The oral mucosa is resistant to many irritants, although it is daily exposed to external mechanical influences: brushing teeth, eating solid foods, and others. For some reason, injuries, various pimples, and balls can sometimes occur. Very often, various types of formations appear in the most delicate sublingual area. Blisters can be different, but in any case, a bubble under the tongue, even the smallest size, brings a lot of inconvenience. There is discomfort when talking or eating. In some cases, the ball under the tongue interferes with normal life due to its size and pain.
Injury
In case of traumatic injury, a kind of capsule is formed in the oral cavity, which is filled with secretions and pathogenic microorganisms. The lights enter the food cavity.
Trauma can cause the gland to become clogged with saliva, leading to the formation of a cyst.
It is not difficult to get such damage; it often occurs as a result of:
- Contact with sharp, chipped teeth.
- Rough food, various metal objects.
- If you hit the jaw, you can injure the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue.
- In contact with reagents and hygienic devices.
You can get injured while taking medications, eating food, or using dental floss. As a result, the mucous membrane swells and secretions accumulate in it. It can be transparent, bloody or bloody.
The capsule or bubble may burst on its own, without medical intervention. But education, in case of poor immunity, disruption of the body’s natural protective functions, becomes inflamed, which is fraught with consequences.
Antihygiene
Violation of the rules of oral hygiene leads to the following problems:
- pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the mouth;
- they lead to an inflammatory process, thinning the mucous membrane;
- as a result, a purulent formation may appear.
Pathogenic agents, as well as leukocytes, accumulate in the bladder, which indicates the development of inflammation. The formation often bursts on its own, the contents come out. Following the rules of hygiene and installing drainage will help to avoid its reappearance.
Syphilis
Classified as a venereal disease of bacterial origin. The bacterium infects the lymph nodes, leading to the appearance of hard chancre.
A dense formation appears on its own; other signs may not bother you at all. After a short period of time it disappears, and then the chancre appears again.
Syphilis is dangerous because it leads to the death of the patient if not treated up-to-date.
A course of antibiotic therapy, which is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, will help get rid of the signs of the disease.
It is believed that the formation appears on the genitals, but in the case of oral contact, the chancre can also appear in the oral cavity.
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
Complications after illness
Even common colds and flu lead to similar complications if:
- The person has poor immunity.
- There are metabolic disorders.
- Systemic diseases of internal organs of bacterial origin were diagnosed.
- Measures to treat influenza or ARVI were not taken in a timely manner.
In some cases, the formation in the form of a bubble is an inflamed lymph node. In such a situation, antiviral or antibacterial therapy is required.
Infection
A large number of bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity and cause inflammation. Thinned areas of the mucosa are easily affected by pathogenic microorganisms. As a result, a bubble forms.
Table 1. Associated symptoms and causes of the development of the infectious process:
| Why does the bubble appear: | What are the signs of concern: |
| As a result of untimely or poor-quality surgical intervention. | Against the background of an inflammatory or infectious process in the human body, body temperature rises. |
| Failure to follow doctor's recommendations after tooth extraction or other dental procedures. | Intoxication of the body is observed, general weakness worries, performance and appetite decrease. |
| The infection also enters the body if hygiene rules are not followed. | In the area of inflammation, the bubble, redness of the mucous membrane is observed, the patient complains of unpleasant sensations that intensify when eating. |
Infection leads to various consequences and is the cause of atrophic changes. Ulcers appear in the mouth, on the mucous membrane, which disrupts the usual process of eating.
If a person has signs of an oral infection, he should consult a doctor. Refusal of medical care can lead to sepsis and other serious complications.
Symptoms
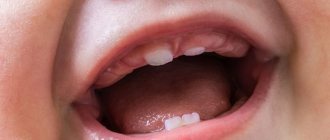
The clinical picture will depend on the cause that caused the formation of bubble formations. The injury usually results in a single blister. It can be located in different places of the sublingual region: in its central part, on the sides. If the bubble is red, it is a hematoma, that is, blood has accumulated inside the bubble. This should be somewhat alarming, since blood is an excellent medium for the proliferation of microorganisms.
An inflammatory process may begin. With a superficial injury, blood does not form, then the color of the bubbles is pink or without changing the color of the mucous membrane. Typically, blisters that form as a result of injury go away on their own.
A bubble or several bubbles may appear due to a lack of vitamins in the body. More often than not they do not cause much inconvenience. Such blisters are painless and quickly disappear after a course of vitamin therapy.
The great danger is ranula . Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland occurs, the ducts narrow, and a cyst-like bladder appears. At the beginning of inflammation, the only concern is dry mouth. Then a blue ball with transparent contents begins to grow under the tongue. The blister is painless, but under pressure it can burst and fluid flows out of it. After some time, the cyst begins to grow again. Ranula can appear in adults and children.
Sometimes infants develop a hematoma under the tongue. This is a hemangioma that goes away on its own.
A sign of pemphigus, as well as a manifestation of syphilis, is the appearance under the tongue of a large number of small bubbles with liquid. The appearance of a large number of small tubercles over the entire surface of the tongue, especially under it, may indicate glossitis. The disease manifests itself as pain and burning in the mouth. The tubercles turn into pustules, as the disease is caused by pathogenic microorganisms.
Oncology
It is no secret that these types of formations have specific symptoms. With malignant tumors, a bubble appears in the oral cavity that is prone to growth.
Other associated manifestations:
- the mucous skirt darkens, which is noticeable during a visual examination and collection of material for research;
- the tumor rapidly increases in size, grows and affects the tissue of the lymph nodes;
- a person loses weight, his performance decreases, and the skin acquires a peculiar, earthy tint.
Oncology manifests itself late; in the early stages it occurs without severe symptoms, which is its main danger.
Diagnostics
The appearance of any blisters in the mouth can be a sign of serious illness. If a ball appears under your tongue, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will conduct a visual examination,, if necessary, prescribe additional diagnostic measures and prescribe the correct treatment. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following measures are taken:
- Visual inspection.
- Collecting anamnesis using a survey to determine the cause.
- Laboratory blood test.
- Laboratory examination of saliva.
- Puncture of the contents of the bladder and its laboratory examination. This procedure is prescribed to diagnose ranula.
- Radiography.
- Cystography.
Before visiting a specialist, you must adhere to certain rules:
- You should not puncture the blisters, as this can cause infection and worsen the condition.
- Closely monitor your condition and the growth of the bubble.
- Eat bland food.
- Perform oral hygiene carefully.
- It is strictly forbidden to make an independent diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
- Go to a medical facility as soon as possible.
Food and medicine
Some foods and medications cause a bubble to appear under the tongue. What are the possible reasons:
- Aggressive substances thin the oral mucosa.
- Rough food injures and damages sensitive membranes.
Alcohol, nicotine, and aggressive substances cause serious damage to the mucous membrane and can lead to the formation of cysts and other problems. Long-term, systematic smoking is regarded as one of the causes of cancer.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Ranula
This is a benign, cystic formation that occurs for several reasons. Often a cyst is a consequence of a gland being blocked by saliva.
Associated symptoms:
- the formation does not cause pain or serious discomfort;
- at the initial stage it does not interfere with eating, it increases in size slowly;
- there are no accompanying symptoms: body temperature is stable, no intoxication is observed;
- with a cyst, a person pays attention to increased salivation, which is often disturbing when a bubble appears under the tongue.
Types of bubbles
Bubbles that form under the tongue are of different origins, differ in color, size and content. Some formations do not require any therapeutic effect, while others are a symptom of serious diseases that require immediate treatment. Based on the nature of the ball formed under the tongue, specialists can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Bubbles in the sublingual area, depending on the cause of their occurrence, vary in color:
- without changing the color of the mucous membrane - the bubble has a characteristic physiological color;
- red color indicates accumulation of blood inside the bladder;
- white blisters occur with stomatitis;
- a bubble with a blue tint may indicate the formation of a ranula.
Bubbles under the tongue can have different contents. There are bubble formations: with a clear liquid inside, with a blood clot, without content.
Blisters under the tongue differ in size and growth pattern: large, small, medium, growing, blisters that do not change in size.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnostic procedures are as follows:
- It all starts with collecting anamnesis, the doctor interviews the patient for complaints.
- Examines his oral cavity and may take a swab from the throat.
- Writes out directions for blood and urine tests.
If necessary, prescribes other specific procedures that will help diagnose the patient and differentiate the pathology.
Table 2. What else is carried out as part of the diagnosis:
| The secretion is collected laparoscopically: | The procedure helps to differentiate the pathology. Using a laparoscope, doctors take a certain amount of contents from the formation for analysis. | The procedure helps in diagnosis; it is also performed to remove small tumors. |
| Histological examination: | The material is taken to the laboratory and processed in a special way. | The study helps in diagnosing oncological formations and determines the nature of the tumor. |
| Biopsy: | A study is carried out if, at the time of the operation or under other circumstances, the doctor suspects the presence of oncology. | A biopsy is not performed as part of prevention, but this test is considered inaccurate for a number of reasons. |
The doctor may prescribe a puncture; in this case, a secretion is also collected, which is sent to the laboratory for testing.
Treatment of blisters under the tongue
Therapy has several directions and depends on the cause of the development of education, it includes:
- Taking antibacterial drugs, in particular antibiotics, is prescribed for inflammatory and infectious processes, when the mucous membrane is affected by pathogens.
- Conducting antiseptic rinses that will help destroy pathogenic agents, antiseptics are often prescribed in the form of solutions.
- Treatment may include cleaning the cavity, removing the formation, and installing drainage. Often the edges of the bladder are cleaned and stitched, which helps prevent relapse.
In general, therapy directly depends on the cause of the development of the pathological process; it is prescribed by a doctor, he selects medications and monitors the dynamics.
Growth under the tongue
Growth under the tongue: types, consequences
It happens that a growth appears on the root of the tongue, which can cause discomfort and anxiety due to the reasons for its occurrence.
Growths should be divided by origin and properties. Let's look at the main types.
Growths under the tongue should be divided into:
- Papillomas;
- Polyps;
- Lipomas;
- Cysts;
- Sialadenitis;
- Hemangiomas;
- Lymphangiomas;
- Tumors of a malignant nature.
Human papillomavirus can cause a benign tumor under the tongue. Due to stress, poor immune defense, lack of minerals and vitamins, this disease can become more active. Typically, papillomas are located on the root of the tongue, under the tongue, or on the side of the tongue.
Papillomas can be pointed or flat.
Pointed papillomas
They are tubercles in the form of papillae at the base of the tongue and are pinkish in color. Because of them, unpleasant sensations may arise when eating or communicating.
Flat papillomas
This type of papillomas does not cause a person much discomfort. They are round, flat in shape and have clearly defined boundaries.
If papillomas appear and begin to grow, then they can be removed and treated with antiviral drugs. There is no need to self-medicate and resort to traditional therapy.
This formation is benign, has a flat or convex appearance, and grows above the mucous membrane of the lingual root. A polyp is formed from the gastric mucosa, which has been ectopic.
Lingual polyps are a rare occurrence. They usually look like a bump on the back of the tongue. They do not cause pain, but can cause discomfort if they grow or become injured.
A polyp can develop into cancer. The polyp is removed promptly.
The formation is a benign wen located on the lingual mucosa.
Lipoma can be patchy and vulgar. Flap lipoma has a flat shape and is capable of growing into the tissue. Wen vulgaris is a bulge on the tongue of a simple type.
Lipoma is painless, has a soft consistency, grows slowly, and is usually small in size.
The reasons why a lipoma is formed include heredity, bad habits, poor metabolism, injury, and poor ecology.
To diagnose the disease, you will need to see a dentist.
This growth under the tongue looks like a ball with liquid inside. It occurs under the tongue and on the root of the tongue. It happens that a new growth occurs at the lingual frenulum.
The cyst does not grow quickly, but it can create unpleasant sensations; there is no pain. The symptoms will be as follows:
- The lower jaw is swollen;
- A rupture occurs at the growth shell.
To avoid infection, you need to seek help from a doctor, otherwise an abscess may occur, swallowing will be impaired, speech and breathing may be impaired, and the tongue may become displaced.
The cyst is not dangerous.
The disease is a disease of the salivary gland and sublingual glands. The cause of the disease is infection. The causative agents of infection are harmful bacteria, such as the mumps virus, tuberculosis bacillus, and the causative agents of diseases such as syphilis.
Poor immunity, the presence of oncology, and the presence of infection can be cited as the reasons for the appearance of this disease.
In the acute form of the disease, swelling appears, due to which the tissue thickens, festers, and then a necrotic process occurs.
Symptoms of this disease will be as follows:
- Weakness;
- Temperature,
- Taste in my mouth
- Paroxysmal pain localized in the gland area;
- Swelling;
- Pain and discomfort while eating.
This disease is treated under the supervision of a doctor.
This disease is a benign tumor formed due to disorders of the blood vessels. The tumor grows slowly, but can behave unpredictably. Externally it has a purple or red tint. It is divided into capillary and cavernous.
Hemangioma may occur due to hormonal imbalances, weak immunity, metabolic disorders, or due to injuries to the oral cavity.
The disease must be treated immediately to avoid complications and degeneration into cancer.
The disease is a benign tumor that is located in the lymph nodes. It can affect the entire tongue or one side of it. An enlarged tongue may make it difficult to close your mouth. Many small blisters appear in the oral cavity, growing very quickly.
The causes of lymphangioma are:
- Previously undergone surgical operation;
- Infections;
- Other neoplasias in the body;
- Congenital pathologies;
- Heredity.
Signs of lymphangioma will be the following:
- Glassy small bubbles;
- Plaque on the lingual mucosa;
- Bleeding of vesicles when injured;
- Bite problems;
- Speech problems.
The disease must be treated immediately by removing the tumor in a minimally invasive manner.
Lump on penis
The most dangerous pathology of the oral cavity is cancer. It can be located under the tongue, at its tip, on the side, at the root of the tongue, at the bottom of the mouth. The tumor is of the following types.
Ulcerative tumor
The lump can develop into an ulcer; it hurts, bleeds, and is located at the bottom of the tongue.
Infiltrative tumor
A thickening with a white coating appears on the tip or back of the tongue. It looks like a dense tubercle that constantly and severely hurts.
Papillary tumor
The tumor is a pedunculated growth located on the lateral parts of the tongue. Grows moderately. It develops into malignant due to mechanical injuries, viruses, inflammation, bad habits and poor heredity. It has distinct features:
- Severe pain throughout the mouth;
- A lump or ulcer in the tongue area;
- Swelling of the tongue, neck and face;
- Difficulty swallowing, speaking, closing the mouth;
- Smell from the mouth.
If such symptoms occur, you should contact an oncologist. Next, treatment is carried out. The method of treatment is selected individually and depends on many factors.
Modern diagnostics and new techniques used in the Onco.Rehab clinic treat tumors of any kind, contact our clinic to avoid the dangerous consequences of the disease.
Rinse
To carry out such procedures, dentists prescribe antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions.
Table 3. Names and specifics of medications:
| Chlorhexidine: | It is considered a good antiseptic, which is often used in dentistry as part of sanitation. A clear solution with a bitter taste will not harm the mucous membrane. |
| Stomatophyte: | A herbal drug, alcohol-based, which is prescribed to patients who have undergone surgery. Effective for inflammatory and infectious diseases. |
| Furacilin in solution: | The yellow liquid, which is used for rinsing, has a pronounced antiseptic effect. |
The doctor may prescribe Miramistin or any other antiseptic; aggressive solutions such as hydrogen peroxide are less commonly used, since they can cause damage to the mucous membranes.
Rinsing with herbal solutions has good results, using:
- Chamomile decoction is a natural antiseptic that promotes the death of pathogenic flora.
- Calendula infusion accelerates regeneration processes, promotes healing and restoration of the membranes of the oral mucosa.
- A decoction of oak bark has an excellent astringent effect and promotes the rapid healing of wounds and injuries.
You can also rinse your mouth with propolis tincture; it speeds up recovery and is considered a natural antiseptic. This means it prevents the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Other treatments
In addition to antiseptic solutions, antibacterial drugs can be prescribed. They promote rapid healing of wounds and injuries, and reduce the likelihood of complications.
For a cyst, a different technique is used: a special material is placed into the cavity, which is impregnated with iodine. It is left for several days, then removed and stitched up. Such treatment helps prevent relapse, but even this treatment method cannot completely eliminate it.
If the tumor is oncological, radiation and chemotherapy are often performed. Surgical removal of the formation with excision of the affected tissue is also recommended.
Surgeons recommend opening the bladder cavity, stripping the tissue, removing its contents, and installing drainage (if required). In this case, the risk of complications and relapse is reduced.