Galvanosis
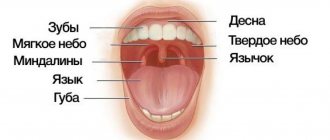
The oral cavity is a complex biological environment, in the soft tissue structures and mucous membranes of which a large number of electrochemical reactions occur under the influence of saliva. One of them is the occurrence of galvanic microcurrents - weak impulses of electricity. They are formed when salivary fluid comes into contact with metal orthopedic devices in the mouth. This process is the norm, however, with an increase in the strength of the impulses, pathologies can form, primarily galvanosis. Previously, this was called intolerance to metal alloys and their inclusions in the oral cavity.
Specialists from the branches of family dentistry West Dental in Vsevolozhsk microdistrict Yuzhny and Yanino-1 will first of all take a detailed allergy history at a consultation appointment and help you choose orthopedic and surgical structures for your convenience. Dentists, orthopedists-surgeons-implantologists Epimakhov Konstantin Vasilyevich and Berkovich Sergey Andreevich will make the installation and selection of the necessary structures comfortable and most suitable for you.
What is galvanic syndrome
Galvanic syndrome is encountered by people who have metal prostheses made of dissimilar metals installed on their teeth (fillings, crowns, inlays, implants). Oxides of certain metals, which have different electrochemical activity and come into contact with a liquid electrolyte medium (in this case, saliva), provoke an increase in galvanic currents in the oral fluid. In a simplified version, electrical impulses appear between prostheses made of different metals due to their chemical properties. This process is called galvanism.
And the pathology called “galvanosis” becomes a consequence of galvanism. That is, galvanosis is already a diagnosis. With galvanosis, the patient notices pathological symptoms - for example, a metallic taste in the mouth (more on this below), and if left untreated, very serious consequences for the entire body are possible. By the way, there are quite a lot of patients who, to one degree or another, have encountered galvanic syndrome in the mouth - from 15% to 35% of all cases of prosthetics.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
Interestingly, the phenomenon of galvanism in a living organism was first discovered, but not studied in detail, by the Italian scientist Luigi Galvani, after whom the process was named. Although in fact, the true meaning of galvanic currents (including in the body) was revealed by Galvani’s student Alessandro Volta. Moreover, Volta went further than his teacher and made many discoveries in the field of electricity, and also developed the first battery, the operating principle of which was based on chemical processes.
Definition of pathology
Galvanosis (ICD code K13.7) is a pathology in dental practice that occurs due to the strong influence of metal currents on the soft tissue structures of the oral cavity. Such currents are formed when metal structures of different potentials come into contact with each other and with salivary fluid.
Characteristic signs of the occurrence of galvanism are:
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- dry mucous membranes;
- decreased taste sensitivity;
- burning of the papillae of the tongue;
- frequent migraines;
- increased irritability.
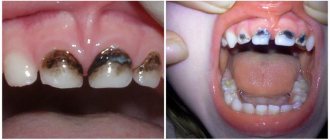
The first symptoms become noticeable within a couple of months after the installation of prostheses containing steel, clasps made of chromium-cobalt, and replacement of the old bridge-like console with a new one made of a gold alloy.
Signs
The syndrome does not develop immediately; the patient does not feel discomfort for some time. But the complexity of the situation is that if it worsens, there is a high risk of developing complications that negatively affect health. Signs of galvanism that you should pay attention to are:
- fatigue, lethargy, without reason;
- sleep disturbances, difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings at night;
- disability;
- sharp headaches;
- colds;
- sudden mood changes, unmotivated irritability.
Additionally, symptoms may develop that indicate the need to see a doctor for examination:
- a metallic taste appears that does not disappear even when eating;
- a sour taste appears, the sense of taste of foods changes;
- itching, numbness of soft tissues, tingling, sharp burning appear;
- a feeling of current appears on the mucous membrane;
- mucous membranes, soft tissues become sensitive to touch;
- change in the amount of saliva produced.
Causes
Modern orthopedic specialists identify a number of fundamental reasons for the formation of galvanosis after prosthetics with devices containing metals. It is very important to understand the causes of galvanosis in order to correctly perform a differential diagnosis in the clinic and draw up the necessary treatment plan.
- Galvanic cell. Reasons for its formation:
- difference in potentials of the metals that make up the alloy of the prosthesis;
- different composition and structure of metal combinations;
- non-compliance with the rules for casting material;
- low-quality alloy;
- error in assigning dissimilar metals.
- Toxic effects of heavy metals.
- Individual patient health characteristics and concomitant diseases:
- intolerance to alloy components of the prosthetic structure;
- characteristics of salivary fluid;
- chronic lesions - caries, periodontitis;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- poor quality oral hygiene.
Prevention of galvanic syndrome
In order to prevent galvanosis, you should carefully choose a doctor and clinic where you are planning prosthetics or implantation. It is also advisable to know what the already installed prosthetic structures are made of, and to communicate such nuances during subsequent prosthetics with another specialist.
The basic rule is to use the same metal for prosthetics. It is optimal to choose chemically inert metals - alloys of gold, platinum, palladium or titanium. And the metal prostheses or inclusions themselves must be manufactured using modern methods - casting or milling using CAD/CAM technology. Before prosthetics, it would be useful to take allergy tests to identify individual intolerance to metal - and if an allergy is detected, then it is better to choose ceramic, zirconium dioxide, acrylic non-monomer prostheses.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
Symptoms of the disease
The diagnosis of galvanosis a couple of months after the installation of prostheses begins to manifest itself with pronounced symptoms:
- persistent metallic taste;
- deterioration of taste sensitivity;
- increased sensations of acidity;
- burning tongue;
- soreness of the cheek mucosa;
- impaired salivation;
- migraine;
- irritability;
- insomnia;
- general weakness.
Symptoms appear in the morning and are often accompanied by disease of the oral mucosa:
- hyperkeratosis—keratinization of the mucous membrane;
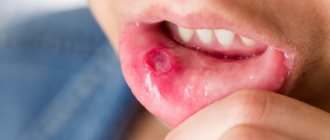
- erosions and ulcers - thinning of the soft tissue structures of the oral cavity.
Classification and stages of development of galvanosis
Modern classification distinguishes 2 forms:
- Atypical. With this form, the conductivity of the salivary fluid, the current strength, and the number of active potential particles increase 4 times more than normal. The atypical form is a difficult pathology to diagnose. With prolonged neglect and failure to carry out timely treatment, growth of tumor-like formations, inflammation of the mucous membrane, and ulceration are possible.
- Typical. The potential increases over 4 times, accompanied by local and general symptoms. Often this form of pathology occurs in patients with destroyed and defective structures. Consequences: allergies to metals, malignancy of tumors and inflammation in soft tissues - gingivitis and papillitis. Possible damage to bone tissue.
Complications
The development of galvanosis is always accompanied by a decrease in the body’s general defense reactions. Electric currents formed during the interaction of prosthetic structures with saliva have a detrimental effect on the natural microbiological composition of the microflora of the oral cavity. All this together creates a favorable environment for inflammation to occur.
Often occur:
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gum tissue, leading to swelling and bleeding;
- papillitis - inflammation of the interdental papillae;
- stomatitis - developed under the influence of “heavy” metals, damage to the mucous membrane;
- herpes;
- frequent colds;
- activation of chronic processes.
If you do not pay attention to the primary symptoms of the pathology, and do not carry out prevention and treatment, the disease will be complicated by allergies and the formation of tumor-like formations.
Why is there a problem?
Recently, dental diseases caused by the presence of metal dentures in the mouth have received increasing attention from expert researchers. In particular, such a diagnosis as “intolerance” is becoming more popular every day - patients’ bodies reject acrylic plastic, cobalt chromium, and stainless steel. Significant difficulties with the “portability” of structures also arise if alloys of several metals are simultaneously present in the mouth.
A burning sensation at the tip (on the sides) of the tongue, increased dryness in the mouth, combined with signs of inflammatory processes or stomatitis on the mucous membrane - manifestations of typical galvanosis
Dentures made of metal or plastic can cause dental problems of allergic, toxic-chemical or mechanical origin. In the specialized literature, any manifestations associated with the presence of certain prostheses in the mouth are called galvanosis or galvanism.
Most experts agree that galvanism should be understood not as a disease, but, most likely, as a certain pathological process (factor) that predisposes to the development or exacerbation of all kinds of diseases. But in the presence of galvanism in combination with signs of damage to the oral mucosa and other symptoms (they will be discussed below), we are talking about galvanosis as a diagnosis.
Additional “triggers” that contribute to the appearance of signs of galvanosis are:
- presence of defects in metal elements of prostheses installed in the mouth;
- mechanical damage to structures during wear;
- “acidification” of saliva against the background of periodontitis, stomatitis, and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnostics
To identify galvanosis in dental centers, diagnosis is carried out using a detailed visual examination of the oral cavity using additional instruments; laboratory tests may be necessary.
The doctor identifies symptoms of failure to adapt to prostheses, disturbances in the structure of the device and its melting technology. The most important diagnostic method through which galvanosis is detected is measurement and evaluation examination.
- Measuring the potential difference between the structures and the salivary fluid with a voltmeter or ammeter. This is the main indicator of the pathological process.
- Measuring the pH of salivary fluid with an ionometer. We determine the saturation of saliva with hydrogen ions.
- Assessment of the composition of salivary fluid by spectral analysis.
In the presence of galvanosis, the potential difference in the mouth is up to 150 mV, and there is also a pH shift to an acidic environment.
It is important to be able to distinguish galvanosis from similar pathological processes:
- Glossalgia. Pain and swelling of the tongue and increasing viscousness of the salivary fluid, which is not typical for galvanosis.
- Lingual neuritis and trigeminal neuralgia. With these pathologies, touching the tongue causes sharp painful sensations.
- Stomatitis caused by toxic and allergic exposure. The digital data of the general blood test change - the ESR increases, and the blood cells increase slightly. This does not happen with galvanosis.
How to identify an abnormal process
Patients who have detected signs of galvanosis in the mouth are subject to appropriate diagnostics:
- measurement of potentials of metal inclusions in prostheses;
- determination of current strength between individual structural elements;
- saliva pH analysis;
- identification of the qualitative and quantitative composition of microelements present in the secretion as an indicator of the severity of electrochemical processes.
Diagnosis of galvanosis involves the use of instrumental and laboratory methods
Important! With galvanosis, the current strength between individual parts of bridges made of certain alloys increases. There was no direct relationship between the severity of clinical symptoms of the disease and electrical parameters. With galvanism, the pH of saliva shifts slightly to the acidic side. Skin allergy tests for chromium, nickel, cobalt and other trace elements give negative results.
Differential diagnosis of galvanosis involves consultations with such specialists as an allergist, oncologist, psychotherapist, and gastroenterologist. Depending on the symptoms, doctors may refer the patient for additional tests: biochemical blood test, immunogram, CT scan of the facial part of the skull, etc.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures to eliminate galvanosis should be a combination of the work of related specialists and include important stages:
- metal structures should be removed from the oral cavity as a priority;
- elimination of local inflammatory and allergic reactions;
- strengthening the body's immune defense.
Before starting treatment, the doctor completely examines all components of the prosthesis and identifies problem areas. The discomfort-producing structure is removed from the oral cavity. Also, an important stage in the treatment of galvanosis is the treatment of inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane. Local and general immune-strengthening therapy drugs are prescribed.
After treatment, the symptoms of the underlying disease disappear within a week, all indicators return to normal.
Galvanic syndrome in the mouth - why it appears and how to deal with it
Article navigation
- What is galvanic syndrome
- Causes
- Classification and symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Complications without treatment
- Prevention
- Cost of treatment
- User Questions
Question for a specialist
Dental prosthetics is sometimes complicated by some rather unpleasant conditions - and a person may not even suspect that the problem is in the prosthesis. One of these processes is galvanism in the oral cavity, which is also called “galvanosis” or “galvanic syndrome”. Next, we will tell you why it occurs, what symptoms it is accompanied by, how it is treated - and whether it is worth doing anything about it at all.
Preventive actions
With correctly performed diagnostic and therapeutic measures, patients have everything they need to fully restore chewing function after replacing prosthetic structures with hypoallergenic ones.
Preventing pathology is much easier than full-scale therapeutic methods. Therefore, prevention is an important stage in caring for one’s health for every patient. In order not to miss the disease at the very beginning, when everything can be corrected as gently as possible, it is important for a patient with orthopedic structures to visit an orthopedic dentist 2 times a year to perform a preventive examination, as well as perform a professional examination. hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity.
Specialists from West Dental clinic branches will always help identify the problem in a timely manner and offer comprehensive, appropriate treatment.