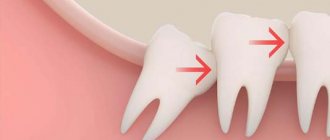
Wisdom teeth often cause dental problems, the most serious of which is an atypical position. “Eights” can grow at an angle, be completely embedded in bone tissue, or only partially erupt.
With their crown, they can injure a neighboring tooth. When such situations arise, dentists recommend atypical wisdom tooth extraction. Timely surgery will help avoid injuries and the occurrence of carious inflammation. Specialists at the Profident Junior surgical dentistry clinic will perform the operation as quickly and painlessly as possible.
When is it necessary to remove an atypical tooth?
You should not think that a person does not need wisdom teeth at all. If they are located correctly and do not create problems, specialists make every effort to preserve them. But there are indications in which atypical wisdom tooth removal is the only correct solution:
- injury to a nearby tooth or cheek;
- inflammation of the gums during partial tooth eruption, especially if there is discharge of pus;
- The 8th tooth causes acute pain or a feeling of swelling of the gums;
- roots or a figure-of-eight crown injure the adjacent tooth.
Atypical tooth extractions are a surgical intervention of increased complexity. Only a specialist of the highest category can carry it out. Sometimes it is necessary to remove part of the jaw bone and apply stitches. The issue of removing an atypical wisdom tooth must be approached very responsibly.
Causes of dystopia
Dental dystopia develops under the influence of various factors, the main ones being:
- deviations in the normal growth of the jaw (delayed growth);
- discrepancy between the size of the teeth and the size of the jaw;
- partial adentia (absence of some teeth);
- deviations in teething;
- hyperdentia (supernumerary teeth);
- atypical anlage of tooth germs;
- significant discrepancy between the sizes of temporary and permanent teeth;
- macrodentia (increase in the size of the dental crown);
- abnormal arrangement of adjacent teeth;
- injuries of tooth buds;
- bad habits (hand biting, thumb sucking by children during sleep);
- early removal of baby teeth and lack of rational prosthetics;
- narrowing of the dentition;
- late loss of baby teeth;
- genetic predisposition;
- absence of a neighboring tooth or an antagonist tooth on the opposite jaw;
- odontogenic neoplasms (cysts, tumors).
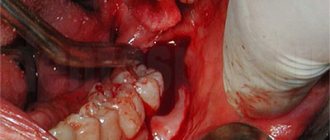
How is atypical tooth extraction performed?
The operation of atypical tooth extraction affects not only the “eight” and mucous membrane, but also the periosteum and bone. Surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia. But if the operation promises to be complex and lengthy, atypical wisdom tooth removal is performed using medicated sleep.
First, a panoramic photograph is taken, which will help determine the condition of the teeth: the length of the roots and their shape, the distance to the maxillary sinus and nerve. If a tooth has partially erupted, the image will show how much bone tissue is located above its crown. This will help you plan atypical wisdom teeth removal and successfully perform the operation.
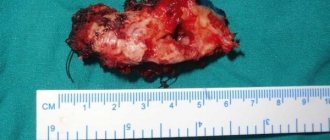
Atypical extraction of the 8th tooth is usually performed in parts. First, the surgeon removes the bone “roof”, then separates the crown from the roots and removes them one by one. After the operation, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Tooth extraction using piezosurgery - main stages
To describe the operation using a piezo knife, consider the removal of an impacted tooth as an example:
Stage No. 1 – anesthesia
. As a rule, local anesthesia is administered, which is sufficient for a comfortable procedure in the oral cavity;
Stage No. 2 - gaining access to the tooth
. Using a laser knife, the hood in the gum is cut to expose the pathological tooth;
Stage No. 3 – working with the root part
. If the root is complex, especially at an angle, the surgeon decides to divide the tooth into two parts. At this stage, it is important to remove the root so as not to damage the bone tissue. Any bone deformities can potentially lead to long-term rehabilitation and complications;
Stage No. 4 – working with the gums
. Sutures are placed on the gum, a sterile swab is placed in the operating area (socket), and medicine is applied on top to speed up tissue healing.
It is important! Before the operation, it is advisable for the patient not to eat for 1-2 hours, and if necessary, take a sedative. It is better to avoid drinking alcohol and energy drinks the day before.
Atypical extraction of the 8th tooth, complicated at the Profident Junior clinic
Complex and atypical tooth extractions at the Profident Junior clinic are performed using the latest equipment and reliable instruments. Specialists use European techniques that make it possible to painlessly and quickly perform any type of surgical operation, including the removal of a wisdom tooth with cutting of the gums.
Atypical tooth extraction, depending on the complexity, is performed using local or general anesthesia. The staff ensures sterilization and cleanliness to ensure safety during treatment.
You can find out the price for atypical wisdom tooth extraction at the Profident Junior clinic by scheduling a consultation.
This can be done not only by phone, but also online by filling out a simple form on the website. Here the uniform is blue.
Profident Junior uses all methods of atypical tooth extraction. Dental surgeons have the necessary skills and constantly improve their qualifications.
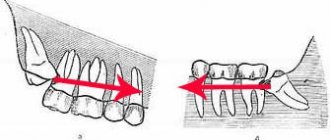
Types of dystopia
Abnormal arrangement of primary teeth is rare; usually permanent teeth are susceptible to dystopia. They can be dystopic within the dentition or outside it, they can be deployed along a vertical axis, and have different inclinations. Depending on the position of the tooth, the following types of dystopia are distinguished:
- Vestibular - the tooth moves outward from the dentition to the vestibule of the oral cavity. Most often, incisors and canines are affected by this type of deviation. A person’s smile with dystopic fangs is commonly called a “vampire smile.”
- Mesial – the tooth moves forward along the dentition.
- Distal – deviation of the tooth back along the dentition.
- Oral: Lingual deviation – a tooth on the lower jaw is displaced towards the tongue. It is observed more often on incisors and premolars.
- Palatal deviation - a tooth on the upper jaw is shifted towards the palate. This dystopia is typical for central incisors.
- Supraposition - the lower jaw tooth is displaced vertically above the occlusal curve (the line that passes through the points of closure of the teeth).
Dystopia of impacted teeth, that is, unerupted teeth, is also diagnosed. Often this anomaly is characteristic of the third molars (wisdom teeth): they are located horizontally or obliquely in the jaw bone or in the gum tissue.
Sometimes an anomaly occurs such as dystopic supernumerary teeth - additional teeth that erupt outside the dental arch (in the palate, on the gums).
Caries - what is it?
More than 95% of the inhabitants of our planet face the disease. Thus, it can be called the most common dental problem. At the very beginning, the pathological process affects only the enamel, and in the absence of therapy it penetrates into the deep hard layers. Then the soft tissues with nerve fibers and blood vessels become inflamed.
The disease is insidious because in the earliest stages it does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient begins to sound the alarm only when acute pain and a large hole appear that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods.
The most problematic wisdom teeth
In dental practice, doctors are often faced with the problem of their patients' wisdom teeth.
These are the eighth teeth in the dentition, so they are colloquially called eights. A wisdom tooth is a third molar (teeth used for mechanical processing of food). The location of the third molars is symmetrical - on the upper and lower jaws. Therefore, an adult has only 4 eights. The eruption of third molars occurs between 14 and 25 years of age. These are the latest teeth, which is why they are called wisdom teeth. In some people, the eights remain covered by bone or gum, causing them to fail to erupt. In the medical literature, teeth that have not erupted are called impacted. A semi-impacted tooth is said to be in cases where the tooth has not fully erupted.
The late appearance of third molars, as well as problems with their eruption, indicates the rudimentary nature of these teeth. As a person began to consume less solid and tough foods, the need for third molars disappeared. Over tens of thousands of years of evolution, when humans began to eat thermally processed food, the average jaw size decreased by about 10-12 mm, which is why the eights became cramped. Some people have no third molars at all, and this is not considered a pathology.
Is it necessary to remove a dystopic tooth?
Not every dystopic tooth needs to be removed; the decision to extract or preserve it must be made by the doctor based on examination data.
Abnormally located teeth are removed in the following cases:
- semi-impacted third molar;
- an impacted wisdom tooth putting pressure on the second molar, or in the presence of odontogenic neoplasms at its apex;
- supernumerary teeth;
- impossibility of orthodontic treatment.
Periodontitis, a cyst at the top of an erupted dystopic tooth - relative indications for removal.
If dystopic teeth are located outside the alveolar process of the upper jaw and are directed with the crown into the nasal cavity, towards the maxillary sinus, they are removed in a hospital setting.
Sometimes the doctor may decide to extract a less significant tooth than the dystopic one in order to make room for the latter in the dentition and return it to the correct position with the help of orthodontic structures.
To understand what to do in each situation specifically, you need to consult an orthodontist for advice. The doctor will do all the necessary studies, photographs and offer solutions based on the current situation.
- Installation of braces without removing teeth. In this case, it is necessary to prepare space for the dystopic tooth by moving the neighboring ones. Then, after freeing up space, the dystopic tooth is gradually placed in the correct position. Treatment lasts a year or more, depending on the degree of development of the anomaly.
The procedure leads to lengthening of the dentition and may lead to a change in the relationship of the jaws. To avoid these phenomena, the following method is used.
- Installation of a braces system with extraction of less significant teeth. After their removal, space is freed up for the movement of dystopic teeth. With the help of a brace system, the teeth gradually fall into place, the dentition is leveled and the morpho-functional restoration of dental function occurs. This method of treatment, despite the need to remove healthy permanent teeth, has some advantages: the proportions of the face do not change;
- teeth take the most correct position;
- the efficiency of the chewing function of the dental system increases due to the formed correct bite;
- The roots of the teeth in the jaw are located more freely, which makes the result of orthodontic treatment more reliable.
Duration of healing of the dental alveoli
Many doctors' clients are interested in how long it will take for the dental alveolus to heal after the removal of a damaged tooth. Typically, this process takes from 5 to 7 days. After 3-4 weeks, the gum area adjacent to the socket heals completely. It is important that the jaw is not damaged during the removal process. Such an injury will cause the healing process to take six months. To prevent this from happening, make an appointment at the As-Praktika clinic, where experienced dental surgeons work. In Samara, the price for tooth extraction is quite reasonable; this procedure is available to absolutely everyone. You can make an appointment at this clinic online by indicating the desired date of visit.
Methods of treating the disease
If the doctor was able to determine why a person has dental caries, he will be able to develop therapeutic tactics and help him recover quickly. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated non-invasively, that is, without the use of a drill. If the lesions are deep, drilling and medical treatment cannot be avoided.
Traditional methods will not help in the fight against the disease. But home recipes show an excellent effect as part of complex therapy to consolidate the results and prevent relapses.
Conservative treatment without preparation
At the initial stage of infection, the dentist will not drill crowns. The doctor will carefully remove plaque and tartar, and then apply a special composition to mineralize the enamel. The procedure lasts about an hour. Procedure:
- visual inspection;
- gum isolation;
- removal of deposits;
- application of remineralizing solutions.
If all manipulations were carried out according to the rules, the pathological process will stop. No additional methods are required.
Treatment with preparation of hard tooth tissues
Severely affected dental units can only be cured by mechanical removal of the diseased areas. The stages of intervention depend on the stage of the disease, usually as follows:
- use of anesthesia or other pain relief option;
- drilling;
- application of medications (antibacterial, etc.);
- installation of a protective gasket;
- restoring the integrity of the crown (filling);
- correction of the shape of the filling;
- grinding and polishing.
With deep lesions, the risk of pulp involvement increases. It is better to take a targeted photograph of the dental unit and make sure that there is no or no inflammation.
In severe cases, depulpation (extraction of the nerve and cleaning of the canals) and extraction (tooth removal) are indicated. These are extreme measures that are resorted to at the very last moment.
Symptoms
The rate of growth of signs primarily depends on why caries occurs, holes are formed, and the inflammatory process develops in the neurovascular bundle. The most common symptoms of carious lesions:
- darkening of the enamel, the appearance of dots or stripes of a white or dark shade on it (typical of the initial stage);
- increased sensitivity when consuming certain categories of foods (sour, sweet, hot, cold, hard); pain when pressing on the diseased area or in the absence of mechanical action;
- deep black holes, cracks in hard tissues;
- bad breath;
- headache, shooting sensation in the ears.
Diagnosis of dental caries
In some cases, the patient can independently diagnose himself, based on characteristic signs such as the presence of black holes and pain. However, there are situations when only a competent specialist can detect a lesion. This applies to the initial stage of the pathology in the absence of severe symptoms. At later stages, a thorough examination is also important in order to correctly differentiate the pathological process from other disorders.
The main methods used in dentistry:
- visual inspection using a mirror and other tools;
- computer images (panoramic, radiovisiography, CT, 3D study);
- functional diagnostics;
- thermal test;
- probing.
Dentik uses modern X-ray machines with safe radiation exposure and other equipment. We examine adult patients, women during pregnancy and lactation, and small children.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dystopic teeth consists of examining the oral cavity, assessing the bite and obtaining x-ray data. To accurately determine the condition of teeth and jaws, use:
- Teleradiography - X-ray examination is carried out from a large focal length, which reduces the radiation dose to the patient and reduces distortions in the image. Teleradiography is needed not only for diagnostics, but also for predicting the results of treatment and monitoring its process.
- Computed tomography is a layer-by-layer study of tissue. The images are combined into a 3D image, which allows you to more accurately study the position of the tooth in the jaw and develop a treatment plan.
- Orthopantomography - provides a detailed image of the jaw and all teeth, allows you to evaluate the inclination of erupted and impacted teeth, and detect anomalies of tooth germs and hard tissues.