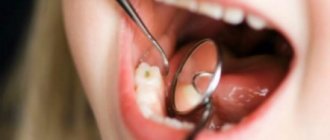
Caries in children
Dental caries in children: features of the disease
Considering the prevalence of caries in children, from the moment the first teeth appear, parents should pay special attention to the child’s hygiene and nutrition, as well as regularly visit the dentist for examinations and preventive procedures. All this is necessary in order to protect baby teeth as much as possible until the moment when they are replaced by molars. Look at the statistics: in children aged a year and a half, caries is diagnosed on average in 10 - 15% of cases, and by the age of five, more than 70% of children already suffer from this disease. Moreover, caries in preschool children develops at a much faster rate than in adults, so if left untreated, the child risks losing all of his baby teeth even before they begin to be replaced by molars. The causes of caries can be very different, which is largely why it is a widespread dental disease.
Types of caries in children
There are several parameters for classifying childhood caries. The key ones are the type of caries at the site of origin and the degree of its development. Below you can see what caries looks like in children in its various manifestations.
- Proximal caries
- Carious lesions are present on both one and the other antagonist teeth. Caries between teeth in children is also common, which some experts also classify as the approximal type.
- Cervical caries
- It is formed at the point of contact of the crown part of the tooth with soft tissues. Often goes deep into the tooth.
- Circular caries
- Unlike cervical caries, which are localized in a specific area, circular dental caries in children spreads along the entire gum line surrounding a specific tooth, so that over time the crown part simply falls off. This type of caries is very common in children with baby teeth.
- Fissure caries
- It affects fissures - grooves on the chewing surface of the teeth. It is considered one of the most common types of caries in both primary and permanent teeth.
Stages of childhood caries
- Initial caries. At first glance, it is almost invisible and appears as a small speck on the enamel. This type of caries is highly treatable because it has not yet penetrated into the layers of enamel and dentin.
- Superficial caries. This type of caries affects the enamel layer, but not deep enough to reach the dentin. Enamel caries in children is also treated quite quickly and effectively.
- Average caries in children. At this stage, caries affects not only the enamel, but also the dentin.
- Deep caries. With deep caries, all tooth tissues (enamel, pulp, dentin) are affected. Root caries in children is the final stage.
In addition to the parameters described above, experts distinguish caries according to the rate of development: from compensated (slowly progressing caries) to decompensated (when damage to tooth tissue occurs very quickly). In addition, the disease can be either local (that is, covering one tooth) or focal, when caries moves from one tooth to another. Caries on a child’s front teeth often follows the second pattern, especially in the absence of timely treatment.
Treatment of dental caries in young children
When we talk about dental caries in young children, we mean the age category from six months to 5 years - it is at this age that a number of baby teeth are fully formed, but the process of their loss has not yet begun. Caries of primary teeth in children usually progresses quite quickly, so parents always need to be on guard in order to detect the disease in time and take the child to the dentist.
Caries in children under one year and at 1 year
When a child is one year old, dental caries is a very unpleasant problem that needs to be corrected urgently. This is the so-called early caries in children, which is becoming more common today. Before the age of one year, a child usually develops front incisors. The treatment is gentle and is carried out without a drill. Usually this is fluoridation and remineralization of teeth. What is used to protect children's teeth from caries? The teeth are saturated with useful minerals (calcium, fluoride, etc.).
Caries in a child at 1.5 years, at 2 years and at 3 years
Caries in children under 3 years of age is also usually treated with gentle methods. At this age, doctors actively use the silvering technique, when teeth are treated with a solution of silver nitrate. This is a very effective technique, the disadvantage of which is the staining of tooth enamel. For more obvious signs of caries, photodynamic therapy is effective - removing damaged tissue and treating the tooth with a laser. When teething in chewing teeth, caries in a 3-year-old child can be prevented by sealing fissures (treating the grooves of chewing teeth). Caries in children's chewing teeth can develop very quickly, so fissure sealing is a good preventative measure.
Caries in a child at 4 years old and at 5 years old
After children reach 3 years of age, ICON technology (polymerization of teeth with treatment of carious cavities with instruments) is actively used for dental treatment. In the early stages, ozone therapy is used, which makes it possible to destroy carious bacteria. For deep caries, depophoresis is effective: copper and calcium hydroxide is injected into the area affected by caries. The solution penetrates the root tubules and destroys pathogenic bacteria.
Caries in a child at 6 years old, at 7 years old, at 8 years old, at 9 years old
At this age, active replacement of milk teeth with molars occurs. During these years, doctors do not recommend placing light and photopolymer fillings. At advanced stages of caries, today, as a rule, glass ionomer fillings or colored compomers are placed on baby teeth.
Caries in a child at 10 years old, at 11 years old, at 12 years old
After ten years, the child receives a set of permanent teeth. Often, molars are treated using “adult” methods, but there are also some nuances here, in particular, different depulpation protocols and more active use of a drill. Caries of the 6th tooth is especially common in children with molars, so sealing the fissures of chewing teeth is also relevant at this age
Caries of permanent teeth in children
If a child has caries of molars, then in the long term this can cause more problems than in the case of baby teeth, because they will no longer be replaced. The peculiarities of caries in children with molars are that they need to be treated in a special format. What do we mean? Firstly, even at 15 years old, a child remains a child and has all the same fears. That is why it is recommended to use gentle techniques and sedation as anesthesia. Secondly, it is still not recommended to put polymer and some other types of fillings on children's molars. On the other hand, the anatomy and structure of molars differ from baby teeth, so in most cases it is quite difficult to do without a drill.
What destroys tooth enamel?
Sugar.
When sugar enters the mouth, bacteria literally within a minute begin to intensively produce acid, which has a detrimental effect on tooth enamel. If sweet food intake is not frequent, then saliva neutralizes the action of bacteria and protects teeth, but if sweets are consumed periodically throughout the day, then the body does not have time to produce a sufficient amount of saliva, and this increases the risk of developing caries.
Advice. You cannot give your child sweets, including sweet carbonated drinks and compotes, uncontrollably and in between main meals! After each meal, it is better to offer him fruit.
There is a genetic predisposition to caries in the structure of the tooth, but with proper nutrition and dental care, the situation can be improved.
Temperature changes and injuries.
A sharp change in temperature and tooth trauma lead to enamel cracks that cannot be cleaned even with a toothbrush, so the risk of developing caries in cracks increases. For this reason, children should not be allowed to crack nut shells with their teeth; It is better to pre-soak crackers and dryers a little in tea or milk; The seeds should be peeled with your hands and not bitten with your teeth.
Vitamins for teeth and gums
The baby should take vitamins to strengthen teeth and gums regularly, without missing a single day. This is the only way the child will receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. The daily complex must include:
- Retinol (vitamin A). An element necessary for bone growth. It is vitamin A that promotes protein synthesis in cartilage and bones, and also increases the cartilage layer in the growth zone. If a child's body does not have enough retinol, the process of bone tissue growth slows down, and new teeth may grow crooked. In addition, with vitamin A deficiency, the development of stomatitis and gum inflammation is often observed. In advanced cases, teeth may begin to fall out.
- Calciferol (vitamin D) is one of the key components of bone development. It is thanks to this vitamin that a child’s bones develop normally and mineral metabolism is regulated. Calciferol, as the name implies, helps absorb calcium and strengthens bone tissue. In summer and spring, a child can get vitamin D from sunlight by simply walking outside often. But in winter and autumn it is important to give children vitamin complexes with calciferol. With a deficiency of this element, mineral metabolism can be disrupted, bone tissue softens, rickets appears, and, of course, tooth enamel becomes thinner.
- Vitamin C is essential for strengthening gums. If there is a lack of ascorbic acid, the child may experience tissue bleeding, in advanced cases, ulcers appear in the mouth, an unpleasant odor disturbs, and teeth begin to loosen and fall out.
- Vitamins B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cyanocobalamin) are also needed to strengthen gums. It is B12 that provides tissue strength and prevents various inflammations, and the lack of cyanocobalamin makes the gums very sensitive.
- Vitamin E is involved in wound healing and helps fight pustules that so often appear on the gums of babies.
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone) strengthens connective tissue and protects gums from bleeding.
- Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) is an important protector of gums from gingivitis, stomatitis and other inflammations.
Until what age is it better not to give a child sweets?
Nadezhda Darbashkeeva, head of the treatment and prophylactic department, dentist of the highest category, Honored Doctor of the Republic of Belarus, excellent student of healthcare of the Russian Federation:
– Sugar is necessary for humans. It performs a number of important functions in the body: energy supply, maintaining a constant level of glucose in the blood, nutrition of muscle tissue, participation in immune and protective reactions. However, excessive consumption at an early age can develop a child's taste for sweets, which lasts for the rest of his life. At the same time, excess sugar has a negative effect on the human body, which consists of excessive energy intake, deposition of adipose tissue (obesity), increased load on the insular apparatus of the pancreas (possibility of developing diabetes mellitus), restriction or deprivation of the body of other important products, and the development of caries . I recommend strictly limiting unhealthy sugars for up to 3 years. Children who already have carious teeth, especially multiple lesions, need to limit sweets until they are 15 years old. It is healthier for your teeth to replace sweets with marmalade, marshmallows, sweet fruits, marshmallows, honey and dark chocolate.
How to choose an electric brush for a child
From the age of 3 you can start using an electric brush. The advantage is that in children's lines you can find great opportunities for interactivity.
Some brands produce electric brushes with the ability to control brushing time via an app. The mobile application synchronizes with the brush and uses animated prompts to teach your child how to brush their teeth correctly. This helps maintain interest in the process.
For children aged 3 to 6–7 years, an electric brush with the softest bristles is suitable. It can be alternated with a regular brush. But remember: the use of an electric brush by a preschool child needs to be supervised.
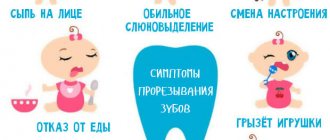
At what age should you start brushing your teeth?
Elena Shoboeva, hygienist:
– Before the appearance of baby teeth, child oral hygiene involves wiping the gums and tongue with a gauze swab or bandage moistened with boiled water. In this way, you can easily remove harmful plaque and cleanse your baby’s mouth of bacteria.
You should start brushing your teeth from the first day after they erupt. After each night feeding, it is recommended to clean your teeth of plaque. First, this is done without toothpaste and brush. Parents should use a piece of sterile bandage to wipe their child’s teeth every day. After a year, you can use special finger tips with silicone bristles. Starting from 1.5 years - brush with a children's brush and a special children's paste. Our clinic conducts course prevention programs developed individually for each patient. We also teach parents and children about proper oral hygiene. 90% of my patients don't know how to brush their teeth, so the best solution is –
contact specialists. Make sure your child brushes his teeth at least twice a day and rinses his mouth with water after eating. Cleaning time is three minutes. Before going to bed, you should treat your mouth with fluoride-containing rinses.
Advice. Once every six months, it is recommended to have your teeth professionally cleaned by a dentist. Using this procedure, the doctor removes all bacterial deposits that cannot be removed at home.
How to choose a toothbrush for a child
In this age group, both manual and electric brushes can be used. Brushes and attachments should be replaced every 2–3 months, as well as immediately after an acute infectious disease.
When choosing a suitable brush, pay attention to the following criteria.
- Age of the child. This is simple - pay attention to the age marking when choosing. For brushes recommended from 3 to 5 years, the length of the handle does not exceed 15 cm and the length of the head is 2 cm. From 5 to 8 years, the handle is up to 17 cm, the head is 2–2.5 cm.
- The stiffness of the bristles. Soft or ultra-soft bristles are suitable for children.
- Handle - should have anti-slip silicone or rubber inserts. Since fine motor skills are still developing, the brush should be such that the child can confidently hold it in his hands.
- Design. A brush with a bright design or with a favorite character will help get your child interested in brushing their teeth.
Is it true that caries is passed on to the child by the mother?
Olga Sambueva, dentist of the highest category:
– Scientists have found that close contact between mother and baby in the first months of life leads to infection of the child with maternal microbes that cause caries. If a mother has untreated teeth in her mouth, she passes on her bacteria to the child. This leads to bottle tooth decay in young children. For this reason, you cannot lick the baby’s pacifier or spoon, you cannot kiss his face, lips, or even his hands, which the child will push into his mouth. Dental caries in children occurs in a more aggressive form and has a faster progression than in adults.
Advice. Adults in the family of a newborn should be sanitized by a dentist before the baby is born.
Caring parents bring their children to the children's dental clinic to prevent caries. The success of prevention depends on regular examinations and home care, the specialist says.
– Teeth erupt “immature” with an insufficient degree of mineralization. Final mineralization and “maturation” occur in the oral cavity within two years for milk teeth and three years for permanent teeth. It is at this moment that caries prevention is very effective - deep fluoridation and fissure sealing! Therefore, as long as your teeth are healthy, we can protect you from caries. If caries has already appeared, it is necessary to treat the teeth at an early stage. The main thing is regular inspection!
Should baby teeth be preserved?
“Do I need to keep baby teeth if they fall out in a couple of years? Do they really need prevention?! But permanent teeth are a different matter!” - this is what many parents think and say. “But if a child has chronic diseases, no one will wait to treat them in adulthood; everyone understands that their trace will go into adulthood,” notes Victoria Korchagina. “The same thing happens with teeth: if baby teeth are damaged, destroyed, they were treated a lot and often removed, it means that the permanent ones will face the same fate.”
There is a direct connection between general immunity and the condition of the oral cavity. Caries develops more actively in children who have chronic diseases. And vice versa, the higher the activity of caries in a child, the more often he stays at home and does not go to kindergarten due to illness, the more prone he is to intestinal problems, allergic reactions, and respiratory diseases.
Typically, the pathogenic and non-pathogenic flora of the oral cavity are in a state of balance, but as soon as a person gets sick, this balance is disrupted, increasing the risk of diseases of the teeth, gums and mucous membranes.
A vicious circle arises. A sick, weakened child refuses to brush his teeth, and his parents sympathize with him - so as not to be capricious again, they stop brushing his teeth. As a result, after another illness, the child develops new carious cavities and gums bleed.
Multiple caries, in turn, supports foci of chronic infection in the body. Therefore, you should always brush your teeth: both in sickness and in health. This will help not only to recover faster, but also not to get sick as often.
What foods strengthen teeth?
To keep your teeth strong, include foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, manganese and copper in your baby’s diet. Calcium is found in milk and dairy products (especially a lot of it in cottage cheese and cheese), parsley, dried apricots, beans and green onions.
Karina Khutakova, head of the treatment and prevention department:
– Phosphorus is included in almost all seafood; there is a lot of it in fish (mostly in sea fish). White cabbage, pumpkin and gooseberries are rich in calcium and phosphorus at the same time. Cheese contains a large amount of magnesium. Zinc is found in meat and fish. Champions in manganese content –
oats, wheat, rye, onions and raspberries. Copper is highest in processed cheese, legumes, beets, lemon and black currants. Fluoride is an essential microelement for teeth. Its main source is fluoridated salt, which must be used in cooking. To strengthen teeth, you need foods that contain calcium - these are dairy and fermented milk products, hard cheeses and cottage cheese. Give your child beans, broccoli, green leafy vegetables and fish (sea fish is considered richer in minerals). Your baby can get vitamin D not only from the sun, but also from products of animal origin - sea fish (tuna, herring, salmon, mackerel, mackerel), egg yolks, cheeses and butter. Fiber in raw vegetables and fruits helps clean teeth from plaque and increases the amount of saliva, which neutralizes bacteria in the oral cavity. For teeth, carrots, apples, pears, celery and quince are considered the best options.
Prices for dental treatment for children
Consultations
| Name | Price |
| Consultation with a pediatric dentist, drawing up a dental treatment plan, conversation with the parent about the characteristics of the child’s life and development, the history of his diseases, their impact on the condition of the teeth; examination of the child’s oral cavity; consultation of parent and child on oral and dental health; recommendations on nutrition, oral hygiene, prevention of diseases of the teeth and oral mucosa; drawing up an optimal treatment and prevention plan with a preliminary estimate and indicating the treatment period. | 690 rub. |
| Consultation with a pediatric dentist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, complex cases of pediatric dentistry - clarification of the diagnosis, selection of the optimal treatment method; incl. conversation with the parent about the characteristics of the child’s life and development, the history of his diseases, their impact on the condition of the teeth; examination of the child’s oral cavity; consultation of parent and child on oral and dental health; recommendations on nutrition, oral hygiene, prevention of diseases of the teeth and oral mucosa; drawing up a treatment and prevention plan with a preliminary estimate and indicating the treatment period. | 1370 rub. |
| Consultation with an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. conversation with the parent about the characteristics of the child’s life and development, the history of his illnesses; history of illnesses in the family and history of treatment of blood relatives under anesthesia; consultation of parents on all issues related to treatment under general anesthesia; examination of the child, determination of indications and contraindications for treatment under anesthesia | 1100 rub. |
| Name | Price |
Diagnostic tests
| Name | Price |
| Orthopantomography is a digital image of all teeth and bone tissue of the upper and lower jaws, with the ability to assess the condition of the maxillary sinus and the structure of the temporomandibular joint | 2130 rub. |
| Targeted intraoral contact radiography intraoral digital image of 1-3 adjacent teeth | 610 rub. |
| Electroodontometry of the tooth is a method for determining the preservation of tooth vitality. Used during the treatment of trauma, pulpitis and periodontitis of permanent teeth | 265 rub. |
| Name | Price |
Therapeutic dentistry
| Name | Price | |
| 5665 rub. | ||
| Restoring a permanent tooth with a filling using materials from photopolymers | 12045 rub. | |
| 10600-15500 rub. | |
| Treatment of pulpitis of a permanent tooth | 11000-36000 rub. |
| 1380 rub. | |
| Instrumental and medicinal treatment of poorly traversed root canal | 2210 rub. |
| Filling the root canals of a baby tooth with paste (3) | 1970 rub. |
| Filling the root canals of a permanent tooth with gutta-percha pins (3) | 7365 rub. |
| 2310 rub. | |
| Application of an immobilization bandage for dislocations (subluxations) of teeth (Ribbond system) 7-8 units | 4175 rub. |
Does a pacifier affect the formation of a bite? When to give it up?
Aldar Damdinov, Head of the Orthodontic Center:
– The sucking function is considered one of the leading functions in a child’s life for the first 6 months, then it gradually fades away. Breastfeeding provides physiological functional muscle load and proper formation of the child’s maxillofacial area. Artificial feeding, especially if there is a large hole in the nipple, pressure from a bottle on one of the jaws, etc., contributes to the formation of malocclusion. It is recommended to stop using pacifiers and bottle feeding by the age of 1 year. When bad habits appear - thumb or pencil sucking –
consult a doctor immediately. If the parents have a malocclusion, take the child to the orthodontist at 1 year of age, then be monitored regularly to start treatment on time.
Tamara Buldaeva, head of the paid services department:
– Parents should understand the need to visit the dentist immediately after the child’s first teeth erupt at 6 –
7 months for the first application of fluoride varnish to an infant's teeth.
We will give you a course of preventive procedures to strengthen your teeth enamel, then
every six months until 4 years
. Frequently ill children and children with chronic somatic diseases need to more carefully monitor the condition of their oral cavity, as they are at high risk of developing caries. Usually, during illness, parents’ attention to the child’s oral hygiene weakens, and due to loss of appetite, children are fed tasty, usually sweet, foods. Medicines for children are produced in the form of sweet syrups; in addition, they reduce salivation, suppress the child’s immunity, and disrupt the microbial composition of the oral cavity. Regular visits for preventive purposes are painless, pleasant for children, good for health and, most importantly, cheaper than treating complications! Instill in your child a healthy lifestyle from the cradle. By treating caries at an early stage, your child will never be afraid of the dentist! Only the joint efforts of both parties –
family and doctors
–
will help keep your child’s teeth healthy, strong and beautiful for life! Be healthy!
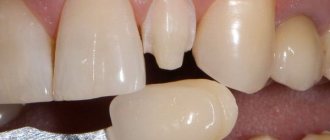
Eruption of a permanent tooth with a missing temporary tooth
The situation is not so rare, but there is only one solution to it: the retained milk tooth must be removed so that the permanent one can take the correct position. It’s good if the temporary tooth is “wobbly,” then the child can handle its removal himself. Otherwise, you will have to seek help from a dental surgeon.
Sometimes, when a permanent tooth has just appeared, but the temporary one is “not loose,” the doctor may recommend loosening the baby tooth at home for 2-3 weeks. This will make the removal procedure easier and psychologically prepare the child for it.
What to do if you can’t brush your teeth?
To prevent tooth decay, you need to brush them with toothpaste twice a day and follow a number of simple dental care recommendations. The list of foods harmful to teeth also includes very healthy ones - fruits, dried fruits, etc. But you should not exclude them from your child’s diet. You just need to brush your teeth with toothpaste every morning and evening and follow simple dental care tips.
Advice. Immediately after eating something sweet or sour, you can rinse your mouth with water, or better yet, with a special rinse or chlorhexidine solution. Brushing your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste would be optimal after 30 minutes.
Also allow your child to use sugar-free chewing gum. It not only cleans the surface of the teeth, but also removes food particles from hard-to-reach places and increases the amount of saliva. It is recommended to chew chewing gum for a maximum of 5–7 minutes and no more than 1–2 times a day.
You can remove food particles with dental floss; toothpicks are not suitable for children's oral hygiene, because... their inept use can injure teeth and gums. Teach your child from early childhood to eat a piece of raw apple, carrot, cucumber, or radish after eating. Modern people have much more problems with their teeth due to the fact that the food they eat has become too soft; such food can be swallowed without practically chewing. Meanwhile, you need to chew each lump of food, performing 40 chewing movements, and only then swallow. The process of more active chewing of food contributes to the thickening of the bone, thanks to which the tooth holds stronger, and the work of the stomach and intestines is facilitated.
How to reduce the risk of developing caries and not give up sweets
If your child has a sweet tooth or you are simply not ready to limit him, offer him an alternative - lollipops and candies with xylitol.
Xylitol or xylitol is found in the fibers of fruits, vegetables, birch bark and even mushrooms and is not a breeding ground for bacteria. When xylitol is added instead of sugar, it stops the growth and development of caries, since it is not absorbed by cariogenic bacteria, and they die.
Products containing xylitol can be consumed at any age. For children, 2-3 pieces of 100% xylitol chewing gum per day are enough to significantly reduce the risk of plaque and tooth decay.
In addition, chewing gum with xylitol will be useful for children who do not have the habit of actively chewing vegetables or meat. Chewing gum is useful as an additional exercise machine.
Lollipop Miradent XyliPOP (blueberry), 5 pcs.
Lollipops miradent Xylitol Drops mint
Chewing gum miradent Xylitol For Kids strawberry