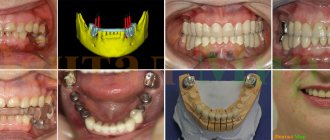
52621
Crooked, unhealthy teeth can ruin the appearance of an otherwise attractive person. Oral health is important not only for our attractiveness, because the main function of teeth is to grind food. The condition of the stomach and intestines depends on this, which directly affects health and life expectancy .
How to determine?
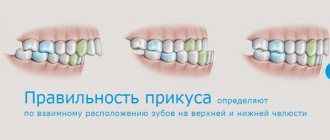
A distinctive characteristic is the tight contact of the upper and lower jaws when closing . The upper teeth are superimposed on a third of the lower crowns, leaving no distance between the upper and lower molars.
photo: this is what a correct bite looks like
The shape of the dentition and their relative sizes are also important. The top row has a semi-oval shape, the bottom row has a parabolic shape. The lower incisors are in contact with the palatal cusps of the upper ones. During chewing, the molars constantly touch without losing contact.
Correct bite forms a harmonious face , the lower and upper jaws are symmetrical, the vertical axis of symmetry of the face coincides with the junction line between the incisors.
Signs of a correct bite are also:
- no speech defects;
- comfortable biting and chewing of food;
- absence of uncomfortable sensations and clicking in the mandibular joint.
If you notice that plaque appears only on individual teeth, this means that they are not involved in the process of grinding food . In this case, it is worth visiting a dentist: this is a sign of a defectively formed dentition.
How much does a Hollywood smile cost?
It is impossible to answer definitively the question of how much it will cost to create a Hollywood smile. It all depends on the source data. Doctors of different specialties often participate in the work - therapists, hygienists, orthodontists, orthopedists, implantologists. The better the condition of your teeth and oral cavity, the cheaper a perfect smile will cost. In rare cases, all procedures end with professional hygiene and whitening.
Additional treatment always increases costs. The final cost of a beautiful smile is determined by several factors:
- Type of treatment;
- Volume of medical procedures;
- Technologies used;
- Types of orthopedic and orthodontic structures used, etc.
To find out the exact cost of your new smile, come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. If necessary, the doctor will refer you for examination and consultation with specialized specialists. After this, we will be able to calculate the prices of all procedures necessary to create a Hollywood smile.
What types are there?
There are temporary and permanent bites. The bite in children before the eruption of permanent teeth is called temporary. 6-9 years – time of replacement bite. During this period, the child has simultaneous presence of permanent teeth and milk teeth.
Peculiarities of eruption influence the formation of the maxillofacial system. Any removal of replacement teeth earlier than a year before natural loss causes the risk of various deformities:
- asymmetrical dentition;
- midline shift;
- blocking chewing movements of the jaw.
A permanent bite is formed when a teenager reaches 15 years of age, when the formation of roots in relation to the position of the teeth ends. Their number during this period is 28 (32 - if the third molars have erupted).
Permanent dentition can be physiological or abnormal.
Physiological
photo: this is what a correct bite looks like from the side
Physiological ones include types of occlusions that provide:
- the most efficient and comfortable chewing of food;
- correct speech formation;
- aesthetic appearance of the maxillofacial area.
There are several varieties:
- Orthognathic. This is the standard bite that provides maximum functionality of the jaws. Premolars and molars intersect with antagonists of the opposite row. The upper incisors and canines overlap the lower ones due to a slight outward slope.
- Straight. It differs from orthognathic in the type of closure of the incisors. The edges of the upper ones do not overlap the lower ones, but touch end to end. The molars have good tight contact. A big disadvantage is the rapid wear of the upper and lower incisors due to contact of the cutting edges.
- Progenic . The lower jaw is pushed forward. The dental arches close tightly, the chewing function of the jaw is preserved.
- Biprognathic. The incisors and canines have a greater angle of inclination forward than with orthognathic. The contact of the anterior teeth is good. The incisors meet at the edges.
- Opisthognathic . The upper and lower incisors are inclined towards the oral cavity. The molars and premolars are tightly closed.
Abnormal
photo: malocclusion
Malocclusion is characterized by a complete or partial absence of tooth contact in occlusion. Such a bite distorts the face, disrupts the chewing process and can affect the formation of speech defects.
There are several types of abnormal bite:
- Deep. Its peculiarity is that the upper incisors overlap the antagonists by more than a third. The wear of the cutting edge is increased, causing the masticatory muscles to experience hypertonicity. This type of bite is also determined by constant sensations of tension in the temporomandibular joint and headaches.
- Open. A rather complex defect that entails disruption of several body systems at once. With the open type, some teeth do not have contact with the antagonists. There are lateral and frontal types.
Symptoms indicating the presence of an open bite are elongation of the mandibular part of the face, constant tension of the facial muscles, speech disturbances, difficulty swallowing, discomfort when chewing.This type may have a rachitic and traumatic origin. The rachitic variety is difficult to correct and usually requires surgical intervention. The traumatic variety is formed in childhood as a result of bad habits or trauma; at a young age it is quite easy to correct.
- Cross. The displacement of the lower jaw to one side forms a noticeable asymmetry of the face, the dentitions close like scissors crosswise.
A person with such a defect has difficulty chewing food and chews only on one side. Poorly chopped food provokes stomach diseases, discomfort in the jaw joint during eating, and the development of periodontal diseases. - Distal. The defect is formed as a result of good development of the upper jaw and at the same time underdevelopment of the lower jaw.
With this anomaly, the upper incisors stick out forward, leaving a large gap between the upper and lower incisors. In the formation of such an anomaly, heredity, poor posture, and removal of baby teeth (more than a year before the appearance of permanent teeth) become decisive. - Mesial . Characterized by a protracted lower jaw. With such a defect, the chin protrudes strongly and the facial profile is curved. The lower teeth are located in front of the upper teeth during occlusion.
Anatomical structure of teeth with pictures
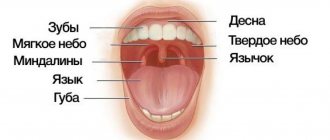
External anatomical structure of a human tooth:
- The crown is the visible area covered with enamel, the hardest part of the tooth. The surface layer performs a protective function and is designed to preserve dentin.
- The root part is a complex of nerve fibers, arteries and veins that provide nutrition and innervation to the tooth. The second function of the root is retaining.
- The neck is the area between the root and the crown, which performs a connecting function. Differs in a narrowed shape.
Diagram: external structure of a human tooth
How does a human tooth work at the tissue level?
All human teeth have a similar internal structure. The diagram below shows all the dental layers - enamel, dentin, cement, pulp.
The figure shows the histological structure of the tooth
Enamel covers the teeth like a cover and makes up 25% of the total mass of all dental tissues. The hardness and strength of this tooth layer is ensured by a high mineral content of 397 kg/mm.
The composition of the enamel layer includes:
- minerals – 96%;
- organic substances – 1.2%;
- liquid, water – 2.3%.
The enamel is covered by an outer shell, the cuticle, which covers the chewing surface of the tooth. Most of the tooth is occupied by dentin, located immediately under the enamel. It has less strength, its hardness is 58.9 kg/mm.
Cement – covers the root part and in most respects is similar to bone tissue. Depending on the type of structure, there are two types of cement:
- acellular or primary - consists of collagen fibers;
- cellular or secondary - the composition includes cemenoblasts.
The internal dental cavity is occupied by the pulp - soft tissue, including:
- numerous nerves;
- blood vessels;
- connective tissue.
Sectional structure of a tooth
Despite the differences in the purpose and structure of the root system, all teeth have the same internal structure:
- Enamel. A very hard surface layer that protects teeth from environmental influences. It is designed as a structure of glued prisms. Thanks to the large amount of mineral salts in its composition, enamel is the strongest tissue in the human body. Its main task is to preserve the dentin of the crown. The presence of a pellicle ensured the tissue's resistance to the effects of acids.
- Dentine. It consists of coarse fibrous tissue, the basis of which is collagen fiber. The structure is similar to porous bone. There are two types of dentin: superficial and internal. The first has a higher density and prevents infection from entering the dental cavity.
- Cement. Consists of collagen fibers saturated with limestone salts. Layer thickness - from 50 to 150 microns, depending on location. There are two types of cement: cellular and acellular.
- Cavity. It has a shape identical to the crown and is located under the dentin. The entire area of the cavity is filled with pulp, a type of tissue responsible for nourishing the tooth and performing a connecting function. The presence of blood and lymphatic vessels ensures high sensitivity of the pulp.
Photo: this is what a tooth looks like in cross-section
Causes of anomalies
Let's look at the main reasons why defects occur:
- Genetic factor. Mesial and distal occlusion are most often inherited.
For parents, knowing about the high risk of such a defect occurring in their child, it is easier to control treatment in childhood, during the formation of the maxillofacial system. - Developmental anomalies in the prenatal period. Various pregnancy pathologies can often affect the formation of the fetal dental system.
- Birth injury. Mesial occlusion is caused by displacement or dislocation of the baby's lower jaw during difficult childbirth.
- “Wrong” habits in childhood. These include constant pacifier or finger sucking, improper nipple latching, and improper sucking during bottle feeding. If the hole in the nipple is too large, the child’s lower jaw practically does not work when sucking and remains undeveloped.
- Frequent sinusitis and rhinitis, due to which the child constantly breathes through his mouth. With such breathing, the development of facial bones is disrupted.
- Violation of tooth change. Early removal of baby teeth often causes abnormal maxillofacial development.
- Incorrect prosthetics, lack of prosthetics.
- Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles due to stress provokes abrasion of the incisors and displacement of the jaws.
- Various injuries of the maxillofacial area.
How to form?
photo: diagram of the correct bite in a person
What do orthodontists advise to form the correct position of teeth:
- Breastfeeding is very important for a child; it lays the foundation for the correct development of the jaws.
If you had to feed your child with formula, it is best to purchase a pacifier that does not spoil the bite. The sucking hole should be made narrow so that the baby has to suck with effort. The lower jaw in infants is underdeveloped and muscle exercises (forceful sucking) are important for its proper functioning in the future. - Formation of correct chewing habits. You should not accustom your baby to a pacifier. From the moment of teething, the baby should be offered complementary foods for the habit of proper chewing.
- Parents should pay attention to how their child breathes. Physiological breathing through the nose. Breathing through the mouth is a sign of ENT diseases. They must be treated: in addition to general damage to health, this is a dangerous factor in the formation of a defective bite.
- From the moment of complete eruption of baby teeth, regular examinations by an orthodontist (every six months). When abnormalities are diagnosed at an early age, they are much easier to treat.
When is formed
The dentist will be able to give a final conclusion regarding the correct or incorrect bite only after the baby teeth have been replaced with permanent ones, although recommendations for the formation of a correct bite are relevant long before this moment.
Before the age of 6 years, dentists should periodically examine the dentofacial apparatus. At the slightest deviation from the norm, after consultation, parents will receive advice aimed at stabilizing the situation. The sooner these corrective actions are implemented, the faster a good result can be achieved. With age, the rate of restoration of correct bite decreases, but it can be achieved at any age.
The formation is influenced by both hereditary and external factors. All stages of development are completed by the age of 15.
Important points for the development of correct bite are:
- breastfeeding for at least six months;
- exclusion of pacifiers and other breast substitutes;
- preventing the development of bad habits such as thumb sucking or other objects;
- physiological position during sleep without tilting the head back;
- normal amount of solid food in the diet.